DumpmeAdrenaline
- 80
- 2
- Homework Statement
- A chemical plant has a storage tank containing toxic chlorine gas at a temperature of -34°C and pressure of 7 bar. The tank has a volume of 100 m3. The tank pressure relief valve has a failure frequency of once every 5 years. The tank piping has a failure frequency of once per year. The tank body has a failure frequency of once every 10 years.
An initial quantitative risk assessment has identified potential accident scenarios involving leaks of varying sizes from the tank. The probability of a small leak (10 kg release) is estimated once every 3 years. The probability of a medium leak (100 kg release) is estimated once every 10 years. The probability of a significant rupture (full tank release) is estimated once every 50 years.
The reliability of the chlorine detection system is 95%. The reliability of the automated emergency isolation system is 90%. The chlorine storage tank is 50 meters south of the plant's worker assembly area and 102 meters west of a highway. There is a possibility of toxic chlorine releases impacting the workers or passing vehicles depending on the leak size and wind conditions.
Probability of release impacting workers: 0.68
Probability of release impacting highway: 0.32
a) Calculate:
1) Overall likelihood of toxic release for small, medium and large leaks. (15/100)
2) The frequency of toxic release impacting workers per year for small, medium and large leaks.
3) The frequency of a toxic release impacts the public yearly for small, medium, and large leaks.
- Relevant Equations
- Boolean Algebra
Storage tank leaks are caused by the failure of the pressure relief valve, tank body, or tank piping.
If the pressure relief valve fails, can't it contribute to tank body and/or piping failure from overpressure? But the tank body and tank piping can fail by other mechanisms (mechanical, corrosion,etc)
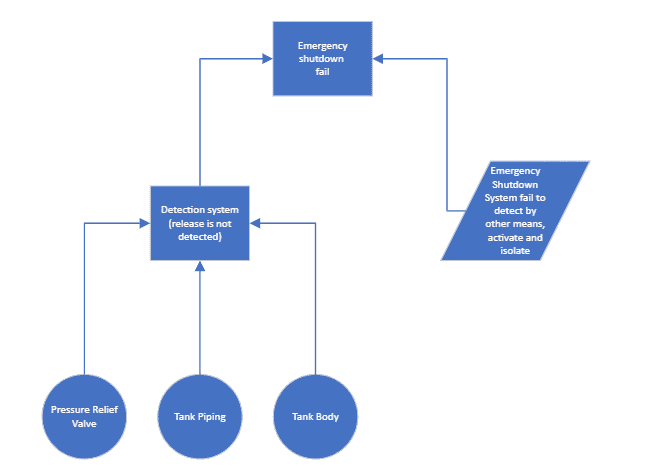
I'm not sure how the gas detection system and the emergency shutdown system interact in emergency situations such as a chlorine (Cl2) leak. The gas detection system will sound an alarm in the control panel to activate the emergency shutdown system and isolate the storage tank. However, there are other indicators besides the gas detector, such as process instrumentation (tank pressure measurement), or operators. Operators serve as a means to detect an emergency situation but are not the cause of system failure. The gas detection system is a part of the emergency shutdown system.
My attempt: Connecting the basic events with the detection system is an OR gate, and the connection from the detection system to the emergency shutdown system failure is also an OR gate.
If the pressure relief valve fails, can't it contribute to tank body and/or piping failure from overpressure? But the tank body and tank piping can fail by other mechanisms (mechanical, corrosion,etc)
I'm not sure how the gas detection system and the emergency shutdown system interact in emergency situations such as a chlorine (Cl2) leak. The gas detection system will sound an alarm in the control panel to activate the emergency shutdown system and isolate the storage tank. However, there are other indicators besides the gas detector, such as process instrumentation (tank pressure measurement), or operators. Operators serve as a means to detect an emergency situation but are not the cause of system failure. The gas detection system is a part of the emergency shutdown system.
My attempt: Connecting the basic events with the detection system is an OR gate, and the connection from the detection system to the emergency shutdown system failure is also an OR gate.