Say17
- 11
- 1
- Homework Statement
- Two trolleys with masses of 3kg and 1kg are connected by a wire. A force of 50N is exerted on the 3kg trolley and a force of 10N on the 1kg trolley. Any friction is negligible.
How much tension exists in the thread between the trolleys?
- Relevant Equations
- F = (m1+m2)a
Hi all,
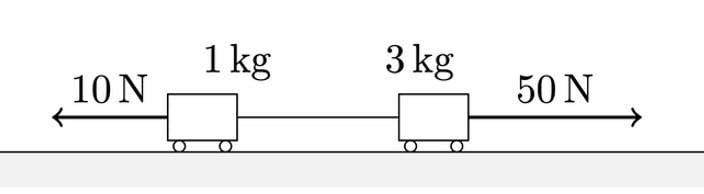
To find out the tension. First I have to find out the a.
1. step
F = ma
F = (m1+m2) *a
F = (1+3)*a
F = 4*a
F/4 = a
F = 10N + 50 N
F = 60 N
60/4 = 15 m/s^2
2.step
T =( m1/ (m1 + m2)) * F
T = (1/ 1+3) * 60
T = 15 N
But the final result is 20N.
Thanks for your help!
To find out the tension. First I have to find out the a.
1. step
F = ma
F = (m1+m2) *a
F = (1+3)*a
F = 4*a
F/4 = a
F = 10N + 50 N
F = 60 N
60/4 = 15 m/s^2
2.step
T =( m1/ (m1 + m2)) * F
T = (1/ 1+3) * 60
T = 15 N
But the final result is 20N.
Thanks for your help!