- #1
Drao92
- 72
- 0
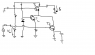
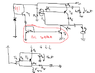
I can't understand why you can remove T2 from this circuit when you make the low signal analysis. Can anybody explain me please ?
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=57825&stc=1&d=1365838694
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=57825&stc=1&d=1365838694
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: