musicgold
- 303
- 19
- Homework Statement
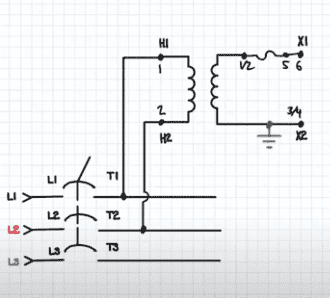
- Not a homework question. I wish to know how do I decide which side of the secondary of an isolation transformer can be grounded.
- Relevant Equations
- At the 6.20 mark in the video below, the instructor says that if a system needs grounded pilot voltage, it is common to ground the X2 terminal of the secondary.
The video is located here. My question, if the secondary side is isolated and the control circuit has no connection to the primary side, why do I have to ground X2 only? This a floating AC system, so why does it matter which side is used as the reference? What will happen if I grounded the X1 terminal?