Conservation of energy Definition and 1000 Threads
-
M
Calculating Spring Constant and Energy Conservation: How Fast Will the Bag Drop?
1. Problem Statement: A vertical spring has one end attached to the ceiling and a 3kg bag attached to the other one. When the system is at rest, the spring is stretched by 40cm. 1) determine the spring constant. 2) Let the bag drop from a position in which the spring is not deformed. Using the...- MarieMarie94
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Spring
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Circular motion in the vertical plane
Homework Statement A light rod ##AB## of length ##2a## has a particle ##P## of mass ##m## attached to ##B##. The rod is rotating in a vertical plane about a fixed smooth horizontal axis through ##A##. Given that the greatest tension in the rod is ##\frac {9mg}{8}##, find, to the nearest degree...- WhiteWolf98
- Thread
- Circuar motion Circular Circular motion Conservation of energy Mechanics Motion Newton 2nd law Plane Vertical
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Law Conservation of Energy: Starting off a solution for 11b
Homework Statement Homework Equations ΔEsystem + ΔEsurroundings =0 The Attempt at a Solution I have solved 11a and got 5m/s. I can do 11b just by just jumping to Ek = Fs (from the work kinetic energy theorem), but I would like to do it formally from first principles using the Law of...- Jigga
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Law
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Energy Confusion (Conservation of Energy?)
Anyone know if the following statement is true (and why)? "Getting to higher ground would increase his gravitational potential energy, decreasing the effects of non-conservative forces, which would allow him to move easier." CLARIFICATION: "move easier" refers to a lack of friction and not the...- Generally Confused
- Thread
- Confusion Conservation of energy Enegy Energy Gravitational potential energy Potential energy
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanics
-
I
Find the launch speed of a ball in a spring mechanism
Homework Statement I have a question asking me to find the launch speed of a ball (mass 0.39kg) when released by a spring mechanism made of 2 springs each with force constant 25Nm^-2. they are pulled back 12 cm. the ball is initially at rest.Homework Equations [/B] v^2=u^2+2as f=ma f=kx...- Izwx2000
- Thread
- Ball Conservation of energy Elastic potential energy Kinetic energy Launch Mechanism Speed Spring Suvat
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Analyzing Elastic Collisions w/ Conservation of Energy and Momentum
Homework Statement There is a 4 kg mass that has a speed of 6 m/sec on a horizontal frictionless surface. The mass collides head-on and elastically with an identical 4 kg mass initially at rest. The final speed of the first 4 kg mass is: (a) 0 m/s (b) 2 m/s (c) 3 m/s (d) 6 m/s Homework...- A Physics Student
- Thread
- Collision Collisions Conservation Conservation of energy Elastic Elastic collision Elastic collisions Energy Energy and its consevation Momentum Momentum conservation
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Conservation of Energy: Kinetic & Reference Frames
If velocity is reference frame dependent then kinetic energy should also be. Considering this we will have different energies in different frames. Doesn't it violate conservation of energy?- Zubair Ahmad
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Mechanics
-

I Conservation of Energy on the Cosmological Scale
Am I correct in understanding that locally, ie, with respect to circumscribable phenomena, conservation of energy is valid in the cosmos but that otherwise it is/may not be? Otherwise said, the source of dark energy does/may not obey this principle? Or is this a question that does not fall...- Islam Hassan
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Cosmological Energy Scale
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Cosmology
-
C
Finding angular velocity using conservation of energy
Homework Statement In the document below I need to try and find the angular velocity I need help on part b Homework Equations F=ma KE_Translational= 0.5mv^2 KE-Rotational= 0.5Iw^2 Assuming g=10m/s^2 The Attempt at a Solution I have the answer key attached with the question but I am not sure...- Coderhk
- Thread
- Angular Angular velocity Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Energy conservation Velocity
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
D’Alembert Vs Conservation of Energy
Homework Statement A block with a mass of 5kg is pulled up an incline with a 20 degree incline, the coefficient of friction is 0.2 and the distance 10 metres. The block accelerates from 1m/s at point A to 5m/s at point B. I have to use both D’Alembert’s and Conservation of energy principles...- GrimUpNorth
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I On gravity and the conservation of energy
Alright, so this has been bothering me for awhile, and the more I think about it, the more it bugs me. I'm almost guaranteed wrong about what I'm going to say here, but I'm not sure why I'm wrong, so hopefully someone here can explain my wrongness to me. Unfortunately, this is going to take...- Catreece
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Gravity
- Replies: 30
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Thermodynamics - Use conservation of energy to answer these questions....
Homework Statement Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution I understand how they got Q1 and Q2 for the first two columns, but how am i suppose to find Q1 and Q1 for the 3rd and 4th event? Isn't it just 0? Cause it seems like the temperatures just stayed constant. I'm not entirely sure...- lc99
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Thermodynamics
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
M
Conservation of energy (Waterfall)
Homework Statement In a waterfall about 20 billion liters of water per hour drop about 110 m. What is the increase of the water temperature, assuming that the entire gain of heat is transferred to the water? Homework Equations I'm more curious about the question in itself. Perhaps I'm missing...- mk9898
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Heat energy Thermodaynamics
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Intermediate-Calculate a weight using conservation of energy
Homework Statement This problem comes from the Feynman Lectures. However, the author doesn't explain in detail the procedure to solve the problem. I have to calculate the weight W using only the law of energy conservation. Homework Equations In the second picture W it is lowered of 5...- Aleoa
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Weight
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Conservation of Energy with changing masses on ice
Homework Statement Mass 1(75kg) glides on ice at 1.8 m/s to a second stationary mass, (52 kg) How far will the pair slide after the collision if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ice and their skates is .042? Homework Equations Conservation of energy, Kinetic Energy, Work...- Nojins
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Ice
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Finding initial velocity of two elementary particles
<Moderator's note: Moved from a technical forum and thus no template.> I'm not sure how they got the extra (1/2)mv^2? My question is shown using pink font in the image below as well as my attempt.- asilvester635
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Electric potential energy Elementary Elementary particles Initial Initial velocity Particles Velocity
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
Conservation of energy of a perfectly decoherent laser
The energy and momentum of a closed system is always conserved. If a laser can emit perfectly parallel and perfectly superimposed light waves (occupy the exact same space) that are perfectly 180° out of phase and of the same frequency, what can be said about the energy and momentum of the...- K1nem4t1cs
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of charge Conservation of energy Energy Laser Laser beam Superposition
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Optics
-
J
D’Alambert vs Newton’s second law?
I’m a bit stuck with differentiating between the conservation of energy and D’Alambert. For a question I need to find the average resistance of the ground after it has been struck by an object. I chose to look at the equation as Ma + Mgh - Fr = 0. Can you advise if this is correct?- Jon1909
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Conservation of momentum Law Second law
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

B How Does Gravity Influence Energy Production in Hydroelectric Generators?
Hi everyone! I'm here for a little conveyance towards a question that is disturbing me for days. Just suppose, you and I design a hydroelectric generator that provokes energy from the downflow of precipitating rain. These falling drops of rain surely have originated from the vapours of the...- Gaurav Samanta
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Gravity
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

Conservation of energy question -
A cylindrical container of water has a diameter of 7.98 m and a perpendicular height of 2 m. It is filled with water (1000 kg = 1000 l) and placed on top of a 4 m stand. Calculate the: A) potential energy of the water B) kinetic energy of 20 kg of water just before it reaches the ground, if the...- KieronB
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
B How Is the Coefficient of Restitution Linked to Conservation of Energy?
Where does the Coefficient of Restitution equation come from, in terms of the Conservation of Energy? The measure of efficiency is the velocity after the collision divided by the velocity before the collision, but how does it get to that point? I'm trying to view this focused on an object that...- Generally Confused
- Thread
- Beginner Coefficient Coefficient of restitution Conservation of energy Gravitation potential energy Kinetic energy
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

Conservation of energy in x vs y direction
Homework Statement A child goes down a water slide. The slide is 9.0 m tall. She pushes off with an initial speed of 2.0 m/s (in the horizontal direction). If the slide is frictionless, how fast will she be going at the bottom of the slide? Homework Equations In the book, they use a...- Wes Turner
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Direction Energy
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
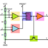
Calculate the contact force between the skis and the track
Homework Statement 14.37 A 75-kg ski jumper starts his run in the position shown on the parabolic track. The equation of the parabola is ##y = (12/225)x^2##, where x and y are in meters. Neglecting friction, calculate the contact force between the skis and the track at O. Homework...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Contact Contact force Force Potential energy Track
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Determine the smallest possible speed of the bob at A
Homework Statement 14.34 The 0.5-kg bob of the pendulum travels a complete circle about the pivot point O. Determine the smallest possible speed of the bob in position A if it is suspended from (a) a rigid rod of negligible mass; and (b) a string Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Potential energy Speed
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

The 2.5-kg wieght is released from rest -- Determine the spring constant k
Homework Statement 14.27 The 2.5-kg weight is released from rest in position A, where the two springs of stiffness k each are undeformed. Determine the largest k for which the weight would reach position B Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution Hi. Can you check if I am going at...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Constant Potential energy Rest Spring Spring constant
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Conservation of electrical energy on a conductor
I'm having trouble seeing how electric potential energy production on a conductor follows conservation of energy. Let's use the photoelectric effect as an example. A photon with energy E = hν strikes a conductor, ejecting a photoelectron with a maximum kinetic energy of hν - φ. Assuming the...- G Cooke
- Thread
- Charge Conductor Conservation Conservation of energy Electric potential energy Electrical Electrical energy Energy Photoelectric effect
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

A ball is placed on the spring and launched vertically, Find k
Homework Statement 14.28 The spring of stiffness k is undeformed in the position shown. The 30-g ball is placed on the spring and launched vertically by compressing the spring 150mm and releasing it. If the ball reaches an elevation of 14.25m above A, determine the value of k. Homework...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Ball Conservation of energy Potential energy Spring
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Conservation of Energy: block on a table
Homework Statement Homework Equations ∑F=ma W = - ΔUs ΔUs = 0.5 k (xƒ)^2 - 0.5 k (xi)^2 W = ΔUs + ΔKE d = viy t + 0.5 * t^2 * a The Attempt at a Solution A) [/B]W = - (0.5 k xƒ^2 - 0.5 k xi^2) = - (0-100) W = 100 J B) W = ΔUs + ΔKE 100 = 0.5 m vf^2 -0 + 0 - 0.5 k xi ^2 100 = 0.5 * 2 * vf^2...- Fatima Hasan
- Thread
- Block Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Table
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Conservation of Energy -- Toy car hits and compresses a spring
Homework Statement A toy car has a mass of 2 kg moves with initial speed of 2 m/s on a rough horizontal plane of μκ=0.14.A spring with constant of 250 N/m is fixed. Which of the following statements is true ? A) The toy does not approach the spring B) The toy just touch the spring[/url][/IMG]...- Fatima Hasan
- Thread
- Car Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Spring
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I What does Noether's theorem actually say?
I don't know much about classical physics(such as lagrangian function), but as i was reading conservation of energy, i came to this theorem and it tells that if a system is symmetrical in certain transformations(such as translation, rotation etc) then it will have a corresponding law of...- parshyaa
- Thread
- Conservation laws Conservation of energy Noether's theorem Theorem
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

