- #1
Ollie359
- 4
- 0
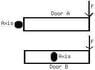
The drawing shows the top view of two doors. The doors are uniform and identical. Door A rotates about an axis through its left edge, and door B rotates about an axis through the center. The same force is applied perpendicular to each door at its right edge, and the force remains perpendicular as the door turns. Starting from rest, door A rotates through a certain angle in 3.00 s. How long does it take door B to rotate through the same angle?