oslon
- 3
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Difference between PUT vs POST from a system administrator POV?
I believe it’s important to learn concepts from a POV of X, when trying to learn something very confusing that could mean multiple meanings.
These are what I wrote in my college notes of TCP IP that I did 6 years ago.
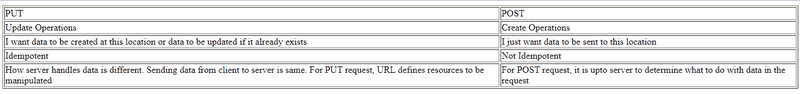
Much of it is confusing as both seem to be doing the same thing.
Can you tell me what’s the benefit of being idempotent? As far as I know idempotent means no matter how many times you repeat a input, you get same output.
These are what I wrote in my college notes of TCP IP that I did 6 years ago.
Much of it is confusing as both seem to be doing the same thing.
Can you tell me what’s the benefit of being idempotent? As far as I know idempotent means no matter how many times you repeat a input, you get same output.