aquastor
- 2
- 0
please post homework questions in the homework forum and fill the template
Hello,
is someone able to explain why these two are wrong. I am not sure how to figure out the enthalpy direction as the reaction is not changing state of matter, nor is it changing temperature.
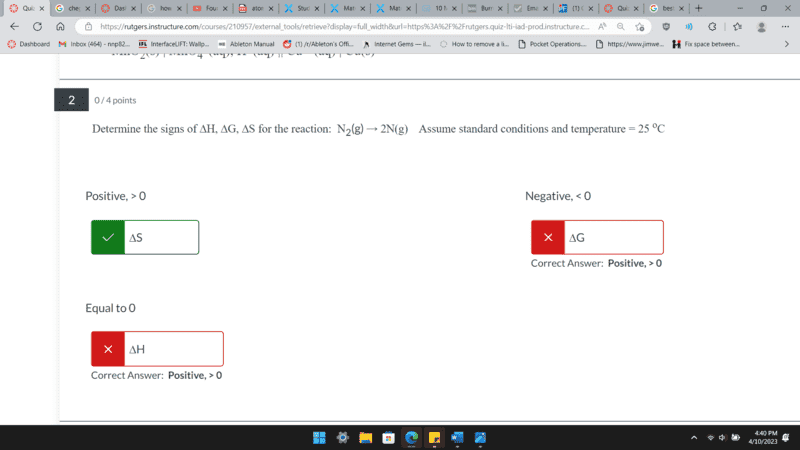
(Please solve without calculating anything)
Thank you
is someone able to explain why these two are wrong. I am not sure how to figure out the enthalpy direction as the reaction is not changing state of matter, nor is it changing temperature.
(Please solve without calculating anything)
Thank you