- #1
frozen7
- 163
- 0
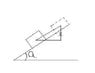
When lift up the box to 2m forward. Find out the work done by the gravitational force.
I find it by W = mg (x)
But my lecturer encourage me to do it in this way: W = 2mgsin(a), and told me that my method is correct in trigonometric but not really correct in physics.
I would like to know whether my method is really not suitable or it is correct actually?
I find it by W = mg (x)
But my lecturer encourage me to do it in this way: W = 2mgsin(a), and told me that my method is correct in trigonometric but not really correct in physics.
I would like to know whether my method is really not suitable or it is correct actually?