chwala
Gold Member
- 2,827
- 415
- Homework Statement
- see attached problem below;
- Relevant Equations
- conditional probability
My question is on part ##c## of the problem.
Kindly see attached question,...is the second approach correct?
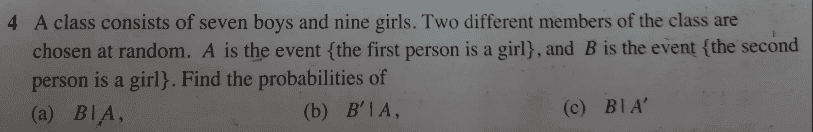
Kindly see attached question,...is the second approach correct?