- 20,685
- 28,052
Summary: Lie Algebras, Commutative Algebra, Ordering, Differential Geometry, Algebraic Geometry, Gamma Function, Calculus, Analytic Geometry, Functional Analysis, Units.
1. Prove that all derivations ##D:=\operatorname{Der}(L)## of a semisimple Lie algebra ##L## are inner derivations ##M:=\operatorname{ad}(L).##
2. Give four possible non-isomorphic meanings for the notation ##\mathbb{Z}_p.##
3. (solved by @Office_Shredder ) Let ##T\subseteq (\mathbb{Z}_+^n,\preccurlyeq )## with the partial natural ordering. Then there is a finite subset ##S\subseteq T## such that for every ##t\in T## exists a ##s\in S## with ##s\preccurlyeq t.##
$$
\alpha \preccurlyeq \beta \Longleftrightarrow \alpha_i \leq \beta_i \text{ for all }i=1,\ldots,n
$$
4. (a) Solve the following linear differential equation system:
\begin{align*}
\dot{y}_1(t)=11y_1(t)-80y_2(t)\;&\wedge\;\dot{y}_2(t)=y_1(t)-5y_2(t)\\
y_1(0)=0\;&\wedge\;y_2(0)=0
\end{align*}
(b) Which solutions do ##y_1(0)=\pm \varepsilon\;\wedge\;y_2(0)=\pm \varepsilon## have?
(c) How does the trajectory for ##y_1(0)=0.001\;\wedge\;y_2(0)=0.001## behave for ##t\to \infty##?
(d) What will change if we substitute the coefficient ##-80## by ##-60##?
(e) Calculate (approximately) the radius of the osculating circle at ##t=\pi/12## for both trajectories with initial condition ##\mathbf{y}(0)=(-1,1).##
5. (solved by @bpet ) Consider the ideal ##I =\langle x^2y+xy ,xy^2+1 \rangle \subseteq \mathbb{R}[x,y] ## and compute a reduced Gröbner basis to determine the number of irreducible components of the algebraic variety ##V(I).##
6. (solved by @benorin ) Define the complex function gamma function as
$$
\Gamma(z):=\lim_{n \to \infty}\dfrac{n!\,n^z}{z(z+1)\cdot\ldots\cdot(z+n)}
$$
and prove
(a) ##\Gamma(z)=\displaystyle{\int_0^\infty}e^{-t}\,t^{z-1}\,dt\;;\quad\mathfrak{R}(z)>0##
(b) ##\Gamma(z)^{-1}=e^{\gamma z}z\,\displaystyle{\prod_{n=1}^\infty}\left(1+\dfrac{z}{n}\right)e^{-\frac{z}{n}}##
where ##\gamma :=\displaystyle{\lim_{n \to \infty}\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}+\ldots+\dfrac{1}{n}-\log(n)\right)}## is the Euler-Mascheroni constant.
7. (solved by @benorin) Let ##u\, : \,[0,1]\times [a,b]\longrightarrow \mathbb{C}## be a continuous function, such that the partial derivative in the first coordinate exists everywhere and is continuous. Define
$$
U(\lambda):=\int_a^b u(\lambda,t)\,dt\; , \;V(\lambda):=\int_a^b \dfrac{\partial u}{\partial \lambda}(\lambda,t)\,dt.
$$
Show that ##U## is continuously differentiable and ##U'(\lambda)=V(\lambda)## for all ##0\leq \lambda\leq 1.##
8. A cardiod is defined as the trace of a point on a circle that rolls around a fixed circle of the same size without slipping.
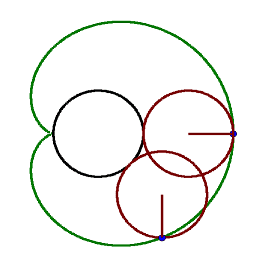
It can be described by ##(x^{2}+y^{2})^{2}+4x(x^{2}+y^{2})-4y^{2}\,=\,0## or in polar coordinates by ##r(\varphi )=2(1-\cos \varphi ).##
Show that:
(a) (solved by @etotheipi ) Given any line, there are exactly three tangents parallel to it. If we connect the points of tangency to the cusp, the three segments meet at equal angles of ##2\pi/3\,.##

(b) (solved by @etotheipi ) The length of a chord through the cusp equals ##4.##
(c) (solved by @etotheipi ) The midpoints of chords through the cusp lie on the perimeter of the fixed generator circle (black one in the first picture).
