hello478
- 165
- 14
- Homework Statement
- what is percentage efficiency of transfer of KE from child to PE in spring
- Relevant Equations
- energy equations
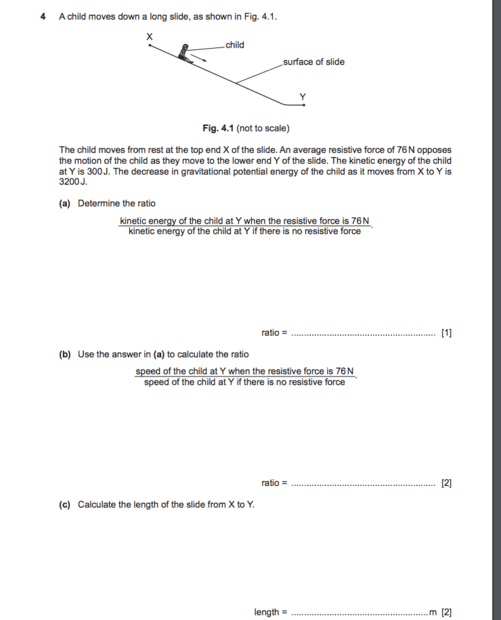
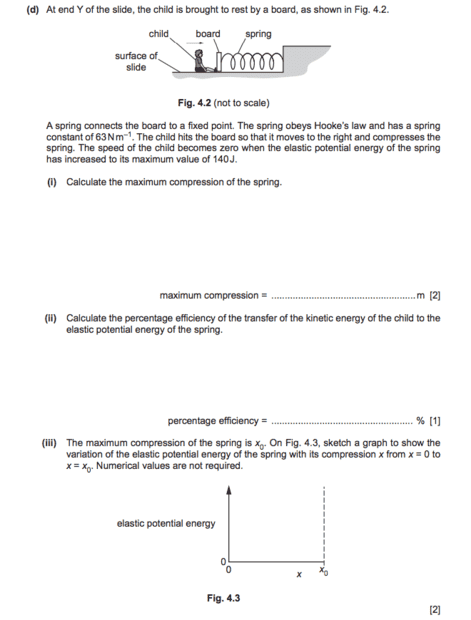
part d- ii and iii
ii) my answer is
300-140/300 *100
ke at y = 300
and spring energy at max compression is 140
iii) e is directly proportional to x^2
so it increases exponentially
is my explanation correct?
ii) my answer is
300-140/300 *100
ke at y = 300
and spring energy at max compression is 140
iii) e is directly proportional to x^2
so it increases exponentially
is my explanation correct?