chwala
Gold Member
- 2,827
- 415
- Homework Statement
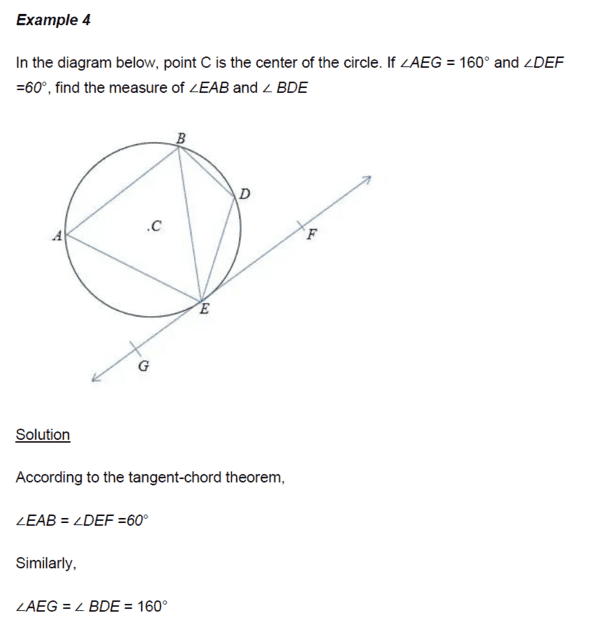
- see attached.
- Relevant Equations
- Tangent- chord theorem
This is a textbook problem...clearly angle ##AEG≠ 160^0## there is something wrong with the value given,...I am trying to analyse this...