stuidvkook
- 1
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Hi I'm super stuck in understanding bronsted lowry theory. I understand how it supposed to function but I can't wrap my brain around it. Generally any tips and advice in helping identifying bases and acids would greatly help me.
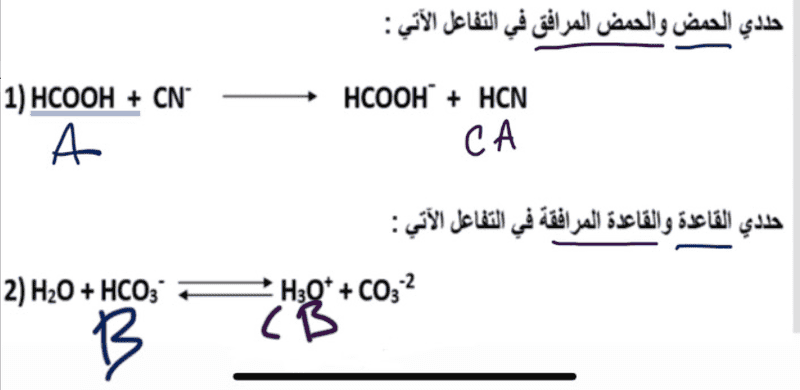
In the attempt at a solution is my possible take on this challenge, my friend offered to check it for me and said he is certain that the second one is completely incorrect.
Translation: First equation find acid and the conjugate acid.
Second equation find the base and the conjugate base.
- Relevant Equations
- bronsted lowry conjugate acids and conjugate bases.
1) HCOOH + CN- ---> HCOOH- + HCN
2) H2O + HCO3- <===> H3O+ + CO3-2
2) H2O + HCO3- <===> H3O+ + CO3-2
Last edited: