zenterix
- 774
- 84
- Homework Statement
- Write the Lewis structure of the species chlorine nitrate, ##ClONO_2##.
- Relevant Equations
- At this point, this problem incorporates material on simple Lewis structures and exceptions to the octet rule.
Looking up on the internet the structure is
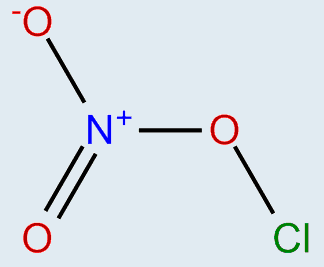
My question is why (or, better, how) do we know that there is that positive charge on the nitrogen?
Wouldn't the overall molecule have a positive charge in it? Then why is this not denoted in the formula ##ClONO_2##?
My question is why (or, better, how) do we know that there is that positive charge on the nitrogen?
Wouldn't the overall molecule have a positive charge in it? Then why is this not denoted in the formula ##ClONO_2##?