m3dicat3d
- 19
- 0
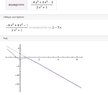
View attachment 819Why is the slant asymptote pictured here correct for this function? I was under the impression an asymptote was never crossed by the function. I get that the dividend gives the equation for the asymptote for a non zero remainder, but seeing this graphically is a bit confusing. Thanks! (EDIT: NVM, I just answered my own question:p) Thanks anyways though!
Attachments
Last edited: