You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Specific heat Definition and 481 Threads
-
B
Finding specific heat capacity of a non-monatomic (ideal gas)
Homework Statement Suppose that 31.4 J of heat is added to an ideal gas. The gas expands at a constant pressure of 1.40x104 Pa while changing its volume from 3.00x104 to 8.00x104 m3. The gas is not monatomic, so the relation CP = 5/2R does not apply. (a) Determine the change in the internal...- BOAS
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Thermodynamics. Finding specific heat capacity
Homework Statement Ideal gas of point particles is expanding so that its molar heat capacity Cx is constant and the work done by gas is W = 156J. Then the gas is isochorically heated to the initial temperature by receiving the quantity of heat which is Q = 125 J. Find Cx. Homework...- Rugile
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
F
Thermal physics - entropy change (latent heat, specific heat etc)
Hi all, could somebody have a look over my answers for this question please? The value I got for the second part seems quite feeble. Homework Statement The Attempt at a Solution Part a) Key m = mass cs = specific heat bronze cm = specific heat molten bronze Tfus = melting...- Flucky
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
How can I find the specific heat of Normal Saline 0.9% ?
I have to use this specific heat value to calculate the heat load for designing a machine as refrigerator. Could you please help me to find accurate value. ps. This normal saline is used for medication.- Prin
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Heat Normal Specific Specific heat
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-

Help with English units. Specific Heat
Homework Statement I have a problem that I've mostly solved using Ideal-gas specific heats for Oxygen. It has the form C_p = a + bT + cT^2 + dT^3 I am supposed to give the answer in English units of \frac{Btu}{lbm}, but I am having some difficulties in my conversion. Homework...- MacLaddy
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
M
Is the Specific Heat of Ice Constant Below Zero Degrees Celsius?
The portion highlighted in the paint document, is the only the specific heat for ice at -10 deg celc? What is the specific heat of ice in the interval of [-273.15,-10) and (10,0] (In deg celc) ??- Miike012
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Heat Specific Specific heat
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
Specific heat capacity and heat capacity?
A spark does not cause injury when it strikes the skin of a child. If you touch the burning stem, it can cause severe burn on your fingers? WHY? What's the difference between specific heat capacity and heat capacity?- threy
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

Specific Heat Capacity of a body
How does the amount of heat absorbed by a body depend on the mass of the body and surrounding conditions such as pressure?- andyrk
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Cast iron specific heat in function of the temp
Hi all, I need the relationship between cast iron specific heat and temperature in order to perform a disc brake thermal analysis. Where could I get this data? I just need average values for a typical cast iron used for disc brakes. Any suggestion is appreciated Thanks- serbring
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
M
Time to achieve specific heat transfer for fluid flowing in a pipe
I am currently in the process of designing a section of pipe in which a fluid will flow within, and would like to determine the specific heat transfer which may occur once the fluid enters the pipe, until it exits. The fluid will be flowing at a constant velocity "V" at a Temperature "T1" at...- MoeHij
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-
L
Approximation of specific heat, Debye model
Hi everyone I have trouble with this task Homework Statement the specific heat cv is given by c_v =\frac {N_A k_b \hbar^2}{{\Omega_D}^3 {k_b}^2 T^2} \int \limits_{0}^{\Omega_D} \! \frac {\Omega^4 exp\frac{\hbar \Omega}{k_b T}}{{(exp\frac{\hbar \Omega}{k_b T}-1})^2} \, d\Omega I...- Lindsayyyy
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
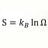
Entropy Of Mixing and Specific Heat
Homework Statement 100g of lead, specific heat .0345 cal/g/C at 100 C is mixed with 200 g of water at 20 C. Find the difference in entropy of system at end from value before mixing. Note: I think the book has wrong answer of 1.42 cal/K Homework Equations Before mixing entropy for water =...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
What is the Difference Between Latent Heat and Specific Heat?
Homework Statement I took a test and got it back I'm wondering if my prof. definition is correct. The heat required per unit mass of a substance to produce a phase change is called? A. specific heat B. Specific heat capacity C. latent heat I said it was C. He say's B Please...- Jbreezy
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Y
Higher Specific Heat Capacity: Explained
Now consider two objects,A and B. A has a higher specific heat capacity that B. When both object is subjected to same amount of thermal or heat energy, rise in temperature in A is lower as our common reason(A has a higher specific heat capacity) But what stated by First law of thermodynamics...- Yh Hoo
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
R
Specific Heat Capacity, Heat Energy, Thermodynamics Physics
Homework Statement A block of ice has a mass of 150g and a temperature of -4°. The ice is melted by supplying 60KJ heat energy. Determine the final temperature of the melted water. Homework Equations Equations i think can be used: Q = ml and H = mcΔθ The Attempt at a Solution...- RCF
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
What to solve for in specific heat energy problem
Homework Statement You have a position working with a group investigating biological mechanisms that determine a predisposition to obesity. Your assignment is to measure the rate that energy is output by certain types of cells when a nutrient is introduced. To begin this study, you have...- Violagirl
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Photon energy and specific heat capacity
If I use the answer given in the book for part a, I can get the correct answers for b and c. However, I do not know what I have done wrong in part a? My best guess would be that assuming the blood evaporates at 100 degrees is incorrect? The answer given in the book is 5.1*10^{-3}J- Fluxthroughme
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Diethyl Phthalate Specific Heat Capacity
Does anyone know where I can find the specific heat capacity of Diethyl Phthalate? I tried google but couldn't find it. Any help would be appreciated. -
N
The Specific Heat of a Free-Electron gas calculated by using the Fermi
Homework Statement Here g(ε_f) is the density of levels at the Fermi energy and T is the temperature. Calculate the specific heat of the electron gas in potassium (K) treating it as a free gas. For a free gas the density of electrons at ε_f is: g(ε_f)=(3/2)(n/E_f) where n is the electron...- nboogerz
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fermi Gas Heat Specific Specific heat
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Specific heat capacity of Argon dependence on temperature
Hi boys and girls. I am looking for Specific heat capacity of Argon dependence on temperature but i can't seem to find it anywhere. Do you have some source where I could get it from?. I need it for temperatures up to 1300K since i need to evaluate enthalpy of fumes at the exit from a gas...- jakub.gongol
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

The specific heat capacity of solids
Why is the specific heat capacity of most solids around 25JK-1mol-1? I remember being told ages ago that is was something to do with the theory of equipartition but I'm not really sure how that theory affects it or why it's around 25JK-1mol-1- Saxby
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

What do the symbols H and U represent in thermodynamics equations?
Can someone please tell me what does the symbol H and what does the symbol U represent in these equations: http://www.taftan.com/thermodynamics/CP.HTM"][/PLAIN] http://www.taftan.com/thermodynamics/CP.HTM- Saxby
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
E
Finding Final Temperature of Boiling Water and Potatoes
Homework Statement I have some boiling water that I am adding potatoes to. I am asked to find the final temp after the potatoes have been added to the boiling water. Tiw=100C (initial boiling water temp) Tip=30C (initial room temp potatoes) mp=0.5kg (mass of potatoes) mw=1.5L or 1.5kg (mass...- erok81
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Heat Specific Specific heat
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Calculating molar specific heat capacity - not a monatomic gas
1. Suppose that 25 J of heat is added to one mole of an ideal gas. The gas expands at a constant pressure of 2.62 x 10^4 pascals while changing its volume rom 4.97 x 10^-4 m^3 to 7.02 x 10^-4 m^3. Calculate C_p and express in Joule / (mole * Celsius) 2. Relevant equations Q =...- PhysicsFriend
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Y
Latent Heat + Specific Heat Problem
Homework Statement Suppose molten (liquid) lead, mass ml = 9.83 kg, is at its melting point. The lead is poured into water of mass mw = 585 g and initial temperature Tw = 16.2 C. Find mwb, the amount of the water that boils. NOTE: Reaching the boiling point is not enough; the question asks...- yaylee
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Finding molar specific heat at constant pressure
Homework Statement Let 25.6 J of heat be added to a particular ideal gas. As a result, its volume changes from 41.0 to 82.0 cm3 while the pressure remains constant at 1 atm(= 101 kPa). a) By how much did the internal energy of the gas change? -- 21.5 J got this part b) What is the molar...- dinospamoni
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Finding the specific heat capacity of water using the gradient of a graph
Homework Statement Hi. I have an assignment to find the specific heat capacity of water. We did an experiment in class where we used an electric kettle with power output of 1850W-2200W to heat up 1,400g of water (we actually used 1,400 mL of tap water but we were told to assume that the tap...- sungholee
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Hard molar specific heat question?