A block is released from rest, determine its velocity
Homework Statement 14.10 Solve Prob. 12.47 by the work-energy method 12.47 When the 1.8-kg block is in the position shown, the attached spring is undeformed. If the block is released from rest in this position, determine its velocity when it hits the floor Homework EquationsThe Attempt...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Block Conservation of energy Rest Spring Velocity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Body describes a closed trajecty on a free-to-spin disk
[Moderator's Note: Thread title changed to better reflect the problem statement] Homework Statement A body of mass m is on a disk of mass M=2m and radius R, initially static and free to spin around its center. The mass mm goes around a trajectory described in the image below with constant...- Gena
- Thread
- Body Closed Conservation of energy Disk
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Why is mgh equal to mgx in this conservation of energy problem?
Homework Statement Homework Equations W spring = 1/2kx^2 Ug = mgh The Attempt at a Solution I have the work in the above problem, but I'm kinda confused how there is any potential energy here besides the spring potential energy that we get in the final state. Why is mgh here mgx? why can h...- Lori
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
B What is the ΔEp = ΔEk + W equation used for in thermodynamics?
What is ΔEp = ΔEk + W I have come across this formula, but i haven't seen it before. What is it used for?- kburkus
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Energy Kinetic energy Potential energy Work
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
L
Is this a conservation of energy problem?
Homework Statement I'm sorry but I don't have the exactly problem written down but I know the givens. So the question involves finding work done on a pendulum hanging from the ceiling. Homework Equations I was given the the length of the string is 1m. That a mass hangs at the bottom of...- Lori
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Algodoo and Physics Analysis of Interactions
Homework Statement [/B] I have created a very simple Rube Goldberg device in Algodoo, and I need to analyze 3 correlating steps within it, using physics descriptives and equations. My primary focus is the ball as it hits the windmill, which I need to describe and calculate its velocity at that...- Noe Wong
- Thread
- Analysis Conservation of energy Energy transfer Interactions Physics
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Derive Formula for Velocity of Object Approaching Earth
Homework Statement A particle of mass m is dropped from a height h, which is not necessarily small compared with the radius of the earth. Show that if air resistance is neglected, the speed of the particle when it reaches the surface of the Earth is given by ##\sqrt {2gh}## ##\sqrt {\frac {R_E}...- directory_NA
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Derive Earth Formula Gravitation Physics Velocity
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Conservation of Energy and projectile motion
I am finishing up a lab write up for conservation of energy, where we launched a projectile into the air and measured the initial velocity and height of the projectile. ( 10 trials) One of my questions asks if I wanted the ball (projectile) to travel twice as high, how much faster would it have...- vlmstudent
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Motion Projectile Projectile motion
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Conservation of Energy: Spring pushing a block up an incline
Homework Statement "Consider a 250 gram block on a 10 degree frictionless incline and in contact with a spring of constant 1.2 N/cm. If the block is launched from rest by the spring with an initial compression of 6cm, how fast is the block moving at the point of release from the spring? How...- CrazyCatMom
- Thread
- Block Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Energy and its consevation Incline Spring Spring block Spring compression Velocity
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
Is the Law of Conservation of Energy Valid in a Non-Local Context?
Is it accepted that the law of conservation of energy can be considered in a non-local context? If this is not accepted, then why not?- Kyle Nemeth
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Law
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-
C
MHB Using the idea of conservation of energy
Dear Everybody There is a ball which has mass of 11 grams is thrown straight up with an initial speed of 4 m/s. Assume the air drag is negligible. a. What is the kinetic energy of the ball (in J) as it leaves the hand? b. How much work is done by the gravitational force during the ball's rise...- cbarker1
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Idea
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Math
-
R
Conservation of energy -- Two charges separated by a spring
1. Two identical charged particles which are point masses are fastened to the two ends of a spring of spring constant 100 N/m and the natural length 10cm.The system rests on a smooth horizontal table.The charge of each particle is 2*10^(-8)C.the extension of spring if the extension is small as...- Roxas ross
- Thread
- Charges Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Spring
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Train Conservation of Energy Question
I go to work on the train and I get on at the back and get off at the front. I can choose when to walk through the train. If I walk when the train is accelerating forwards it is harder for me to get to the front and I do more work. If I make the trip when the train is stopped or at a constant...- Guy135
- Thread
- Conservation Conservation of energy Energy Train Work
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Mechanics
-
W
(Spring constant) I can't figure out what I did wrong.
Homework Statement Two springs which have spring constant of k1 and k2 respectively are vertically hung in a series. Then, a mass m is attached to the end. Find the displacement and the spring constant of this series. Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution I got the displacement x1+x2...- Winvoker555
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Constant Figure Spring constant Work and energy
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
B What Are Reversible Machines and Feynman's Limitations?
I am no able to understand the reasoning of Feynman in deducing that it is impossible to build a machine that will lift a weight higher than it will be lifted by a reversible machine. I am also not able to understand what reversible machine is. So, please help me.- Ankush07
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Feynman lecture on physics Gravitational potential energy Machine Perpetual motion Reversible
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Does work energy theorem fail while dealing with friction?
Let's consider a setup consisting of a table with friction, and a block on top of it. Suppose we drag the block across the table with a constant speed. The applied force ##f_{app}## acting through a distance ##d## does a work ##f_{app}d##. The frictional force ##\mu N## is equal to ##f_{app}##...- NoahCygnus
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Energy Friction Theorem Work Work and energy Work energy Work energy theorem
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Mechanics
-
L
B Why is resistivity important in solving this problem?
In free space there are two masses: - Metallic sphere of mass M, radius R and total charge equal to 0. It has also a resistivityρ. - Metallic sphere of mass m, radius r and charge q. The distance between the masses is D. We can assume r <<R<<D and m<<M. The masses start accelerating until they...- LAph
- Thread
- Conducting sphere Conductors Conservation of energy Free space Space
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
S
Dropping a Block on a Spring with Completely Inelastic Collision
Homework Statement [/B] A block of mass, m, is dropped from height, h (above the plate), onto a plate of mass, M, which is attached to a spring with spring constant, k. The block sticks to the plate and the system starts to oscillate. What is the amplitude of the oscillations. Homework...- SeventeenForever
- Thread
- Block Collision Conservation of energy Inelastic Inelastic collision Spring
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Additional Velocity Required for a Satellite Already in Orbit to Escape
Homework Statement A satellite is orbiting the Earth around an orbit of radius R=2.5R0, where R0 is Earth's radius. What additional velocity is needs to be directed along the radius of the orbit so that satellite escapes Earth's gravity? Homework Equations Total Energy= K + U Conservation of...- SeventeenForever
- Thread
- Conservation of energy Escape Gravity Orbit Satellite Velocity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Conservation of Energy for Unwinding Mass
As a spinning mass is unwound, angular momentum is conserved, meaning ##Iω## remains constant. However, since rotational energy is proportional to the square of the angular velocity, how is it possible for energy to be conserved as well?