- #1
Gunther_Guss
- 4
- 0
- Homework Statement
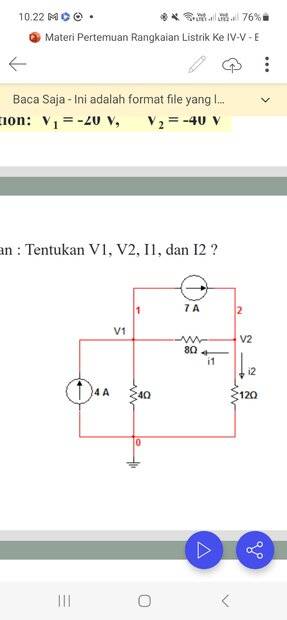
- Please, help me to find the value of V1, V2, I1 and I2.
- Relevant Equations
- i have my own answers but i need to confirm wether my answers are correct or not. Thanks.
-
Last edited by a moderator: