- #71
Devin-M
- 1,055
- 764
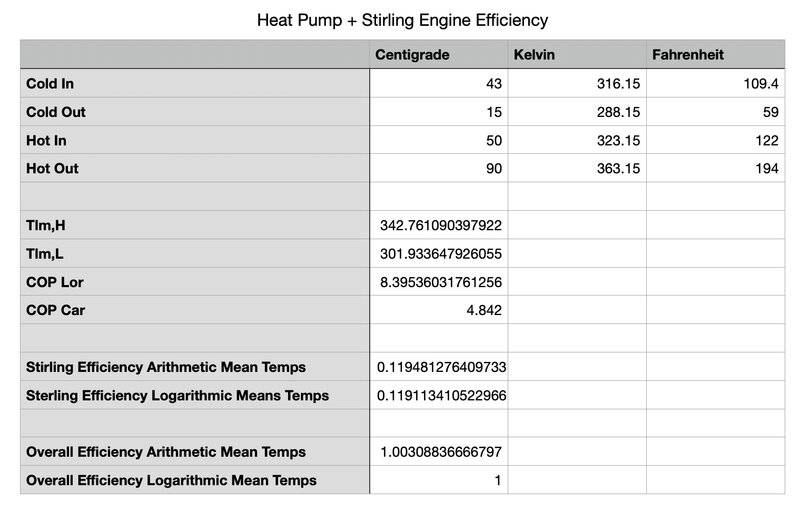
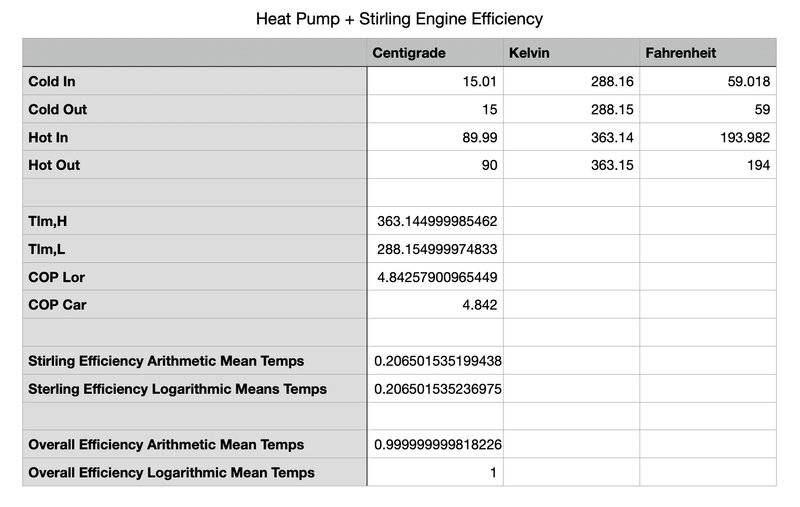
So if the CO2 stays a gas (never a liquid -- no phase change), and as it comes out of the expansion valve it's 15C, it heats (from the some water) to 43C, after compression, it's 90C, and as it transfers heat to another fluid, the CO2 gas cools to 50C (as shown in the table below), the COP of the heat pump is 8.39 (the lorenz cop). If it was a vapor/liquid mixture at constant 90C after the compressor and constant 15C after the expansion valve, the COP would be 4.84 (the carnot cop), and the lorenz cop would be the same as the carnot cop (see second table).