Conductors Definition and 299 Threads
-
D
Charge flow when two conductors having same charge are connected
Can anybody pleasez answer my question...? --->>No charge will flow when two conductors having the same charge are connected to each other. IS this statement true or FALSE?... what i think is ..it is not necessary that the potential of both conductors is also same.. So due to potential...- D_DaYwAlKeR
- Thread
- Charge Conductors Flow
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
K
Conducting and Insulating Conductors: why uniform and 'surface' charge distribution?
Why is it that when you have an insulator, the charges are uniformly distributed but in a conductor, the charges are only at the surface?- Kuhan
- Thread
- Charge Charge distribution Conducting Conductors Distribution Surface Uniform
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
R
Electromagnetism Problem (conductors, dielectrics)
Homework Statement http://img209.imageshack.us/img209/1508/problemhd.jpg Homework Equations The Ampere law: \oint_C \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{l} = \mu_0 I_{enc} The field and flux is proportional to the current: \Phi = LI The Attempt at a Solution (a) \oint_C \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{l} = \vec{B}...- roam
- Thread
- Conductors Dielectrics Electromagnetism
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Solving Charge in Conductors: Find Q1, Q2 & Combined Potential
Homework Statement A sphere conductor of radius 18 cm has potential 27 Volt. Another sphere conductor has potential 18 Volt. Both of them are connected and the combined potential is 24 Volt. Find: a. the charge of second sphere b. the charge of each sphere now Homework Equations Q = CV...- songoku
- Thread
- Charge Conductors
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Calculate capacitance of conductors
Problem: (a) What is the capacitance of the 2 conductors +20nC and -20nC? (b) If the voltage difference between the 2 conductors increase to 250 V, then what else changes? a). I calculated that ΔV = 100 V. So then I plugged into the formula C = Q/ΔV. I thought 20 nC = 2 x 10^-8 C, which...- s-f
- Thread
- Capacitance Conductors
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Understanding the Relationship Between Electric Fields and Conductors
There are some very basic questions about conductors that are bugging me: 1. I know that E=0 for a conductor is only if the fields remain static, If there was a time varying field, the electrons would be in constant motion across the conductor, meaning that at any point of time, a net tangential...- vig
- Thread
- Conductors Electric Electric field Field
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
F
Superconductors and best conductors
Hello Forum gold, silver, copper are the best electrical conductors are room temperature. But they cannot be superconductors: there is no finite, low critical temperature at which they become superconductors... But what if we could bring their temperature to 0 kelvin? I believe that all...- fisico30
- Thread
- Conductors Superconductors
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
M
Spin liquid states and conductors
Hi, All articles on spin liquids I've seen treat them as insulators. This is understandable in the context in which they were first introduced i.e. the resonating valence bond state in which every electron is singlet-ed with every other, and thus essentially blocking conduction. Given...- mavipranav
- Thread
- Conductors Liquid Spin States
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
N
Parallel plate conductors question
Homework Statement "An electron is fired from a negative plate towards a hole in a positive plate. It then passes between two parallel plates that are 3 cm long and 2 cm apart with a voltage of 550 volts across them. If the accelerating voltage across the two original plates is 900 volts what...- newageanubis
- Thread
- Conductors Parallel Parallel plate Plate
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
What are the Forces on parallel ac conductors
The Scenario: Two long parallel conductors A and B are carrying an ac current with a wave length of λ. The conductors are separated in distance at all points by λ/4 and the ac current phase of conductor A leads the ac current phase of conductor B by λ/4 at all points mutually at right angles...- Tracer
- Thread
- Ac Conductors Forces Parallel
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
M
Electromagnetism question involving two stationary conductors and crossbars
Homework Statement Question and diagram below Homework Equations F=BIL F=QVB Vback=(epsilon)-Ir The Attempt at a Solution F=QvB ma=QvB QvB/m=a ? I really don't know how to start this question.- mrcheeses
- Thread
- Conductors Electromagnetism
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Thermal gradients in electrical paths of thermocouple conductors
I recently inherited a problem related to temperature measurement. Thermcouples (d- and k- type) are being used in a high-pressure, high-temperature environment, with the measuring junction suspended in an electrically-insulating solid. The leads of conductors A and B extend out of the...- erichp
- Thread
- Conductors Electrical Thermal Thermocouple
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
S
Planning an Experiment: Excellent Thermal and Electrical Conductors
i have to plan and design an experiment based on this outline: " excellent thermal conductors are also excellent electrical conductors" could i get any ideas please?- Shordaay
- Thread
- Conductors Electrical Experiment Thermal
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Longitudinal magnetic forces in conductors
Is there a simple way to understand within classical electrodynamics (or QED) the experiments that show longitudinal forces in conductors that are capable of breaking wires when enough current is conducted and are not due to melting or pinch effect?- TrickyDicky
- Thread
- Conductors Forces Longitudinal Magnetic
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
N
Why when two conductors connected by a conducting wire gain the same potential?
