- #1
Rito3d03
- 4
- 0
1. Homework Statement
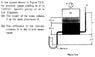
enclosed, thanks for checking
2. Homework Equations
P = ρgh
3. The Attempt at a Solution
I have try to add up all pressure in the tank
(including gauge pressure, pressure of the oil(ρg*0.5), pressure of the water(ρg*0.8))
but still can't balance out the equation since the answer of part A is 1.4m
also, I don't have any clue about part B
thanks if anyone can give me any help
enclosed, thanks for checking
2. Homework Equations
P = ρgh
3. The Attempt at a Solution
I have try to add up all pressure in the tank
(including gauge pressure, pressure of the oil(ρg*0.5), pressure of the water(ρg*0.8))
but still can't balance out the equation since the answer of part A is 1.4m
also, I don't have any clue about part B
thanks if anyone can give me any help