- #36
mananvpanchal
- 215
- 0
Hello,
The below images show O's accelerating motion with respect to R. As speed changes desynchronization becomes bigger with respect to R.
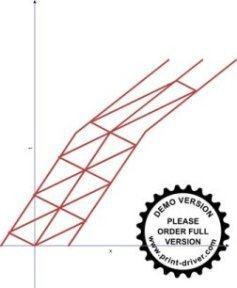
Please, look at first frame of below image. It shows desynchronization of clocks when frame is in motion. But, it is with respect to R.
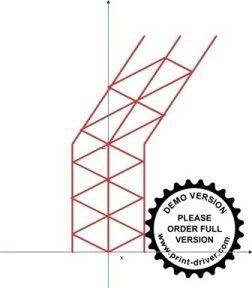
When we transform to first frame, as below image shows there is no longer desynchronization with respect to O. But, second frame is desynchronized with respect to O.
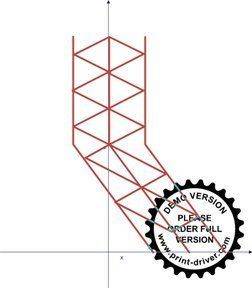
But, again we transform to second frame. there is no longer desynchronization with respect to O. But, first frame is desynchronized with respect to O.
So, desynchronization is only there when we see other frame. Our own frame cannot have desynchronization with respect to itself.
So, as I understand constant speed of frame would not create desynchronization, and changing in frame (acceleration) also would not create desynchronization.
Can you explain me how acceleration can create desynchronization with respect to O?
The below images show O's accelerating motion with respect to R. As speed changes desynchronization becomes bigger with respect to R.
Please, look at first frame of below image. It shows desynchronization of clocks when frame is in motion. But, it is with respect to R.
When we transform to first frame, as below image shows there is no longer desynchronization with respect to O. But, second frame is desynchronized with respect to O.
But, again we transform to second frame. there is no longer desynchronization with respect to O. But, first frame is desynchronized with respect to O.
So, desynchronization is only there when we see other frame. Our own frame cannot have desynchronization with respect to itself.
So, as I understand constant speed of frame would not create desynchronization, and changing in frame (acceleration) also would not create desynchronization.
Can you explain me how acceleration can create desynchronization with respect to O?
Last edited: