Contraction Definition and 689 Threads
-
T
I Length Contraction: Muon vs Earth Frames
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Relativ/muon.html https://newt.phys.unsw.edu.au/einsteinlight/jw/module4_time_dilation.htm#equivalence I was looking at these links and got confused. It seems to me that they are saying the same thing but the UNSW link uses the clock in the other...- TheWonderer1
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
T
I Is Expansion the Same as Contraction?
How do you tell the difference of expanding outwards and contracting inwards? Part of my intuition tells me that it would be impossible to tell the difference. If you are on the natural numbers heading from zero to infinity I might say that is expanding outwards. So if you are sitting at...- theoretical symmetry
- Thread
- Contraction Expansion
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
K
I Inconsistency in Length contraction
Let there be 2 astronauts A and B in uniform relative motion and they are moving towards each other. Let A be moving in a spaceship of length L and there are 2 clocks ca1 and ca2 attached to the front and back of the spaceship respectively and let clock of B be cb. The moment when the front of...- KallaNikhil
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Relativity
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
Relation between s=d/t and length contraction ?
Homework Statement A 16m long vessel moved passed you at a relative speed of 0.86c. What was the length of the vessel recorded by your measuring device? Homework Equations Speed = distance/time t=to/√1-v2/c2 L=Lo⋅√1-v2/c2 The Attempt at a Solution Ok, so I can just sub the 16m and 0.86c in...- Frank_Mennella
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Relation
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Prove Lorentz-Fitzgerald Contraction w/ Michelson-Morley Experiment at Any Angle
I find this question rather difficult! Q1. I take Fig 1-11 to be the laboratory frame and ##v## to be the velocity of the ether wind. Since Lorentz length contraction occurs only horizontally, the right mirror should be further to the right horizontally in the ether frame. This makes the angle...- Happiness
- Thread
- Angle Contraction Experiment
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

B Length Contraction: Real Compressive Forces?
I'd like to get some conceptual clarification on whether or not length contraction is only apparent to an observer or if it's physically real in the sense that the object under contraction would experience compressive forces? My thinking on this has been along the lines of: I know that time...- ibkev
- Thread
- Contraction Forces Length Length contraction Sr
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Length contraction -- numerical problem
Homework Statement Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution a) t' = l0/c b) ct1 = l0 /ϒ - vt1 t1 = l0 /ϒ(c + v) c) t2 = l0 / (ϒ v) Is this correct?- Pushoam
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Numerical
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Length contraction numerical problem
Homework Statement Homework Equations 1) k.e. = (1/2)mv2, non- relatvistic 2)K.E. = m0 c2 (ϒ -1), relativistic 3) L=L0/ϒ , Length contraction The Attempt at a Solution (A) Taking 1019 eV to be the kinetic energy of the proton, Non- relativistic calculation (1/2)mv2 = 1019 eV = 1.6 v =...- Pushoam
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Numerical
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Derivation of length contraction
Problem : To measure length of a scale Rest frame : The frame w.r.t. which scale is at rest Moving frame : The frame w.r.t. which the scale is moving with speed v along +ve x-axis In rest frame ,the positions of the two ends of the scale are (measured simultaneously ) x1 and x2. So length L =...- Pushoam
- Thread
- Contraction Derivation Length Length contraction
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
B Entangled particles and lorentz contraction?
can lorentz contraction be measured via quantum entanglement with one of the entangled particles moving near the speed of light? would the particle in motion be affected by lorentz contraction? if so, would the particle at rest follow suit and appear affected?- letumio
- Thread
- Contraction Entaglement Entangled Entangled particles Length contraction Lorentz Lorentz contraction Particles
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Special Relativity: Length Contraction Problem
Hello! I have a small problem with a task professor gave us. I tried many options (you will see below) but I cannot seem to get the right solution. Any advice or guideline how to solve this would be really helpful. In advance I thank you for helping me. Homework Statement Our professor of...- peroAlex
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Modern physics Relativity Special relativity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
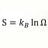
B Does Distance Contraction Cause Time Dilation?
Its my understanding that relativistic length contraction l = l0√ 1-v2 also applies to the space itself in the moving S' system. For example a rocket traveling at .6 c. A distance that is 1000 meters in S frame is contracted to 800 meters in rockets frame. (1000/γ) Therefore the elapsed time /...- morrobay
- Thread
- Cause Contraction Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Length Contraction & Time Dilation: Relative Velocity Impact?
So an object moving close to the speed of light will be length contracted. Does that mean the distance it covers also contracts in length? From the traveling object's point of view it's surrounding's would contract as he sees them moving along. In these scenarios wouldn't velocity be a...- sqljunkey
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Time Time dilation Velocity
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
R
Velocity of electron at the end of a contraction
Homework Statement :[/B] Velocity of an electron at point A1 is Vo where cross sectional area is A. The velocity of electron at the end of contraction at point B where cross sectional area is 2A is V1.Find correct option a)V1< V0 b)V1= V0 c)V1> V0 d)V1<=V0/2 I have attached a picture of the...- randomgamernerd
- Thread
- Contraction Electron Electrostatics Velocity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Gravity: Contraction of Space?
Specifically, what I am wondering is gravity considered to be a physical contraction of space? For instance the space between any two points A and B shrinks as gravity grows stronger. Is this the right concept?- mpolo
- Thread
- Contraction Gravity Space Spacetime
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Is Lorentz contraction explained by space time diagram ?
Is there a way to explain Lorentz contraction on space-time diagrams ? I cannot find a way by myself. Your teaching will be appreciated.- sweet springs
- Thread
- Contraction Diagram Lorentz Lorentz contraction Space Space time Time
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Distance and Time for a Moving Muon
Homework Statement A muon is created in the atmosphere 3 km above Earth's surface, heading downward at speed 0.98c. It survives 2.2 * 10-6s in its own frame of reference before decaying. Relativistitically, according to the muon, what is the distance from the point in the atmosphere where the...- Pouyan
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Muons
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
B A supplementary length contraction question
Sorry community, I know I have another outstanding relativity question but something else is currently troubling me. What got me thinking was the question of muons moving towards earth. Now according to their half lives very few of them should make it through 12Km of atmosphere... ANALYSIS...- Glenn G
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
G
B Time dilation and length contraction question
Hi All, Bob and Alice are both 21. I'm imagining a scenario where Alice starts on a journey at 0.8c towards a distant planet. Bob (stays still) says this planet is 16 light years away and that it takes Alice 16/0.8 = 20 years to get there (so Bob is 41 years old when Alice gets there). So Bob...- Glenn G
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Time Time dilation
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
I Length Contraction & Time Dilation Beyond Planck Scale: Correct?
If an object was traveling fast enough relative to an observer such that it's length is contracted down to the Planck scale (as with time), I would imagine that any further increase in speed would result in no more observable relativistic effects? Please correct me if I'm wrong.- Flatland
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Planck Planck scale Scale Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
J
I Solving Length Contraction Paradox
Hello there, Suppose there are two inertial frames of reference ##S## and ##S'## with coordinates ##(x,ct)## and ##(x',ct')## such that ##S'## is moving relative to ##S## with velocity ##v##. Suppose ##v>0##, that implies ##\gamma >1##. We know that a Lorentz boost is given by: $$ x' = \gamma...- Jonsson
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Paradox
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Contraction between Levi-Civita symbol and Riemann tensor
How to proof that εμνρσ Rμνρσ =0 ? Thanks.- mhob
- Thread
- Contraction Levi-civita Riemann Riemann tensor Symbol Tensor
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Is there permanent size loss in metals from contraction?
I install automatic pool covers for a living. The tracks that our cover rides on are composed of extruded anodized aluminum. These tracks come in 22' lengths. Usually there is more than one section of track, set end to end, on a given side of the pool. We drill and anchor these sections to...- Gary Weller
- Thread
- Aluminum Contraction Expansion Loss
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

B Length Contraction equation derivation
I recently saw the derivation of length contraction in Special Relativity . At the end , it said x' = (x - vt) γ(gamma) x = (x' + vt') γ(gamma) Where γ(gamma) is Lorentz transformation . It is = 1/√(1- v²/c²) Then derivation continued , with expansion of x' = (x + vt)γ As t = 0 in this case...- Inderjeet
- Thread
- Contraction Derivation Length Length contraction Special relativity
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Is the Contraction of a Mixed Tensor Always Symmetric?
Is that true in general and why: $$A^{mn}_{.~.~lm}=A^{nm}_{.~.~ml}$$- arpon
- Thread
- Contraction Mixed Tensor Tensor analysis
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

V=? for Relativistic Mass,length contraction & time dilation
Homework Statement Velocity Equations for Relativistic Mass,length contraction and time dilation. I was able to figure out one. This is not for homework. I want to learn these equations for future reference. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Length Contraction : v = c...- Axidecimal
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length contraction Mass Relativistic Time Time dilation Velocity equation
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

QFT Wicks theorem contraction -- different fields terms of propagation
Homework Statement I am trying to express ##T(\phi(x1)\Phi(x2)\phi(x3)\Phi(x4)\Phi(x5)\Phi(x6))## in terms of the Feynman propagators ##G_F^{\phi}(x-y)## and ##G_F^{\Phi}(x-y)## where ##G_F^{\phi}(x-y) =\int \frac{d^{4}k}{(2\pi)^{4}}e^{ik(x-y)} \frac{ih}{-k.k - m^2 -i\epsilon} ## and...- binbagsss
- Thread
- Contraction Fields Propagation Qft Terms Theorem
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
F
I Length contraction vs expansion
I'm coming across a contradiction that I can't resolve. Two points on the ground are separated by 30km. If you're in a moving frame at velocity +v relative to the ground and you view those two points on the ground, would those two points be greater or less than 30km apart? At first, I thought it...- freshman2013
- Thread
- Contraction Expansion Length Length contraction
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
G
B Why Contraction in Relativity Theory?
I have a very hard question: why in the Relativity theory the contraction is present always - along the x-axis or a speed v, instead of an expansion along the other dimensions, transversal to the v? Is there any mathematical proof, the contraction is the one correct, and any other possibility...- gamb
- Thread
- Contraction Expansion
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
Length Contraction of spaceships
Homework Statement Two identical spaceships are under construction. The constructed length of each spaceship is 1.5 km. After being launched, spaceship A moves away from Earth at a constant velocity (speed is 0.850c) with respect to the earth. Spaceship B follows in the same direction at a...- LeafMuncher
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
Lorentz Transformation, Time Dilation, Length Contraction
Homework Statement [/B] A spaceship is approaching Earth from the far side of the sun. The Earth and sun are 8 light minutes apart and the ship is traveling at .8c. Two events are indisputable. 1) the ship is at the sun 2) the ship is at the earth. Assume that the Earth and sun are at rest...- Kunhee
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Lorentz Lorentz transformation Time Time dilation Transformation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Length contraction and time dilation from Lorentz S
I'm trying to understand special relativity well enough to explain it to others, ANY others, including myself. I am trying to use Robert Resnick's Introduction to Special Relativity to inform my thinking. In introducing length contraction, he introduces L' as the length measured by an observer...- Michael C Fowler
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Lorentz Time Time dilation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I How Does Length Contraction Affect Train Wheel Rotation at Near Light Speeds?
There's a section in my astronomy book on relativity. The image shows a train traveling at a slow speed and a second image of the train approaching the speed of light. The text says the second train is length contracted, but only in the horizontal direction. In the vertical direction the train...- Sentosa
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Train
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Lorentz derivation of length contraction in electrodynamics
Here is a quote from this website: My question is: is this derivation of length contraction considered to be sound and correct today? Are they treated in modern textbooks?- Babbeus
- Thread
- Contraction Derivation Electrodynamics Length Length contraction Lorentz Lorentz contraction
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Subbing Planck length into length contraction equation?
I was wondering if it is possible to work out the maximum amount of energy an object with mass can have using the length contraction equation (i.e. "actual" length divided by Lorentz factor). The way I thought of doing this was by rearranging e = mc^2 to get c^2 = e/m. Then, substitute e/m into...- Zahidur
- Thread
- Contraction E=mc2 Length Length contraction Lorentz contraction Planck Planck length Special relativity
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Why can't you use Simultaneity when doing Length Contraction
Suppose that frame O' moves at speed v = 0.6c relative to frame O. A rod with two balls is attached to its ends is 10 meters long in its rest frame, O'. Length contraction will tell you that in frame O, the rod is 8 meters long. But aren't the two balls at the ends "events"? They are clearly...- Afterthought
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Relativity of simultaneity Simultaneity
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
R
Lorentz Fitzgerald contraction
Does the lorentz fitzgerald contraction hypothesis contradicts the classical motion of rigid body? I am not sure but i think it doesn't contradicts the classical motion of rigid body.- Ritika
- Thread
- Contraction Lorentz
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Planck's Length, Length Contraction?
Would Planck's length be subject to length contraction if an object hypothetically of the length had a velocity near c? I suspect that it won't becuase Planck's length is defined by the invariant, physical constants of G, c and the reduced Planck's constant. Thus, Planck's length would not be...- Einstein's Cat
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Proofing Contractive Functions: Difficulties Solved
I am having a hard problem with working on this proof. -
R
B Some basic questions about length contraction in SR
Imagine there are two space ships, Ship A and Ship B. Ship A sees Ship B traveling at 0.865c towards him. (And of course vice versa) From Ship A's FOR there is a marker 9,000,000 km away which is at rest wrt Ship A. The marker, Ship A and the path of Ship B therefore form a straight line. When...- rede96
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Sr
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Do Higher-Dimensional Objects Experience Length Contraction in 3D Space?
Please excuse any stupidity, but I'm under the impression that objects that travel "along" 3- dimensional" space (therefore the objects are three dimensional) with velocity v are subject to length contraction. However would objects of 3+ dimensions and with velocity v still be subject to length...- Einstein's Cat
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Consequences of length contraction
If you are in a space ship, traveling near light speed, will length contraction enable you to se astronomical events lightyears away, before it is possible to see them from earth? This because the distance is shorter for you in the spaceship and light speed is constant. Example: A star 100 ly...- Vidar Martinsen
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
How does pipe thickness affect head loss at entrance?
Homework Statement I was told that for loss of head at entrance , the degree of contaction depends on how thick the pipe walls is . i really don't know the meaning , can someone clarify ? the author also stated that the loss coefficients will vary , for very thin tubes , k is very high ? head...- foo9008
- Thread
- Contraction Head Head loss Loss
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
B Does space contraction regard the moving body or the path?
Consider the path of a proton at 7 TeV Ke at LHC. Wikipedia says: Length contraction is the phenomenon of a decrease in length of an object as measured by an observer which is traveling at any non-zero velocity relative to the object. This contraction (more formally called Lorentz contraction...- alba
- Thread
- Body Contraction Path Space
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Why Can't Lorentz Boosts be Used for Length Contraction?
Let's say you have a rod that is 10 meters long. Observer O sees the ends of the rod at (t=0, x=0), and (t=0, x=10). Observer O' moves at speed v = 0.8c relative to O. What is the length of the rod in O's perspective? Using the length contraction formula L' = γL, we find that O' sees the rod as...- Afterthought
- Thread
- Contraction Lorentz Lorentz contraction Lorentz transformation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Contraction, integral, maximum norm
Homework Statement Hi everybody! Here is another problem about contraction and Banach fixed-point theorem that I don't get: The function ƒ: C([0,½]) → C([0,½]) is defined by: [f(x)](t) := 1 + \int_{0}^{t} x(s) ds ∀ t∈[0,\frac{1}{2}]. Is ƒ a contraction with respect to the norm || ⋅ ||∞? If...- JulienB
- Thread
- Contraction Integral Maximum Norm
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

B Torch Contraction Problem in SR: A and B Observe Differently
Dear PF Forum, There's a problem in SR that I cannot solve (or understand) This is, I think, a well known SR problem. The picture is telling the problem itself. A and B and C are in the same frame (let's call it ABC frame) D and E are in the same frame (DE) wrt DE D stays and E stays above...- Stephanus
- Thread
- Contraction Length contraction
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
Radial contraction of a stretched hyperelastic cylinder
Hi, I'm trying to work out how much strain potential I can produce in a cylinder but I want to know how much is stored for any specific part of the cylinder. The problem then is this: I have a cylinder of original dimensions r and h, where h is the original height and r is the radius. It is...- SerArthurRamShackle
- Thread
- Contraction Cylinder Radial
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Engineering
-
A
I Dark Energy vs Gravity: Expansion vs Contraction
Hi all, A naive question: My understanding is that dark energy drives the expansion of space - that is, the distance between two points in space increases over time - with the important note that it is space itself that is expanding. However, when talking about gravity (where one says that...- asimov42
- Thread
- Contraction Dark energy Energy Expansion Gravity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
B Length contraction vs Space time
Does length contraction means the contraction of space time?- fredreload
- Thread
- Contraction Length Length contraction Space Space time Spacetime Time
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Special and General Relativity