- 10,410
- 1,588
Wiki describes the PIGA, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PIGA_accelerometer. I want to see if I have a basic intuitive understanding of how it works.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PIGA_accelerometer#/media/File:PIGA_accelerometer_1.png

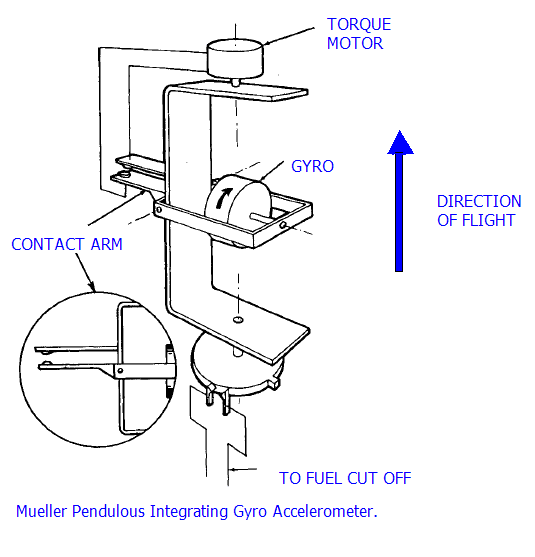
Lets imagine that the device, as shown, is at rest on the Earth's surface, with the "direction of flight" on the diagram being upwards. Let us also imagine that the motor on the top of the instrument is powered off. What I think should happen is that the gyroscope simply acts as pendulum, and falls downwards at the end of the pivot arm due to the Earth's gravity. While the gyroscope attempts to precess in a direction given by the right hand rule between the axis of rotation of the gyroscope and the applied torque due to the Earth's gravity, the mounting of the gyroscope prevents precession in this direction and the pendulum essentially falls in the same manner as it would if the gyroscope were not spinning.
Let us now imagine that as the gyroscope falls, it activates the torque motor. The resulting torque, assuming the motor is wired to rotate in the right direction, causes the pendulum to rise due to the cross product of the spin axis and the applied torque.
Thus, as Wiki describes, if a feedback loop holds the pendulum in the horizontal position, the angular velocity of rotation of the torque motor is proportional to the acceleration along the axis of flight, in this case that is the Earth's gravity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PIGA_accelerometer#/media/File:PIGA_accelerometer_1.png

Lets imagine that the device, as shown, is at rest on the Earth's surface, with the "direction of flight" on the diagram being upwards. Let us also imagine that the motor on the top of the instrument is powered off. What I think should happen is that the gyroscope simply acts as pendulum, and falls downwards at the end of the pivot arm due to the Earth's gravity. While the gyroscope attempts to precess in a direction given by the right hand rule between the axis of rotation of the gyroscope and the applied torque due to the Earth's gravity, the mounting of the gyroscope prevents precession in this direction and the pendulum essentially falls in the same manner as it would if the gyroscope were not spinning.
Let us now imagine that as the gyroscope falls, it activates the torque motor. The resulting torque, assuming the motor is wired to rotate in the right direction, causes the pendulum to rise due to the cross product of the spin axis and the applied torque.
Thus, as Wiki describes, if a feedback loop holds the pendulum in the horizontal position, the angular velocity of rotation of the torque motor is proportional to the acceleration along the axis of flight, in this case that is the Earth's gravity.