- #1
jknight291
- 4
- 0
I am attempting to solve an ODE using a Calculus add-in for Excel. I am an industry professional and I have not even thought about Differential Equations in 8 years. The equation that I am attempting to solve is in the form:
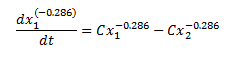 (1)
(1)
The ODE solver that I am using solves equations of the form:
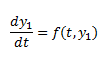 (2)
(2)
The results that I get by solving equation 1 above using my Excel Add-in for ODEs is a sinusoidal type reaction. However, when I solve numerically I get the expected result.
I think my ODE solver may be solving for
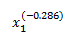 and not just x`1. I tried to transform the results using algebra but the results were still obscure.
and not just x`1. I tried to transform the results using algebra but the results were still obscure.
I think I may need to transform equation 1 to match the format of equation 2 before solving, but I am not sure. Like I said, it has been several years since taking a DE course so I am little rusty.
Can anyone offer some help?
Thanks!
The ODE solver that I am using solves equations of the form:
The results that I get by solving equation 1 above using my Excel Add-in for ODEs is a sinusoidal type reaction. However, when I solve numerically I get the expected result.
I think my ODE solver may be solving for
I think I may need to transform equation 1 to match the format of equation 2 before solving, but I am not sure. Like I said, it has been several years since taking a DE course so I am little rusty.
Can anyone offer some help?
Thanks!