You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Solubility Definition and 244 Threads
-
R
Gas solubility in gas versus liquid
Hopefully this question makes sense; when talking about solubility of a gas does this have any relation to its ability to mix with another gas? i.e. gas solubility in gas, versus, gas solubility in liquid In ultrasonic cavitation some say that a more soluble gas can more easily enter the...- rwooduk
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gas Liquid Solubility
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
N
Why Does Benzoic Acid Have a Higher Ka but Lower Solubility than Acetic Acid?
why is Ka of benzoic acid greater than acetic acid in aqueous medium yet water solubility of benzoic acid is less than acetic acid . (water solubility of acetic acid is infinite) ?- #neutrino
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility Water
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-

A question about the special case of calcium hydroxide
Hi! I am having trouble understanding how a substance only slightly soluble in water is considered as a strong base. Isn't the definition of a base a substance that will increase the amount of OH- in a solution? In that case, shouldn't calcium hydroxide be considered a weak base because of its...- Dong Aleta
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Chemistry
-
Y
Ozone Solubility in Water and Its Potential Health Impact
Hi everyone Let say i have a 60 liters water tank filled with tap water (no fluoride). And i keep this 60 liters of water saturated with ozone at 600 ORP for 24 hours. The saturation method is just simple airstone zone diffusing method. so, will this ozone gas leaks(or diffuse out) out to the...- yesiamdumb
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ozone Solubility Water
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Chemistry
-
R
Which fluoride is the most soluble in water?
Homework Statement The fluoride which is most soluble in water is: a)CaF2 b)BaF2 c)SrF2 d)BeF2 Homework Equations none The Attempt at a Solution the answer given is D. but BeF2 is covalent in nature and is soluble in organic solvents. Due to more electropositivity of Ba, BaF2 will have more...- Raptor
- Thread
-
- Tags
- solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
H
Calc Solubility of PbCl2: 0.12g/0.015L
Homework Statement Suppose 200 mg of PbCl2 was added to 15.0 mL of water in a flask, and the solution was allowed to reach equilibrium at 20.0 C. Some solute remained at the bottom of the flask after equilibrium, and the solution was filtered to collect the remaining PbCl2, which had a mass of...- henry3369
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

Are the Two Statements About Ksp and Solubility Consistent?
Homework Statement I read this line in my textbook: "##PbS,CdS## are precipated in dilute solution only due to higher ##K_{sp}##" And I googled about the relation between solubility and ##K_{sp}## and I found that: "More is the ##K_{sp}## of a salt more it is soluble in a solution(I think...- mooncrater
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility Value
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
B
How to calculate the solubility of AgCl in a solution containing NaCl?
Homework Statement What mass of AgCl will dissolve in 1 L of water containing 0.0144 moles of NaCl. Ksp = 1.7 x 10^-10 Homework Equations Ksp = [x][x] and ICE table The Attempt at a Solution So, the common ion effect is taking place here and the equilibrium taking place is: AgCl(s) ↔ Ag+ +...- brake4country
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Mass Solubility
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

What is the solubility of K2Cr2O7 in water at 20 °C?
Homework Statement 5. The solubility of K2Cr2O7 in water is 125 g/L at 20 °C. A solution is prepared at 20 °C that contains 6.0 grams of K2Cr2O7 in 50. mL of water. This solution is (A) dilute. (B) saturated. (C) supersaturated. (D) unsaturated. Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution Hi...- jdawg
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
B
Which Expression Represents the Solubility Product for Cu(OH)2?
Homework Statement Which of the following expressions represents the solubility product for Cu(OH)2? (A) Ksp=[Cu2+][OH-]2 (B) Ksp=[Cu2+]2[OH-] (C) Ksp=[Cu2+]2[OH-]2 (D) Ksp=[Cu2+][OH-] Homework Equations Ksp= [A][ B] The Attempt at a Solution Okay, so I understand equilibrium expressions and in...- brake4country
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Product Solubility
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
T
What Are the Solubility Rules for Predicting Precipitate Formation?
Homework Statement Ok, so basically, our teacher gave us some solubility rules... then we did a problem where we mixed two solutions and checked to see if a precipitate would form. So he calculated Qsp for one of the products and compared it to Ksp for that product, he did not calculate Qsp...- ThatDude
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

Chloride Sulphate in "L S, B C L, S P A" ? Mnemonic?
I came across this in a thread on Na & K carbonates "Basically, just remember, L S, B C L, S P A All potassium,nitrate salts are soluble.. however, chlorides,carbonates and sulphates are an exception.For chlorides, all chlorides are soluble except lead chloride and silver chloride..all...- Merlin3189
- Thread
-
- Tags
- solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry
-

Inverse Solubility of Solid Solutes
Why is the solubility of some solids lower when the solution is heated? I read that it is because the process is exothermic (heat from breakdown is greater than the heat needed for breakdown). But why would having extra heat from outside sources inhibit the dissolving process, wouldn't it only...- Misha Kuznetsov
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Inverse Solid Solubility
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Chemistry
-
V
Selective precipitation, purity and yield of precipitate
Homework Statement An aqueous effluent contains 12 M Cd2+ and 10 M Mg2+ as solution of nitrates. Current practice is use NaOH to selectively precipitate the metals. (a) Is it feasible to get 0 Cd impurities in Mg ppt by using NaF instead of NaOH (back up your answer with adequate calculations)...- vickyvoo2
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

Solubility and Precipitation of Unknown Ion
Homework Statement A colorless solution is known to contain one of these ions. Which ion is present if adding dilute HCl produces a white precipitate that dissolves when the solution is warmed? (A) Ag+ (B) Cu2+ (C) Hg22+ (D) Pb2+ Homework Equations N/A The Attempt at a Solution I know it...- Teemo
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ion Precipitation Solubility
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
P
What Units are Used for Hansen Solubility Parameter?
For those of you who know what a Hansen Solubility Parameter is, does the "hydrogen-bonding" part means the actual hydrogen bond energy between molecules? I'm confused as to why they used mPa^0.5 instead of kJ/mol^-1 for measurement.- Pen Rie
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
E
Solubility of Ammonia gas in Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Hi Everyone, I'm writing a research plan for a college lab and I need the solubility of Ammonium Gas in Dimethyl Sulfoxide at STP and RTP. I've been searching internet and I haven't found anything. Please let me know the solubility or where I can find this information. Any help is greatly...- ejnovek
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ammonia Gas Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-
E
Will (NH4)HCO3 Form in Polar Solvents?
I know aqueous Ammonium Bicarbonate forms when NH4+ and HCO3- ions are present in water after they've dissolved from their gaseous states of NH3(g) and CO2(g). This occurs in the reaction: NH3(g) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) => (NH4)HCO3(aq) If Ammonia gas and CO2 are present above a polar organic...- ejnovek
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
I
Solubility & Size of Substances with London Forces
Hello, How can you tell if a substance like CO(2) is small enough to be soluble while having the London forces holding it together? is there an equation? how am I supposed to know if a substance is too big to be soluble while having London forces? thank you ;D- ilii
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry
-
D
Simple concentration problem but something's wrong
Ok so I think I have a suitable answer to my question but because of certain circumstances I have reason to believe my answer is wrong. The question is: calculate the amount of phosphoric acid in mgH3PO4/L in a solution of concentration 2.92X10^-5 mol/L. seems pretty straight forward but...- delsaber8
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Concentration Solubility
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
O
Infinite Solubility: Solving Ethanol in Water Without Limit
"The extent of solubility ranges widely, from infinitely soluble (without limit) (fully miscible[1]) such as ethanol in water, to poorly soluble, such as silver chloride in water." from wiki page of solubility So does it mean that you can solve ethanol in water as much as you want? Even if...- onurbeyaz
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Infinite Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Chemistry
-
E
Solubility in Relation to Partial Pressure vs. System Pressure
Hi Physics Forums, The solubility of a gas according to Henry's Law depends on partial pressure. Would an increase in pressure in a system increase the solubility of a specific gas, even if the partial pressure of that particular gas doesn't change? The system described above increases in... -
E
How does superheating affect solubility?
During my summer chemistry course yesterday, I asked my teacher this question and she said she didn't know.- ejnovek
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry
-
P
Ksp: Not Defined for Soluble Salts? Equilibrium Impact
Why is Ksp not defined for soluble salts? Also, when an equilibrium is established between the solid, undissolved salt and the ions in the saturated solution, won't adding more solid shift the equilibrium to the left causing more ions to form?- PFuser1232
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Product Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-

Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) Problem
5g of AuBr3 (Ksp = 4.0 x 10^-36) are placed in 25 ml of water, how many grams of Au ions are dissolved in the 25 ml? My instructor used the conversion factor (6.2 x 10^-10 mol Au ions) to get from 25 ml H2O to grams Au. I believe the conversion from ml of H2O to grams of Au is: 25ml H2O x...- Neptune2235
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Constant Ksp Product Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
A
Why Is the Maximum Solubility of PbI2 Not Divided by Two?
Hi, Can you look at the answers sheet of my notes? There seems to be a mistake with the maximum solubility of PbI2. Why do they not divide by two? I get 0.000187M.- alingy1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dissociation Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
B
Will a precipitate form? Molar solubility question
Homework Statement Hello all, This is a problem on a worksheet I was given and I am stumped! Statement: Will a ppt form when 35.00 mL of 1.0x10^-3 M CoSO4 is mixed with 15.00 mL of 7.50x10^-4 M Al2(SO4)3 and 200 ml of a buffer which is .200 M NH3 and .200 M NH4Cl? I do not need the answer...- BrettJimison
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Form Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
A
Solubility Product, finding molar concentration
Homework Statement If the 2.0 x 10-5 mol of Cu(IO3)2 can dissolve in 2 L of NaIO3, find the molar concentration of the NaIO3 solution. Ksp = 1.4 x 10-7 for Cu(IO3)2.Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Let y = [IO3-(aq)] present in the solution from NaIO3 Cu(IO3)2(s) ↔ Cu2+(aq) +...- Ace.
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
Q
Solubility of Metal Hydroxide in Solutions
Homework Statement Of the following solutions, the solubility of calcium hydroxide (s) is least in: 1) 0.4 M calcium chloride 2) 0.2 M barium hydroxide 3) 0.25 M calcium nitrate 4) 0.3 M potassium hydroxide 5) 0.45 M sodium nitrate Homework Equations Either I haven't gotten to...- Qube
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Metal Solubility
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
Q
Calculating Ksp for Iron(II) Hydroxide
Homework Statement A saturated solution of iron(II) hydroxide has a molar solubility of 3.65 x 10^-6 M. Calculate the Ksp for Fe(OH)2. Homework Equations Ksp = [A]^a[B]^b The Attempt at a Solution Fe(OH)2 --> Fe^2+ + 2OH- Ksp = [3.65 x 10^-6 M] * (2*[3.65 x 10^-6 M])^2...- Qube
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Constant Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
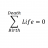
Predicting Precipitates: A Double Displacement Homework Exercise
Homework Statement Which of the following combinations of compounds will produce a precipitate? 1. Barium hydroxide and ammonium phosphate 2. Silver nitrate and potassium acetate 3. Copper(I) sulfate and sodium chloride Homework Equations Double displacement. The Attempt at a...- STEMucator
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
M
What is the Correct Molar Solubility for Barium Chromate and Silver Phosphate?
Homework Statement I have worked these two problems to the best of my knowledge and I keep getting the wrong answer (I'm not sure what the right answer is). Here are the questions: 1. At a certain temperature the solubility of barium chromate (BaCrO4) is 1.9×10-5 mol/L. What is the Ksp of...- mainzelmadchen
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
A
Solving Nonpolar Solubility: CO2 & CH4
This is not a homework question. It's the beginning of August for pete's sake. I read that like dissolves like, but what about the density of the molecules that are being dissolved? For instance in a solution (gaseous or liquid) of CO2 and CH4, they are both nonpolar, so they mix...- aclark609
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Chemistry
-
S
What is the correct concentration of Cl- in various aqueous solutions?
Homework Statement Which of the following aqueous solutions has a Cl– concentration of 2 m at 25°C? A. 271 g of HgCl2 in 55 mol of H2O B. 271 g of HgCl2 in 22.5 mol of H2O C. 53 g of NH4Cl in 55 mol of H2O D. 53 g of NH4Cl in 22.5 mol of H2O. Correct Answer...- silversurf
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Homework Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

I need to understand this derivation on solubility
Homework Statement This is a derivation of the relation between solubility of a salt and pH of the solution in which it is dissolved from our textbook. Consider a salt MX whose Ksp=[M+][K-] If this were dissolved in a solution of the acid HX whose Ka=[H+][X-]/[HX] then what would be its...- Sunil Simha
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Derivation Solubility
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

NIOSH indicates solubility in percentage. What is the meaning?
Usualy solubility is presented in grams per volume or mols per volume but NIOSH indicates in percentage? Where can I find a reliable source that explains what does this mean?- tsuwal
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-
B
Systematic Treatment of Molar Solubility
How do we systematically calculate the molar solubility of a substance with regards to its Ksp? In other words, where does the value of "molar solubility" fit into the equilibrium calculations? This should build up so that I can understand how to systematically treat the common ion effect... -
Why is solubility of HBr Less Than HCl ?
The maximum concentration of dissolved HBr , 8.9 moles/L is less than HCl 12 moles/L The values from table below from various sources suggest that HBr should be more soluble at STP in 1 liter water ? .........HBr.......HCl enthalpy of formation....-53kJ.mole >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>-96kJ/mole...- morrobay
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Hcl Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-
R
Measuring CO2 Solubility in Various Liquids: Experimental Setup Suggestions
I have a few liquids and I want to determine the solubility of CO2 in each of these liquids. How can I set up an experiment to do so? Put the liquids through a CO2 environment and weigh the difference? Set up an upside-down glass tube (like a mercury barometer) with a CO2 bubble and see how...- refind
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gas Liquid Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
S
Ranking question about solubility
Rank the following of increasing solubility in acetone, (CH3)2C=O A. Oxygen B. CH3CH2CH2OH C. HOCH2CH2CH2OH I know that acetone has dipole-dipole interactions but it is capable of hydrogen bonding as it has 2 hydrogen bond acceptors. So in A, there are only London Dispersion interactions so...- sgstudent
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ranking Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Chemistry
-
M
Why is the salt solubility curve flat?
I know most salts' have increased solubility in 100g of water with an increase in temperature, a few have an inverse relationship, but why does NaCl flatline regardless of temperature? Like is there a mechanism that explains this phenomenon? Thanks in advance.- MadViolinist
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Curve Flat Salt Solubility
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Chemistry
-
F
Preparing solution of low solubility organics in water
I'm making a stock solution of xylene in water. The solubility of xylene in water is 200 mg/L (Andrews and Keefer 1949). The density of xylene is 864 mg/mL. Making 1 L stock solution is too much and a waste. 0.23mL (or 230µL) of xylene is equivalent to 198.72mg. To make the stock...- FaNgS
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility Water
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Chemistry
-
D
What is the solubility of Al(OH)3 in 0.0010 M Al(NO3)3?
Homework Statement The Ksp of Al(OH)3 is 1.0 x 10-33. What is the solubility of Al(OH)3 in 0.0010 M Al(NO3)3? Give your answer using scientific notation and to 2 significant figures (i.e., one decimal place). Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution I can solve easier...- dolpho
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ksp Solubility
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
N
Is the solubility of a salt affected by how much salt you add to a solution?
Hey. Will a saturated solution of a salt at a constant temperature and pressure have a constant amount of dissolved salt even as you add more salt? Let us pretend that acid-base or metal-complex reactions don't happen.- Nikitin
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Salt Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry
-
A
I dont understand how solubility product (Ksp) work?
Suppose the Ksp value of AgCl is 2 x 10^-10. Lets say we have a saturated solution of AgCl, i.e concentration of Ag+ ions = concentration of Cl+ions = (2 x 10^-10)^0.5=1.41 x 10^-5 Ok so what i know is that if we add more Ag+ ions in the solution, precipitation of AgCl would occur since... -
J
What is mole fraction solubility?
As asked above, what is mole fraction solubility? From what I've been taught, it is the following equation: mole fraction solubility = (number of moles of solute)/(number of moles of solute + number of moles of solvent) Is that even correct? In actual fact, there's a question that deals with... -
P
Acetanilide Solubility: Is It Soluble?
Hey guys. Really amateurish question but I just wanted to check something. I was doing an experiment a little while ago and from what I recall my acetanilide sample was soluble in petroleum ether but I just read somewhere that some other fellow got a result suggesting it is insoluble. So my...- PhiPhenomenon
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Solubility
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Chemistry
-
N
Chemistry Acid/base solubility question
Homework Statement Each of the following salts can be prepared from an acid and a base. Write the balanced molecular equation and the net ionic equation for the preperation of each. indicate states of the reactants and producys . Review solubility rules if neccesary to determine the...- Nellen2222
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Chemistry Solubility
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

Some doubts I have while trying to compare boiling points/ solubility
I was trying to compare some solubilities (in water) and some boiling points, and I could not explain it for some molucules. Also, I have some doubts in the theory itself. Why is 2-pentanone more soluble than pentanoic acid? Why is a ketone more soluble than the respective aldeyde... -

Solving Solubility Doubt: Sodium Benzoate vs. Toluene
I was solving an exercise where I had to judge (true or false) 5 statements. One of them said: "Sodium benzoate is more soluble in water than in toluene" The book answer is true, but I don't know how to compare it. I mean, sodium benzoate is ionic, and water is very polar, so the...- jaumzaum
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Doubt Solubility
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry