- #1
damu123
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
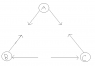
We are given a picture like the one I attached, in the question we are told that ATLEAST 2 are positive which one (if any) is negative
a) Only A
b) Only B
c) Only C
d) None of them
Homework Equations
None really all you need to know is that when the lines are pointing away from a charge its positive and if its going in that means its positive (but it really doesn't make much sense in this picture to me)
The Attempt at a Solution
I said that none of them are negative because A is def. not negative and B and C are the same so I assumed that they are all positive although it doesn't really make sense to me how B and C can be negative if arrows are going towards them (unless its like a vector diagram and we can move it from going into going out the other side of it which kindof makes sense but hard to explain)