MasonJ1989
- 17
- 2



MasonJ1989 said:I thought that as soon as current met ground it was gone
anorlunda said:No that is a misconception. Voltages are always voltage difference between two points. The ground symbol just identifies the arbitrary place that we label zero volts. If you always remember to name the two points where you measure voltage, then you can remove the ground symbol from the circuit.
The important thing to remember is that current always flows in a closed path, back to the point where it started.
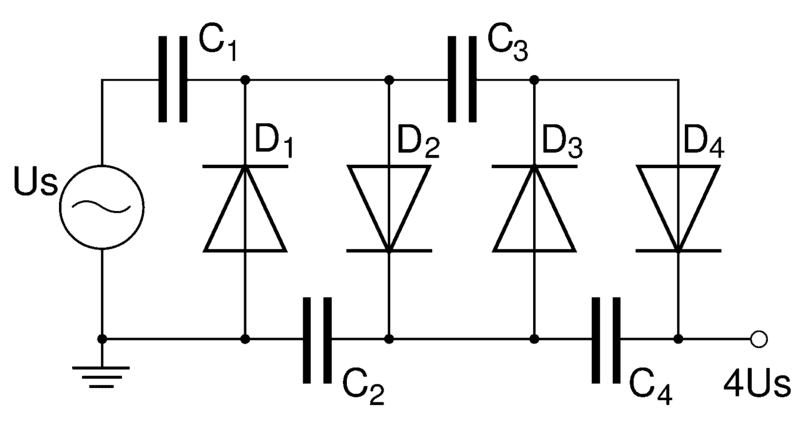
Look up ‘Cockroft-Walton voltage multiplier’. The caps are charged on alternate half-cycles and end up behaving like high-voltage cells in series. The high voltage output is between 4Us and the ground symbol.MasonJ1989 said: