Juanda
Gold Member
- 439
- 144
Turnbuckles have a right hand thread and a left hand thread.
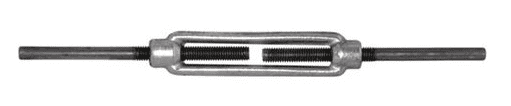
That implies that if I pull from both ends, the turnbuckle will resist the tension because the inner body would need to twist both ways simultaneosly to become unscrewed. The same applies to the compression case.
However, can they become loose against vibration? From what I just wrote about them it'd seem like that's not possible but it feels very weird to me. As long as the threaded rods are not allowed to turn, the turnbuckle should not be able to do it either so the preload/position will remain the same.
I know turnbuckles are sometimes locked in place using jam nuts or lock wire but I don't know if that's in cases where the rods could turn independently or if there is a mechanism that could cause a loss of preload even in the scenario I described.
I assume, as a safety measure, it's always convenient to use something like a jam nut but I would like to confirm if it is really necessary in the case where the threaded rods are not allowed to turn.
That implies that if I pull from both ends, the turnbuckle will resist the tension because the inner body would need to twist both ways simultaneosly to become unscrewed. The same applies to the compression case.
However, can they become loose against vibration? From what I just wrote about them it'd seem like that's not possible but it feels very weird to me. As long as the threaded rods are not allowed to turn, the turnbuckle should not be able to do it either so the preload/position will remain the same.
I know turnbuckles are sometimes locked in place using jam nuts or lock wire but I don't know if that's in cases where the rods could turn independently or if there is a mechanism that could cause a loss of preload even in the scenario I described.
I assume, as a safety measure, it's always convenient to use something like a jam nut but I would like to confirm if it is really necessary in the case where the threaded rods are not allowed to turn.