(d) (solved by @etotheipi ) Calculate length, area and curvature.
9. (solved by @nuuskur ) Let ##A## be a complex Banach algebra with ##1##. Prove that the spectrum
$$
\sigma(a)=\{\lambda\in \mathbb{C}\,|\,\lambda\cdot 1-a \text{ is not invertible }\} \subseteq \{\lambda\in \mathbb{C}\,|\,|\lambda|\leq \|a\| \}
$$
for any ##a\in A## is not empty, bounded and closed.
10. (a) Determine all primes which occur as orders of an element from ##G:=\operatorname{SL}_3(\mathbb{Z}).##
(b) (solved by @Office_Shredder ) Let ##I \trianglelefteq R## be a two-sided ideal in a unitary ring with group of unities ##U##. Show by two different methods that
$$
M:=\{u\in U\,|\,u-1\in I\} \trianglelefteq U
$$
is a normal subgroup.

High Schoolers only (until 26th)11. (solved by @Not anonymous ) If ##a,b,c## are real numbers such that ##a+b+c=2## and ##ab+ac+bc=1,## show that ##0\leq a,b,c\leq \dfrac{4}{3}.##
12. Determine all pairs ##(m,n)## of (positive) natural numbers such that ##2022^m-2021^n## is a square.
13. (solved by @archaic , @Not anonymous )
(a) Prove for any ##n\in \mathbb{N},\,n\geq 4##
$$
Q(n):=\dfrac{4^2-9}{4^2-4}\cdot\dfrac{5^2-9}{5^2-4}\cdot\ldots\cdot\dfrac{n^2-9}{n^2-4}>\dfrac{1}{6}.
$$
(b) Does the above statement still hold, if we replace ##1/6## on the right hand side by ##0.1667\,?##
14. (solved by @Not anonymous ) Determine all pairs ##(x,y)\in \mathbb{R}^2## such that
\begin{align*}
5&=\sqrt{1+x+y}+\sqrt{2+x-y}\\
2-x+y&=\sqrt{18+x-y}
\end{align*}
15. (solved by @Not anonymous ) Given a real, continuous function ##f:\mathbb{R}\longrightarrow \mathbb{R}## such that ##f(f(f(x)))=x.##
Prove that ##f(x)=x## for all ##x\in\mathbb{R}.##
1. Prove that all derivations ##D:=\operatorname{Der}(L)## of a semisimple Lie algebra ##L## are inner derivations ##M:=\operatorname{ad}(L).##
2. Give four possible non-isomorphic meanings for the notation ##\mathbb{Z}_p.##
3. (solved by @Office_Shredder ) Let ##T\subseteq (\mathbb{Z}_+^n,\preccurlyeq )## with the partial natural ordering. Then there is a finite subset ##S\subseteq T## such that for every ##t\in T## exists a ##s\in S## with ##s\preccurlyeq t.##
$$
\alpha \preccurlyeq \beta \Longleftrightarrow \alpha_i \leq \beta_i \text{ for all }i=1,\ldots,n
$$
4. (a) Solve the following linear differential equation system:
\begin{align*}
\dot{y}_1(t)=11y_1(t)-80y_2(t)\;&\wedge\;\dot{y}_2(t)=y_1(t)-5y_2(t)\\
y_1(0)=0\;&\wedge\;y_2(0)=0
\end{align*}
(b) Which solutions do ##y_1(0)=\pm \varepsilon\;\wedge\;y_2(0)=\pm \varepsilon## have?
(c) How does the trajectory for ##y_1(0)=0.001\;\wedge\;y_2(0)=0.001## behave for ##t\to \infty##?
(d) What will change if we substitute the coefficient ##-80## by ##-60##?
(e) Calculate (approximately) the radius of the osculating circle at ##t=\pi/12## for both trajectories with initial condition ##\mathbf{y}(0)=(-1,1).##
5. (solved by @bpet ) Consider the ideal ##I =\langle x^2y+xy ,xy^2+1 \rangle \subseteq \mathbb{R}[x,y] ## and compute a reduced Gröbner basis to determine the number of irreducible components of the algebraic variety ##V(I).##
6. (solved by @benorin ) Define the complex function gamma function as
$$
\Gamma(z):=\lim_{n \to \infty}\dfrac{n!\,n^z}{z(z+1)\cdot\ldots\cdot(z+n)}
$$
and prove
(a) ##\Gamma(z)=\displaystyle{\int_0^\infty}e^{-t}\,t^{z-1}\,dt\;;\quad\mathfrak{R}(z)>0##
(b) ##\Gamma(z)^{-1}=e^{\gamma z}z\,\displaystyle{\prod_{n=1}^\infty}\left(1+\dfrac{z}{n}\right)e^{-\frac{z}{n}}##
where ##\gamma :=\displaystyle{\lim_{n \to \infty}\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}+\ldots+\dfrac{1}{n}-\log(n)\right)}## is the Euler-Mascheroni constant.
7. (solved by @benorin) Let ##u\, : \,[0,1]\times [a,b]\longrightarrow \mathbb{C}## be a continuous function, such that the partial derivative in the first coordinate exists everywhere and is continuous. Define
$$
U(\lambda):=\int_a^b u(\lambda,t)\,dt\; , \;V(\lambda):=\int_a^b \dfrac{\partial u}{\partial \lambda}(\lambda,t)\,dt.
$$
Show that ##U## is continuously differentiable and ##U'(\lambda)=V(\lambda)## for all ##0\leq \lambda\leq 1.##
8. A cardiod is defined as the trace of a point on a circle that rolls around a fixed circle of the same size without slipping.
It can be described by ##(x^{2}+y^{2})^{2}+4x(x^{2}+y^{2})-4y^{2}\,=\,0## or in polar coordinates by ##r(\varphi )=2(1-\cos \varphi ).##
Show that:
(a) (solved by @etotheipi ) Given any line, there are exactly three tangents parallel to it. If we connect the points of tangency to the cusp, the three segments meet at equal angles of ##2\pi/3\,.##
(b) (solved by @etotheipi ) The length of a chord through the cusp equals ##4.##
(c) (solved by @etotheipi ) The midpoints of chords through the cusp lie on the perimeter of the fixed generator circle (black one in the first picture).
(d) (solved by @etotheipi ) Calculate length, area and curvature.
9. (solved by @nuuskur ) Let ##A## be a complex Banach algebra with ##1##. Prove that the spectrum
$$
\sigma(a)=\{\lambda\in \mathbb{C}\,|\,\lambda\cdot 1-a \text{ is not invertible }\} \subseteq \{\lambda\in \mathbb{C}\,|\,|\lambda|\leq \|a\| \}
$$
for any ##a\in A## is not empty, bounded and closed.
10. (a) Determine all primes which occur as orders of an element from ##G:=\operatorname{SL}_3(\mathbb{Z}).##
(b) (solved by @Office_Shredder ) Let ##I \trianglelefteq R## be a two-sided ideal in a unitary ring with group of unities ##U##. Show by two different methods that
$$
M:=\{u\in U\,|\,u-1\in I\} \trianglelefteq U
$$
is a normal subgroup.
High Schoolers only (until 26th)11. (solved by @Not anonymous ) If ##a,b,c## are real numbers such that ##a+b+c=2## and ##ab+ac+bc=1,## show that ##0\leq a,b,c\leq \dfrac{4}{3}.##
12. Determine all pairs ##(m,n)## of (positive) natural numbers such that ##2022^m-2021^n## is a square.
13. (solved by @archaic , @Not anonymous )
(a) Prove for any ##n\in \mathbb{N},\,n\geq 4##
$$
Q(n):=\dfrac{4^2-9}{4^2-4}\cdot\dfrac{5^2-9}{5^2-4}\cdot\ldots\cdot\dfrac{n^2-9}{n^2-4}>\dfrac{1}{6}.
$$
(b) Does the above statement still hold, if we replace ##1/6## on the right hand side by ##0.1667\,?##
14. (solved by @Not anonymous ) Determine all pairs ##(x,y)\in \mathbb{R}^2## such that
\begin{align*}
5&=\sqrt{1+x+y}+\sqrt{2+x-y}\\
2-x+y&=\sqrt{18+x-y}
\end{align*}
15. (solved by @Not anonymous ) Given a real, continuous function ##f:\mathbb{R}\longrightarrow \mathbb{R}## such that ##f(f(f(x)))=x.##
Prove that ##f(x)=x## for all ##x\in\mathbb{R}.##
Last edited:
