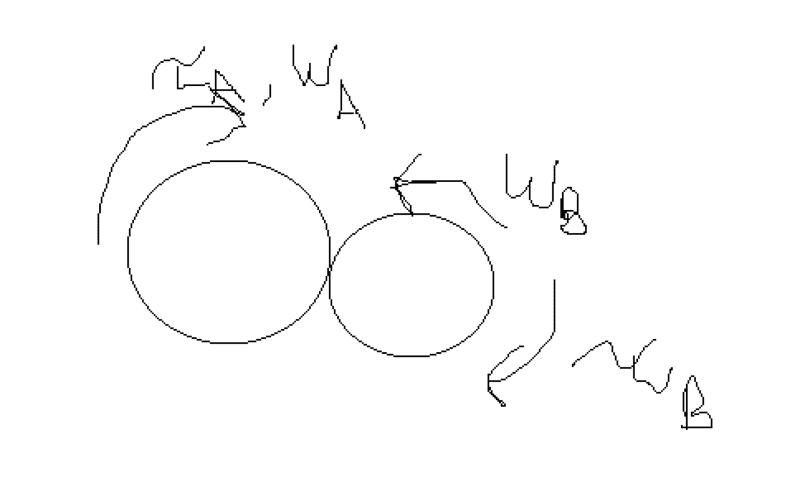annamal
- 393
- 33
- TL;DR Summary
- Two gears (A and B) are spinning with their centers fixed with the left one being the driver driving the left gear clockwise. Why is the driven gear (gear B to the right) torque clockwise as well?
We have two gears A and B (left and right). Gear A is driven with a clockwise torque. Why is gear B's torque also clockwise? I would say that if gear B is driven to turn counterclockwise, the torque should be in the counterclockwise direction.