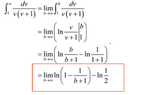- #1
yeny
- 7
- 0
View attachment 8443
Hello everyone,
I am stuck on this homework problem. I got up to (ln (b / (b+1) - ln 1 / (1+1) ) but I'm not sure how to go to the red boxed step where they have (1 - 1 / (b+1) )
if anyone can figure it out Id really appreciate it.
thank you very much.
Hello everyone,
I am stuck on this homework problem. I got up to (ln (b / (b+1) - ln 1 / (1+1) ) but I'm not sure how to go to the red boxed step where they have (1 - 1 / (b+1) )
if anyone can figure it out Id really appreciate it.
thank you very much.