- #1
Alhanouf
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
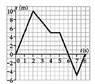
The position versus time for a certain particle
moving along the x-axis is shown in Figure 1.
Find the average velocity in the time intervals
0 to 2 s,
2 s to 4 s,
0 to 8 s.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I do not understand the question?
I want to know how to be dissolved