- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Understanding Voltage Dividers to Redrawing and Solving Ladder Networks
- Thread starter qwerty321
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Voltage Voltage divider
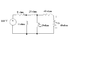
In summary, qwerty321 is trying to figure out how to determine the voltage at a junction in a circuit with two resistors in series and another resistor in parallel. He is looking for a solution that can be worked through.
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
qwerty321
- 56
- 0
ok like using ohm's law,so can anyone help me solev this circuit?
- #3
The Electrician
Gold Member
- 1,393
- 208
Can you show an example of what your text shows as a voltage divider?
- #4
qwerty321
- 56
- 0
i didn't understand what you mean?
the picture is attached..and by the way,the electrician, thansk for always helping me:d
the picture is attached..and by the way,the electrician, thansk for always helping me:d
- #5
Proton Soup
- 223
- 1
you determine the equivalent resistance of everything except the 8 ohm resistor. then you use a voltage divider to determine the voltage across this equivalent resistance.
then you use a similar process to determine the voltage at the node where the 24, 20, and 40 ohm resistors connect. then finding V0 should be trivial.
then you use a similar process to determine the voltage at the node where the 24, 20, and 40 ohm resistors connect. then finding V0 should be trivial.
- #6
The Electrician
Gold Member
- 1,393
- 208
The Electrician said:Can you show an example of what your text shows as a voltage divider?
In another post you said you were studying for CCE. What is that? Is it a course, or is it a study guide for a test of some sort.
Don't you have course materials that explain what a voltage divider is? Is there a picture (schematic diagram) of a single voltage divider? If there is, post an image of it here.
- #7
tiny-tim
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 25,839
- 258
qwerty321 said:I have the figure below,and i do not understand the question..
Hi qwerty321!
See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage_divider
- #8
qwerty321
- 56
- 0
umm cce means computer and communications engineerig at university..i have a course named electric circuits and signals..
- #9
- 12,180
- 182
And do you have a textbook (or other written material) for this course?
What The Electrician is getting at is: your book (or other written material) would be a good place to look up what a voltage divider is ... or any other term that comes up in your homework problems.
What The Electrician is getting at is: your book (or other written material) would be a good place to look up what a voltage divider is ... or any other term that comes up in your homework problems.
- #10
dortec
- 13
- 0
can someone post the solution, i know its an old post but now i need the answer:) i have the same question in my year.. I am studying cce too ! can someone help?
- #11
Proton Soup
- 223
- 1
dortec said:can someone post the solution, i know its an old post but now i need the answer:) i have the same question in my year.. I am studying cce too ! can someone help?
did you try to work through the suggestion in post 6 ?
you'll see, this stuff is real easy. but you've actually got to work through a few.
- #12
vk6kro
Science Advisor
- 4,079
- 41
You need to start at the right of the diagram.
There are two resistors in series. What is their total resistance?
These are in parallel with another R. What is the combined resistance?
Now, this combination is in series with another resistor, so what is the combined resistance?
You go from right to left keeping a note of all these combinations.
If you have two resistors R1 and R2 in series with 100 volts across them, the voltage across R2 will be...100 times R2 / (R1 + R2 ) .
Now, you move from left to right starting with the supply voltage. What is the voltage at the junction of the first two resistors knowing the equivalent resistance to the right of that point?
Then move to the next junction and so on.
There are two resistors in series. What is their total resistance?
These are in parallel with another R. What is the combined resistance?
Now, this combination is in series with another resistor, so what is the combined resistance?
You go from right to left keeping a note of all these combinations.
If you have two resistors R1 and R2 in series with 100 volts across them, the voltage across R2 will be...100 times R2 / (R1 + R2 ) .
Now, you move from left to right starting with the supply voltage. What is the voltage at the junction of the first two resistors knowing the equivalent resistance to the right of that point?
Then move to the next junction and so on.
FAQ: Understanding Voltage Dividers to Redrawing and Solving Ladder Networks
1. What is a voltage divider?
A voltage divider is a circuit arrangement that divides the input voltage into smaller output voltages. It is made up of resistors connected in series and is commonly used in electronic devices to regulate and reduce voltage levels.
2. How does a voltage divider work?
A voltage divider works by using the principle of Ohm's Law, which states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance. In a voltage divider, the input voltage is divided among the resistors based on their individual values, resulting in different output voltages.
3. What is the purpose of redrawing ladder networks in voltage dividers?
Redrawing ladder networks in voltage dividers can simplify the circuit and make it easier to analyze and solve. By rearranging the resistors into a ladder-like configuration, the equivalent resistance can be easily calculated, and the voltage division ratio can be determined.
4. How do you solve for the output voltage in a voltage divider?
To solve for the output voltage in a voltage divider, you can use the voltage division formula: Vout = (R2/(R1+R2)) * Vin, where Vin is the input voltage, R1 and R2 are the individual resistances, and Vout is the output voltage. Alternatively, you can use Kirchhoff's laws and Ohm's Law to calculate the voltage across each resistor and then add them to get the output voltage.
5. What are some practical applications of voltage dividers?
Voltage dividers have many practical applications, such as in power supplies, level shifting circuits, and sensor circuits. They are also commonly used in electronic devices to power LEDs, control the brightness of displays, and regulate the voltage for different components. Additionally, voltage dividers are used in signal processing and amplification circuits.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
Engineering
How to calculate the interference voltage?
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 945
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 1K
Engineering
Calculating the voltage at a certain Resistor
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 35
- Views
- 5K
Engineering
Circuit with multiple voltage sources
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 1K
Share: