jbriggs444
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
2024 Award
- 13,336
- 8,011
If you close off the far end, the pressure at the near end does not jump to 20 psi. It was already at 20 psi. If you close off the far end, the pressure at the far end does not jump instantly to 20 psi. It jumps instantly to an extreme value and the pipe may break.James Demers said:I think the OP is trying to apply rules appropriate to the static situation (no flow, pressure is equal throughout the pipe) to the dynamic situation, where the fluid is in motion. There's nothing "common sense" about the latter, at least not when it comes to the math.
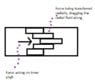
Imagine 20 psi at one end of a mile-long 1-inch pipe, and explaining "what happened" to the pressure at the far end, where the water is barely dripping out. Close off the far end, though, and the pressure jumps instantly to 20 psi. Chestermiller can explain it, but it's baffling to the amatuers in the room.
It is only after the system has settled down into a new equilibrium after some seconds (speed of sound in water is in the neighborhood of one mile per second) that it attains a condition of 20 psi throughout.
Which, I suppose, makes your point about the details not being intuitively obvious.