- #1
brenfox
- 71
- 1
Homework Statement
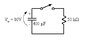
Determine the voltage drop across the resistor when the capacitor has been discharging for 10μs.
Capacitance=400 pico farad and is charged to 10v through a 50kΩ resistor.
Homework Equations
Vr= V*e -t/CR
The Attempt at a Solution
Vr = V-Vc at the instant of 10μsVc=Ve-t/CR
I get 3.935 volts? (without showing all my workings out)