wnvl2
- 62
- 14
I am reading 't Hooft introduction to general relativity.
https://webspace.science.uu.nl/~hooft10 ... l_2010.pdf
In this text 't Hoof derives the Rindler transformation.
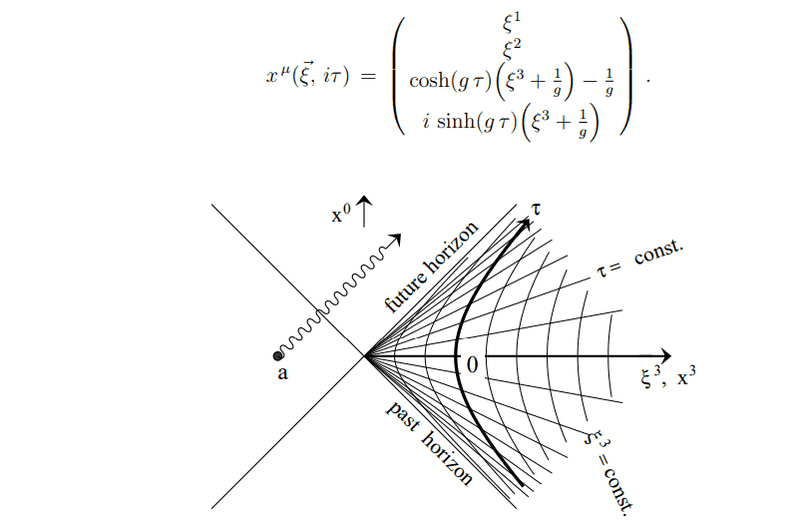
A little bit further he writes
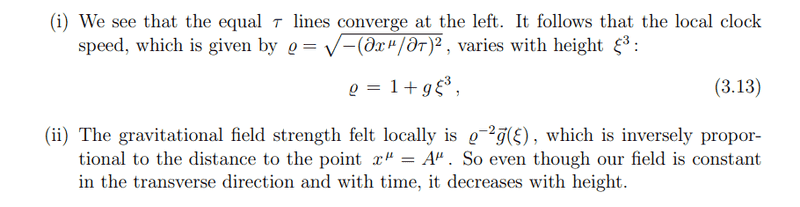
My question is, how does he come to that formula $$\rho^{-2}g(\zeta)$$
https://webspace.science.uu.nl/~hooft10 ... l_2010.pdf
In this text 't Hoof derives the Rindler transformation.
A little bit further he writes
My question is, how does he come to that formula $$\rho^{-2}g(\zeta)$$