simphysics
- 7
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Find Va-Vb in the following circuit.
R=3 OHM
Ɛ1=10V
Ɛ2=4V
- Relevant Equations
- Va-Vb=Ɛ1
Va-Vb=iR-Ɛ2
Hello everyone, I've been struggling with this problem for 1 hour so far.
Here's how I've tried to solve it. as i supposed, the current flows counterclockwise and i=2A.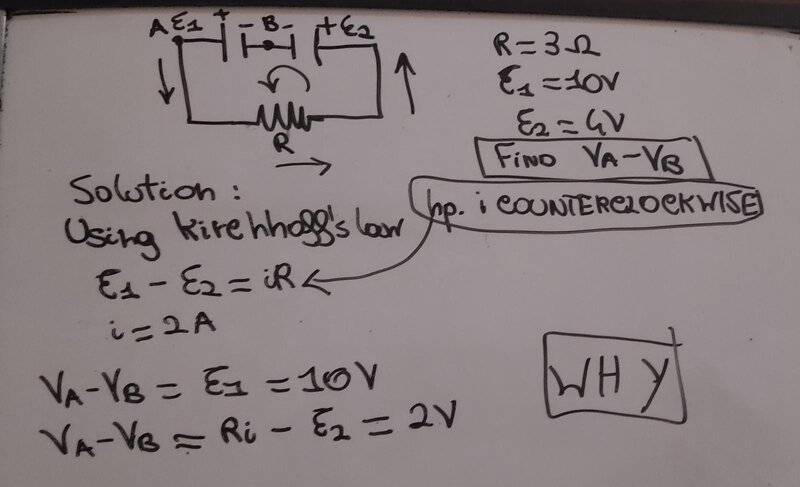
it doesn't matter which path i take, cause i should always arrive at the same potential but i actually don't and i can't get why.
If taking Vab clockwise:
Va-Vb=Ɛ1 and i assume it positive since the current flows through it from the negative pole to the positive one. so Va-Vb=10V
If taking Vab counterclockwise
Va-Vb=iR-Ɛ2=6V-4V=2V
I'm assuming Ɛ2 negative since the current flows through it from the positive pole to the negative pole.
The values are different and I can't get why.
homework-and-exerciseselectric-cirThank you! :)