Homework Statement At very low temperatures, the molar specific heat of many substances varies as the cube of the absolute temperature: C=k*(T^3/To^3), which is sometimes called Debye's law. For rock salt, To= 281K and k= 1940 J/mol*K Determine the heat needed to raise 2.40 mol of salt from...- fantexihong
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Hard Heat Specific Specific heat
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
How to Derive the Electronic Specific Heat Constant γ in 2D?
Homework Statement Hi all. This isn't homework per say, more lack of understanding of something when reading around the notes.My problem is in trying to derive the electronic specific heat constant γ in 2 dimensions. Homework Equations I know the general formula for specific heat is c^{el}...- Sturnn17
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
L
Specific Heat of Water - What is the Heat Capacity?
Homework Statement What is the heat capacity of water in J*g*°C Homework EquationsA 74.8 sample of copper at 143.2g is added to an insulated vessel containing 165ml of water, Density of water = 1.00 at 25.0 °C. The final temperature is 29.7° C The specific heat of copper is 0.385 J*g*°C...- Litcyb
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Heat Specific Specific heat Water
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
K
Calorimetry Problem, calculating the specific heat of a unknown substance
Homework Statement A 500.0-g chunk of unknown metal, which has been in boiling water for several minutes, is quickly dropped into an insulating Styrofoam beaker containing 1.00 kg of water at room temperature (20.0 C). After waiting and stirring for 5.00 minutes, you observe that the water's...- klawlor419
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Metal Low Specific Heat: Why Is It Useful?
Metals have the low specific heat capacity.why is the low specific heat capacity useful?- Smileyxx
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
M
Specific heat capacity for adiabatic & isothermal process
Can we define specific heat capacity for an adiabatic process ?? Would it always be zero since dQ is 0 for an adiabatic process? Also, can we define specific heat capacity for isothermal processes ? Would it be infinity in all cases? Just want to verify if I am thinking along the...- metalrose
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
M
Liquids, internal energy and specific heat capacity
A liquid contained in an adiabatic container is shaked vigorously so that it its temp. Increases. The heat capacity for the liquid is given, the rise in temp. Is given. According to the first law of thermo, dQ=dW + dU here dQ is 0. Asked, is to find the work done on the system, i.e...- metalrose
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
I
How to measure copper sulfate specific heat
Homework Statement I was wondering, how can i measure the specific heat capacity of a solution? Not the exercise, just doing an experimental work to measure it. Homework Equations q=mct The Attempt at a Solution I'm lost.- Ipos Manger
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
E
Specific heat capacity of brass
Homework Statement i getting the wrong the answer i am trying to find the specific heat capacity of brass using copper calorimeter Data : mass of brass bob= 32.5gm mass of calorimeter = 39.7 gm mass of water + calorimeter = 93.9gm mass of water = 93.9 - 39.7 = 54.2g specific...- emmfranklin
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Specific heat capacity and final temperature
Homework Statement A 2.8 kg sample of a metal with a specific heat of 0.43KJ/KgC is heated to 100.0C then placed in a 50.0 g sample of water at 30.0C.* What is the final temperature of the metal and the water? Homework Equations heat loss by the metal = heat gain by the water The...- moimoi24
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Specific heat at constant volume
C_{V} = \frac{∂U}{∂T} This is the specific heat at constant volume so I assume it can only be used at constant volume. However, my textbook uses this to derive the following equation for reversible adiabatic expansion: P_{1}V_{1}^{γ} = P_{2}V_{2}^{γ} Why are we allowed to use C_{V}...- Bipolarity
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
M
Specific Heat Capacity of aluminum rivets
Homework Statement Some aluminum rivets of total mass 170 g at 100°C are emptied into a hole in a large block of ice at 0°C' a. What will be the final temperature of the rivets? b. How much ice will melt? Homework Equations none The Attempt at a Solution Please help me answer...- moimoi24
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Specific Heat of Sodium vs Absolute Temperature
what is the relation between Specific Heat and Absolute Temperature of any material ? Specifically, Sodium. Cp vs T ( not the change in temperature) Any mathematical formula ? Thanks- paawansharmas
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
M
Specific Heat Capacity of Tantalum
I got a problem with this one, please help me, Tantalum is an element that is used in aircraft parts. Tantalum has a specific heat capacity of about 140 J/kg K. The aircraft part has a mass of 0.23 kg and is cooled from a temperature of 1200 K by being placed in water. If 30000 J of heat is...- moimoi24
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
T
Specific Heat of Liquid Saturation Line and Vapour Saturation Line in RefProp
Hello There, So I made a plot of some specific heats in refprop, and I chose the "Draw Saturation Lines" option. When I did this, the follow chart was produced. http://i.imgur.com/h34Pq.png Now my question is, what are these saturation lines representing? -TP- terryphi
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
J
Why are specific heat high in water but low in ethylene glycol?
Im sorry to ask such a question but I've been trying to understand the molecular reasons for why specific heat is high in some molecules but low in others. For example water has a specific heat of 4180 yet has a boiling point of 100 degrees Celsius but ethylene glycol (ethane 1,2 di-ol) has a...- junglefish1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Heat Specific Specific heat Water
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
H
Specific Heat: Bond or Freedom of Degree Based, Or Size?
Specific Heat: Bond or Freedom of Degree Based, Or Size?? Okay so I've been trying to understand what causes one substance to have a higher specific heat then other but I've read quite a few conflicting sources in which one says its due to the freedom of degree, while another says the weight of...- hwall95
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bond Degree Heat Specific Specific heat
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
H
Specific Heat: Degree of Freedom & Energy Storage
Homework Statement Okay I have to write an EEI (Extended Experimental Investigation) for physics in relation to which radiator coolant is best from a thermodynamics point of view, thus the specific heat of the coolant is the main focus. But to incorporate more depth into the report, I was going...- hwall95
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
Question About Measuring Specific Heat Capacity
Recently, I did a physics lab experiment to find the specific heat capacity of an unknown sample material. The lab instructions kept insisting that the sample had to be kept in boiling water for at least 10 minutes. My question is why? Could I have found the specific heat capacity if the sample...- theintarnets
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
C
What determines specific heat capacity of a solid?
Homework Statement Have to do a write up of an experiment on specific heat capacity of metals. Tested 50g of nickel and lead, each heated to 90C and then put into 50g of water and measuring the change in its temperature. Found that lead has a lower specific heat capacity. Homework Equations...- Crushgear64
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Newton's Law of Cooling & Specific Heat Capacity
Newton's Law of Cooling basically states (I believe): TObj = (TInital-TEnv)ekt + TEnv where k is a property of the material. In the equation: Q=mCΔT Specific heat capacity, C, is also a material property. So here's my question: Is there a relation between Newton's Law's k and the...- Bradley Sigma
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
J
Year 12: Cambridge Physics (Calculus in Specific heat capacity)
Below 20K, The specific heat capacity c of silver varies with temperature according to the equationc/\text{J /kg /K} = 1.5x10^{-4}(T/K)^3 + 6.0x10^{-3} T/K. If a small silver sphere of diameter 4am and at 20K is placed in 25g of liquid helium at 4K, what fraction of the liquid will evaporate...- johnconnor
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Radioactivity & Specific Heat Capacity Question
Homework Statement 0.2g of a radium salt was separated from a ton of uranium ore. The radioactive radium nuclide Ra-226 decays by alpha-particle emission with a half-life of 1600 years. 1 year = 3.16x107s. The curie is defined as the number of disintegrations per second from 1.0g of Ra...- Magda|A380
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help