- #1
delsoo
- 97
- 0
Homework Statement
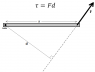
for this question, since area of cutting of magnetic field change, so magnetic flux change, f is unchanged . but i don't understand why the torque will change since the force is unchanged, since torque=FORCE X DISTANCE FROM THE ROTATING PIVOT
![DSC_0150~8[1].jpg](/data/attachments/53/53700-0dda129900f5a08e45f03ff7aa628d64.jpg)