Irreversible Definition and 128 Threads
-

Reversible Vs Irreversible Gas Compression/Expansion Work - Comments
Chestermiller submitted a new PF Insights post Reversible Vs Irreversible Gas Compression/Expansion Work Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.- Chestermiller
- Thread
- Gas Irreversible Reversible Work
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Mechanics
-
J
Entropy -- prove it increases for irreversible process
hi all, this is Entropy Rate Balance for Control Volumes. in the case of throttling process, .throttling process is irreversible process, so (S2- S1) must be greater than zero. what i want to know is to prove that (s2-s1) is greater than zero. Thank you in advance.- jangseok seo
- Thread
- Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
R
Irreversible adiabatic expansion in which P_ext=0
Homework Statement In an adiabatic irreversible expansion of ideal gas , if Pext = 0 then which is true, A. T2=T1 B. Q=0, C. P1V1= P2V2 D. P1V1γ= P2V2γ Homework Equations ΔU = Q - W For ideal gas, PV= nRT[/B] ΔU ∝ ΔT The Attempt at a Solution I know Q= 0, Work done is zero, So ΔU = 0, hence...- Raghav Gupta
- Thread
- Adiabatic Adiabatic expansion Expansion Irreversible
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Thermodynamics. Irreversible and reversible Process
When we were taught these in the class. There were a few terms I did not understand which my school teacher used. Firstly, they told us that the work in a reversible process occurs at the boundary of the system, an acceptable fact. All the energy is converted yo work done, and then showed us a...- Prannoy Mehta
- Thread
- Irreversible Process Reversible Reversible process Thermodynamics
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
R
Entropy change in irreversible processes
The equation for entropy S=delta(Q)/T is derived from reversible processes such as Carnot cycle. The delta(Q) in the equation is the reversible heat added or taken out from the system. So, why is this equation valid in the case of processes like cooling of a body which is irreversible?- rajathjackson
- Thread
- Change Enthalpy Entropy Irreversible Irreversible processes Reversible processes
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
B
Reversible and Irreversible Expansion
What's the difference between reversible and irreversible expansion? I know how they are in formulas, (Irreversible-PV, reversible- integral over P in terms of V), but why are they expressed like this? What's the difference? And I would also like to get an exact formula of these two as I can't...- bubblewrap
- Thread
- expansion irreversible reversible
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry
-
R
Adiabatic irreversible expansion
This example is taken from the wikipedia page describing irreversible processes. I just want to make sure I understand correctly why the initial state can't be reached anymore. I assume the transitions to be quasi-static, but there is friction between the piston and the cylinder. If so...- Razvan
- Thread
- Adiabatic Adiabatic expansion Expansion Irreversible Second law of thermodyanmics Thermodynamics
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
S
Confusion on entropy change calculations for irreversible process
I was studying 2nd law thermodynamics. In that context found the clausius's inequality saying closed integral of dQ/T <0 for irreversible process. And from the reversible process entropy was defined. And from that view they said that for irreversible process dS>dQ/T. Now when I saw some...- Shan K
- Thread
- Calculations Change Confusion Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 41
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
J
Entropy increase in adiabatic irreversible compression
Hi there, I was wondering if you could help me, I think I may have some concepts wrong or incomplete. Homework Statement We have an adiabatic cylinder of volume ##V_1## filled with a gas of pressure ##p_1## and temperature ##T_1## in thermal equilibrium, closed with a piston. All of a suden...- jorgdv
- Thread
- Adiabatic Compression Entropy Entropy increase increase Irreversible
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Why is P_ext different for reversible and irreversible isothermal expansion?
I was able to derive the work done in a reversible isothermal expansion. There as the P changes to P-dP, the volume increases by dV and hence the internal pressure also decreases by dP and equilibrium is maintained. (Thanks to @Nugatory and @Chestermiller fo r explaining it). Now when we take an...- AdityaDev
- Thread
- Expansion Irreversible Isothermal Pressure Thermodynamics
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A
Irreversible vs Reversible process
I know that to calculate the entropy change in a process, I just need to calculate the entropy change in a process that has the initial and final states of the process and is reversible. I just don't understand what the actual difference between the irreversible versus the reversible process is...- arili
- Thread
- Irreversible Process Reversible Reversible process
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
H
How do we measure gibbs free energy for irreversible processes?
I know that gibbs free energy for say a body will be equal to = Gibbs free standard energy at 1M and Ph7(-rtlnkeq) (Where k is the concentration of product/ concentration of reactant at equilibrium)+rtlnk. How can we use the standard gibbs free for irreversible spontaneous processes? Is it...- hongiddong
- Thread
- Energy Free energy Gibbs Gibbs free energy Irreversible Irreversible processes Measure
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
J
Q) Reversible and Irreversible processes
I am studying Reif's Fundamental of Statistical and Thermal Physics. (p.91) he explain about Reversible and Irreversible processes by using "The number of accessible states in equilibrium(Ω)". in his point of view, each accessible states have equal probability. comparing to weather...- jaegu
- Thread
- Irreversible Irreversible processes Reversible
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
D
Change in Entropy of surroundings for irreversible process
Homework Statement I know that the equation ΔSsystem = Q/T is only valid for a reversible process but whenever i see problems involving a irreversible isothermal expansion of ideal gas, the ΔSsurroundings is taken as -Qirr/T. Why is that equation valid for surroundings, is it because the...- dhtikna
- Thread
- Change Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Understanding reversible and irreversible process
Hello, It is said that any process accompanied by dissipating effects is an irreversible process.For instance, a piston cylinder arrangement undergoing an expansion of a gas with heat lost as friction between surfaces is an irreversible process.Here the system does work on the...- Soumalya
- Thread
- Irreversible Process Reversible
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Why are precipitation reactions irreversible?
Why are precipitation reactions are irreversible as NaCl + AgNO3 --------> AgCl + NaNO3- Entanglement
- Thread
- Irreversible Precipitation Reactions
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Chemistry
-
N
Change in Entropy for Irreversible Processes
I was following along in my Thermodynamic textbook and began playing with some definitions. In the following formulation, I somehow managed to prove (obviously incorrectly) that dq = TdS for even irreversible processes. I was hoping someone could point out where in the proof I'm going wrong...- nayanm
- Thread
- Change Entropy Irreversible Irreversible processes
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
P
How to tell the difference between reversible and irreversible process
Imagine a rigid block of steel at 100 degrees celsius which is inserted into water at 0 degrees celsius. They then both get an equilibrium temperature. How can I tell whether this is a reversible or irreversible process? What is the argumentation?- PhyIsOhSoHard
- Thread
- Difference Irreversible Process Reversible
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Irreversible Quasistatic PV Work
Hi 1) I am reading Pippard's Classical Thermodynamics and was confused by one of his examples in the attachment. What I do not understand is the concept of using P' (I am thinking P' as = P_fric + P_interface) for work calculations. If I take the system as composed of just the gas inside... -

Reactions: Irreversible Precipitate & Gas Evolution
Why are precipitate and gas evolution reactions irreversible ( why don't the products react once again ) ??- Entanglement
- Thread
- Irreversible Reactions
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Chemistry
-
C
Entropy change in a irreversible adiabatic process
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas initially at 298 k expands from 1.0 L to 10.0 L. Assume the expansion is irreversible, adiabatic, and no work is done. Calculate delta S of the gas and delta S of the surroundings. I know that delta dS = dq/T but q = 0 in adiabatic processes right? So does dS...- chemkid01
- Thread
- Adiabatic Adiabatic process Change Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
Z
Entropy for Reversible and Irreversible Processes
Hello everyone, I've been reviewing some concepts on Thermodynamics and, even though I feel like I am gaining a level of comprehension about the subject that I could not have achieved before as an undergraduate, I am also running into some situations in which some thermodynamic concepts seem to...- Zag
- Thread
- Entropy Irreversible Irreversible processes Reversible
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
S
How Do You Derive Irreversible Adiabatic Work Equations?
Homework Statement So I came down with something and missed some class and am making it up from others notes which arent entirely clear plus the long weekend for turkey day and I am really hoping someone can help me make some sense of this... I am trying to come up with the derivations for...- speny83
- Thread
- Adiabatic Irreversible Work
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Reversible and Irreversible reactions
There are 2 types of reactions 1) Being fully irreversible and 2) reversible So for 1) the graph of Gibbs energy against the progress of reaction would look like this: http://postimg.org/image/phycri0vr/ So the difference between 100% product and 100% reactant is the ΔG of the reaction...- sgstudent
- Thread
- Irreversible Reactions Reversible
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
R
Thermodynamics: Calculating work done in irreversible expansion
Homework Statement Suppose 100g of ethane (C2H6) expands isothermally at 350C from 50ml to 2L. Calculate the heat and work done by the system and the change in entropy if: i)The process is via a reversible path. ii)The process is non-reversible. I don't know how to answer ii) Homework...- Rocalvic
- Thread
- Expansion Irreversible Thermodynamics Work Work done
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
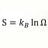
S2 - S1 > Integral 1-2 dQ/T Irreversible Process. What T ?
For an irreversible process: S2 - S1 > ∫12 dQ/T In the case of heat transfer dQ between object with T1 to object with T2, T1 > T2 ΔS in Joules/K is known But for evaluating ∫12 dQ/T = ln dQ/T - ln dQ/T . d/Q is known but what values for T in this case ? Object 1 & 2 have Temperatures before...- morrobay
- Thread
- Integral Irreversible Process
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Irreversible Adiabatic Expansion (Physical Chemistry)
Homework Statement Consider the adiabatic expansion of .553mol of an ideal monatomic gas with CV,m = 3R/2. The initial state is described by P = 6.25bar and T = 306K. Calculate the final temperature if the same gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion against an external pressure of P = 1.25bar to...- djh101
- Thread
- Adiabatic Adiabatic expansion Chemistry Expansion Irreversible Physical chemistry
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
A
Irreversible process Entropie-Change/cylinder
Hi, I have read that for an irreversible process the equation for the entropy is: $$ds>\frac{dQ}{T}$$ But if I regard a cylinder connected to a heatreservoir and want to callculate the entropychange of this cylinder, why can I use the equation: $$ds=\frac{dQ}{T}$$? THX- Abigale
- Thread
- Irreversible Process
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A
Why is Carnot not irreversible?
Hi, I am thinking about the Carnot-Cycle-Process. I know that a heat exchange is always irreversible. But in the Carnot-Cycle, there is heating too. Why is that kind of heating, in the Carnot-Process reversible? Thx Abby- Abigale
- Thread
- Carnot Irreversible
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
A
What is the relationship between entropy and the irreversibility of a process?
Hi, I regard a irreversible cycle process. It is a cylinder filled with gas, which underlies the following processes: 12: isothermal compression (reversible) 23: adiabatic expansion (reversible) 31: isochor heating (irreversible) [This happens by connecting the cylinder with a...- Abigale
- Thread
- Irreversible Process
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
D
Irreversible Carnot Vapor Power Cycle
Two questions: 1. What does the T-s diagram look like for the irreversible cycle? 2. Do the isentropic efficiency equations that you apply to turbines and compressors (especially in the Rankine cycle) apply to the theoretical "turbines" and "pumps" in the Carnot cycle?- dillonmhudson
- Thread
- Carnot Cycle Irreversible Power Vapor
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-

Thermodynamics: Is Stirling engine reversible or irreversible?
Stirling engine: the cycle is composed by two isothermals and 2 isometrica and there are just two heat reservoirs. By the isometrics I would say that that it is irreversible since you exchanging heat with a reservoir at a different temperature than your gas. However my notes say the...- tsuwal
- Thread
- Engine Irreversible Reversible Stirling Stirling engine Thermodynamics
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
C
Area of event horizon and irreversible mass of Kerr black hole
Hi everyone, and happy new year if you happen to be reading this tomorrow. Rather than partying, I am writing up 100+ pages of astrophysics lecture notes, which I think will take infinite time as I keep getting stuck on every other line. My current problem is with the equation for the...- ck99
- Thread
- Area Black hole Event horizon Hole Horizon Irreversible Kerr Mass
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
O
Work done for irreversible process
For reversible, work done =∫P dV Then for irreversible ,we can't use the above equation, because we have to consider the dissipative work. Correct? Thank you- Outrageous
- Thread
- Irreversible Process Work Work done
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Mechanics
-
D
Irreversible Compression and Expansion
Say I have a gas enclosed in a bottle with a weight on top exerting pressure P0. Let the gas pressure be P. If P0 is not equal to P the compression/expansion will be irreversible. If P0>P and the gas is being compressed: Work done on the gas is: -PdV Work done on surroundings by the gas...- dsdsuster
- Thread
- Compression Expansion Irreversible
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
B
Entropy change of the surroundings during irreversible process
According to my textbook, during an irreversible process, the entropy change of the surroundings is given by \frac{q}{T} where q is the heat transferred to the surroundings during the process. Why are we allowed to use this equation, considering that this equation only holds for reversible...- Bipolarity
- Thread
- Change Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

Thermo - Prove that a rapid chemical reaction is irreversible.
Homework Statement Show that processes involving rapid chemical reactions are irreversible by considering the combustion of a natural gas (e.g. methane) and air mixture in a rigid container. Homework Equations Q_{in}+W_{e,in}-W_{b}=\Delta U+\Delta KE+ \Delta PE The Attempt at a Solution I...- JJBladester
- Thread
- Chemical Chemical reaction Irreversible Reaction Thermo
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
R
Question about entropy=0 in an irreversible process
We learned about calculating entropy in my physics 2 class, and i came up with an example that my professor couldn't answer, so I was hoping someone here could shed some light on this for me. We learned that change in entropy for an irreversible process be represented by changes in entropy of...- Ruko15
- Thread
- Irreversible Process
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
O
First Law of Thermodynamics for Irreversible Processes
Hello everyone. I have found quite a lot of conflicting information about the first law applied to irreversible processes and in particular whether the dS term in the equation dU = TdS - pdV only accounts for the entropy transferred or for the total entropy, i.e. dS_transferred + dS_created...- omberlo
- Thread
- First law Irreversible Irreversible processes Law Thermodynamics
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
J
Entropy related questions - Reversible or Irreversible?
Entropy related questions -- Reversible or Irreversible? Homework Statement A 15.0kg block of ice at 0C melts to liquid water at 0C inside a large room that has a temperature of 20C. Treat the ice and the room as an isolated system, assume that the room is large enough for its temperature...- JustinLiang
- Thread
- Entropy Irreversible Reversible
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Are textbooks sloppy with the entropy change of an irreversible process?
Trying hard to understand a basic textbook model meant to illustrate that entropy (of the universe) increases for irreversible processes. Help me out please? I get this part: A gas is compressed isothermally (constant T) and reversibly, getting worked on and expelling heat. To calculate ΔS...- Confusus
- Thread
- Change Entropy Irreversible Process Textbooks
- Replies: 82
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
L
Reversible vs. Irreversible change (gases)
Homework Statement I know how to do the problem so I don't need help actually solving it, I just don't understand the concepts. A sample of 4.5g of methane occupies 12.7L at 310k. a) Calculate the work done when the gas expands isothermally against a constant external pressure of 7.7 kPa...- LogicX
- Thread
- Change Gases Irreversible Reversible
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
T
A possible case of an irreversible process in which total entropy decreases
When a hot stone is dropped into a lake the change in temperature of the lake is negligible, but the stone cools down and so its entropy decreases. Is this therefore a case of an irreversible process in which total entropy decreases? This isn't for homework but for revision towards my resit. I...- ticktock
- Thread
- Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
C
Why are real life process irreversible
From what I've read all processes of a thermodynamic system are irreversible because some energy will be lost to the surroundings but I don't understand why that can't be reversed by getting the surroundings to put that energy back into the system. Let's say I have a gas canister with a piston...- cnidocyte
- Thread
- Irreversible Life Process
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
H
Clausius inequality and irreversible heat transfer
I don't seem to understand Clausius inequality at all. Really. It was deduced to me that the Clausius inequality is given by dS = \frac{\delta Q_i}{T} > 0 where Q_i is the irreversible heat transferred to a system. Though I cannot find a way to prove an assertion my teacher said: through...- Hobold
- Thread
- Clausius Heat Heat transfer Inequality Irreversible
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
G
Irreversible change - thermodynamics
Homework Statement I'm reading a book on Thermodynamic processes, and they argue that for an irreversible change dW\geq-PdV and I can't explain to myself why is this. Can anyone help?- Grand
- Thread
- Change Irreversible Thermodynamics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Isothermal expansion: reversible vs irreversible
1. A sample of methane of mass 4.5 g occupies 12.7 L at 310 K. Assume that the gas behaves ideally. (a) Calculate the work done when the gas expands isothermally against a constant external pressure of 30.0 kPa until its volume has increased by 3.3 L. (b) Calculate the work that would be done...- chemboy101
- Thread
- Expansion Irreversible Isothermal Reversible
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Entropy change of an irreversible process
i can't seem to get something in classical thermodynamics entropy is a state function of a system,that means it only depends on the state of a system not time or path. if i have an irreversible process between state 1 and state 2, and back to state 1, and i want to know the entropy change of...- flasherffff
- Thread
- Change Entropy Irreversible Process
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
Z
What is the Concept Behind 'Irreversible Adiabatic Process'?
What is the concept behind 'irreversible adiabatic process' ? Why is the expression for work done in this case different from that when it is reversible? -
A
Reversible and irreversible reactions
I need some clarification on the following points on the reversible and irreversible reactions. In the examples cited in textbooks, for reversible reaction, isothermal expansion and compression are given. But the adiabatic exp and comp are not given. Why is it not included in the list...- ananthu
- Thread
- Irreversible Reactions Reversible
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics