MatinSAR
- 673
- 204
- Homework Statement
- What should be the magnitude of force F so that the object is definitely moving?(Frictional force is equal to 0.5 for each newton of vertical force on the surface.)
A)25 B)30 C)40 D)50
- Relevant Equations
- ##F_{net} =ma##
##f_{s} =µ_sN##
##f_{k} =µ_kN##
Picture of problem:
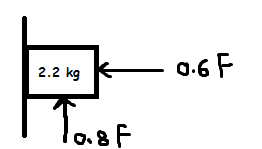
For the object to be moving, it must overcome friction.
##f=0.5*0.6F = 0.3F##
##mg=22N##
Upward motion:
##0.8F>mg+f \rightarrow 0.5F>22 \rightarrow F>44N ##
Downward motion:
##0.8F+f<mg \rightarrow 1.1F<22 \rightarrow F<20N ##
I think correct option is D. Can you please guide me if I'm wrong?
For the object to be moving, it must overcome friction.
##f=0.5*0.6F = 0.3F##
##mg=22N##
Upward motion:
##0.8F>mg+f \rightarrow 0.5F>22 \rightarrow F>44N ##
Downward motion:
##0.8F+f<mg \rightarrow 1.1F<22 \rightarrow F<20N ##
I think correct option is D. Can you please guide me if I'm wrong?