salqmander
- 18
- 0
- Homework Statement
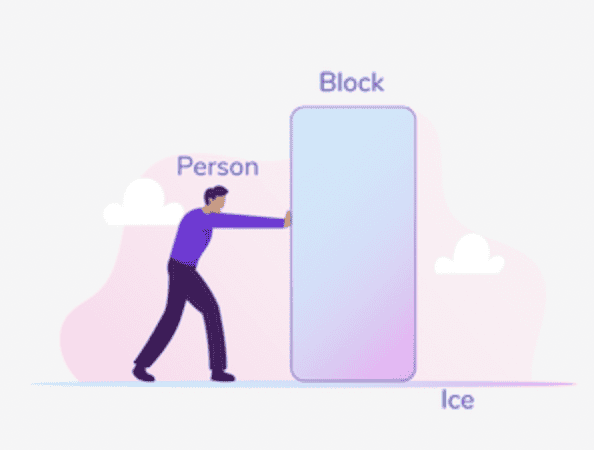
- The following image shows a person pushing a large block on a horizontal ice surface in a straight line to the right at a constant speed.
The figure presents a person pushing a large block toward the right. The block is slightly larger than the person. The person and the block are both on a horizontal surface labeled Ice.
The mass of the block is 20 kg. Frictional forces between the block and the ice are negligible. The block has a wide cross-sectional area, so air resistance is acting on the block, but air resistance on the person is negligible. The person's shoes do not slip on the ice.
As the person pushes the block, the person moves with the same constant speed as the block. In one situation, the person pushes the block with a force of 78 N moving it at a constant speed of 4.00 m/s
(I attached the image with the problem below)
a) Using a dot as a particle model (representing the person), draw and label the forces (not components) exerted on the person. Each force must be represented by a distinct arrow starting on, and pointing away from, the dot.
b) The person now stops and releases the block. Determine the magnitude and direction of the block's acceleration at the instant the block is released. Show your work.
- Relevant Equations
- F = ma
a) For the model, I'm not sure how to include all the forces I think are present. Gravity, normal force from the ice, contact force from ice to person, and person to ice. Is there also a normal force keeping the person's hands from going "into" the ice?
b) As for part b, I would think to use newtons second law, but I'm not sure if that's correct because the force of the person is no longer acting on the block
78 = 20a
a= 78/20
a=3.9m/s^2?
image given with question:
 my attempt at a model part a:
my attempt at a model part a:
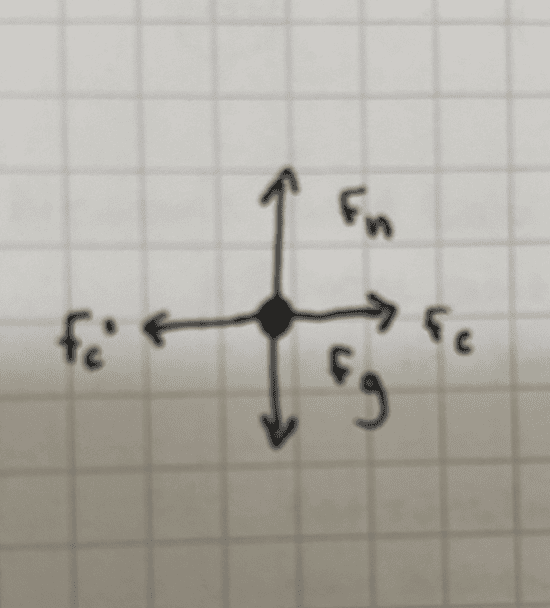
b) As for part b, I would think to use newtons second law, but I'm not sure if that's correct because the force of the person is no longer acting on the block
78 = 20a
a= 78/20
a=3.9m/s^2?
image given with question: