arestes
- 84
- 4
- TL;DR Summary
- Hibbeler's exercise 7.5 uses a cut for computing shear flow q at a junction. However, if I choose another cut, the shear flow turns out zero. Is there a rule for choosing a good cut? Other than not getting zero.
Hello. I am reading Hibbeler's Mechanics of Materials (ninth edition). Example 7.5 computes shear flow at a segment where there are nails attached to different boards.
He chooses a cut like the one shown here:
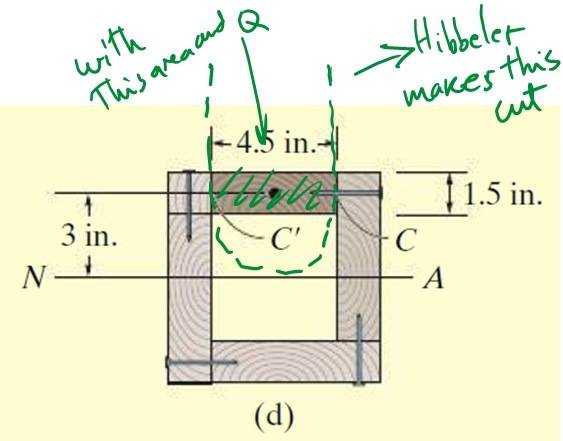
And gets (by symmetry between C and C') the shear flow q computing the first moment of area Q and the location of the cut area y.
However, I believe on can choose any cut and it will be useful as long as there is symmetry (so as to argue that the shear flow is twice the required one and dividing by two if there are two places where the cut passes through). If I choose this cut:
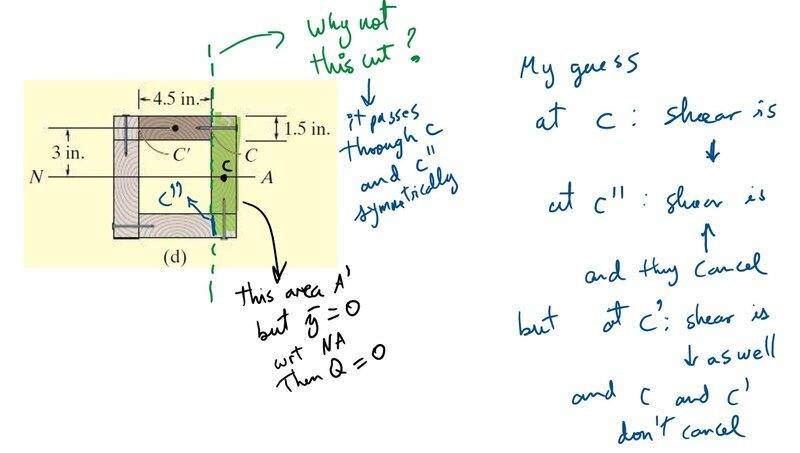
I get y (location of the centroid of the cut area) equal to zero, rendering my Q null. This isn't right.
I am looking to understand what limitations I have, or if there's any rule as to what cuts should be chosen. Or maybe if I'm doing something straight right wrong.
Thanks for any insights.
He chooses a cut like the one shown here:
And gets (by symmetry between C and C') the shear flow q computing the first moment of area Q and the location of the cut area y.
However, I believe on can choose any cut and it will be useful as long as there is symmetry (so as to argue that the shear flow is twice the required one and dividing by two if there are two places where the cut passes through). If I choose this cut:
I get y (location of the centroid of the cut area) equal to zero, rendering my Q null. This isn't right.
I am looking to understand what limitations I have, or if there's any rule as to what cuts should be chosen. Or maybe if I'm doing something straight right wrong.
Thanks for any insights.