Why when two charged conductors connected by a conducting wire gain the same potential . Lets say we have two spheres of different charges why when we connect them by a single copper wire they gain the same potential Thanks in advance- nishantve1
- Thread
- Conducting Conducting wire Conductors Gain Potential Wire
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Mechanics
-
D
Determining Conductors Per Phase: 451 Amps/ Ampacity
How do you determine the number of conductors per phase? From my understand, the full load amperage divided by the desired wire size's ampacity rounded up if there is a remainder. An example: If I have a 361 Full load Amp motor from the NEC table and I calculated the motor circuit...- Dwa
- Thread
- Conductors Per Phase
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
K
Permittivity values in conductors
Hello All, I am a masters student in electronics engg and reading technical electrodynamics. Please let me know when the electric current density becomes more than the displacement current (for a conductor ) why is the value of ε≈-jσ/ω Quick replies will be highly appreciated! Thanks...- ksnf3000
- Thread
- Conductors Permittivity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
G
Why is there close to zero potential difference in conductors in a circuit?
This is why I think this is the case, I can't come up with any other reason and have been researching all over the place. I do have a knowledge of circuits, I'm doing an electronic engineering course, but the reasoning has never been explained, as if it's unnecessary to understand why, but I am... -
R
Spherical conductors connected by a wire.
Homework Statement Two spherical conductors are connected by a long conducting wire, and a charge of 10.2 Micro-coulombs is placed in the combination. One sphere has a radius of 5.99 cm and the other has a radius of 7.99cm. What is the electric field near the surface of the smaller sphere...- rofln
- Thread
- Conductors Spherical Wire
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Resistance and Temperature in conductors and semiconductors
Homework Statement Revered Members, When we increase the temperature, resistance increases in conductors. But resistance decreases in semiconductors. Why? Help in this regard will be highly appreciated. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Due to increase in temperature...- logearav
- Thread
- Conductors Resistance Semiconductors Temperature
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Induction of emf in moving conductors in magnetic fields
In preparation for an upcoming physics exam I have been going through some past paper questions. This question is from the multiple choice section of the paper, so while I can check the answer there is no source from which I can see it being worked through. Homework Statement An aircraft...- tzxn3
- Thread
- Conductors Emf Fields Induction Magnetic Magnetic fields
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Magnetic Forces on Conductors and charges- the motor principle
Magnetic Forces on Conductors and charges-- the motor principle An electron moving through an electric field of 475 V/m and a magnetic field of 0.1T experiences no force. if the electron's direction and the directions of the electric and magnetic fields are all mutually perpendicular, what is...- Hmpca
- Thread
- Charges Conductors Forces Magnetic Motor Principle
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Conductors and their increase of resistance with temperature
Revered members, Conductors have positive temperature coefficient of resistance, that is , their resistance increases with temperature. While for insulators and semi conductors, the resistance decreases with increase in temperature, what we call negative temperature coefficient of resistance...- logearav
- Thread
- Conductors increase Resistance Temperature
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
C
Charge Distribution on Two Neighboring Conductors
Say you have two spherical conductors, of radius r, centers a distance d apart. Both have charges of +Q. What are the charge distributions on them? My physics book more or less handwaves and says it'll be more or less unaffected, but is there a way to solve this exactly?- conquerer7
- Thread
- Charge Charge distribution Conductors Distribution
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
C
Equipotential with Spherical Conductors
For electrostatics, I know that conductors have 0 electric field inside. And I know that the surface of a spherical conductor has equipotential, (Maybe this is true for all shape of conductor in equilibrium right? ). So my question is, is the potential 0 inside a conductor as well? Is it...- calvinjhfeng
- Thread
- Conductors equipotential Spherical
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Electrostatics, infinite concentric cylindric conductors
Hi. I have this problem, and when I tried to solve it, some doubts and questions emerged, I need some help with this. The problem says: The figure shows two concentric cylindrical conductors with infinite length. We'll suppose that between them there's a known potential difference. a. Find an...- Telemachus
- Thread
- Conductors Electrostatics Infinite
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
R
Determining total charge on the surfaces of spherical conductors
In the attached picture is all of the information to complete this problem. The picture is of a solid sphere at the center of a hallow sphere, both of which are conductors. The question asks to find the total charge of the exterior and interior surfaces of the hollow conductor, as well as the...- RichardEpic
- Thread
- Charge Conductors Spherical Surfaces Total charge
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Gauss's Law and charged conductors
A conductor carries a net charge +Q. There is a hollow cavity inside the conductor that contains a point charge -Q. In electrostatic equilibrium,what is the charge on the outer surface of the conductor? A. -2Q B. -Q C. 0 D. Q E. 2Q I know that the answer is 0, however, I cannot...- veevee
- Thread
- Charged Conductors Gauss's law Law
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
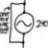
Three concentric conductors, one grounded (Potential)
Homework Statement See figure attached. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution See figure attached. I'm confused how they deduced that V1-V2 is going to be the integral of the electric field from a to b. How do they choose the path from a to b? How can they say...- jegues
- Thread
- Conductors Potential
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
G
Flow of current. Conductors and Insulators.
This is NOT a homework question.. It is just something that is bothering me... 1. If two neutral conductors are made to touch each other, no current will flow.. 2. If a neutral conductor is made to touch with a positive conductor, the current will flow from the neutral to the positive...- girlzrule786
- Thread
- Conductors Current Flow Insulators
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
J
Can we say that bad conductors are good absorbersof heat?
As an element does not conduct heat,then they are good absorber. can we say that?or its like that?- joyever
- Thread
- Conductors Heat
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
L
Force between two long parallel current carrying conductors
Homework Statement Revered members, please see my attachment Homework Equations AB and CD are two straight very long parallel conductors placed in air at a distance a. They carry currents I1 and I2 respectively. B1 and B2 are magnetic inductions. In the book its been mentioned the...- logearav
- Thread
- Conductors Current Force Parallel
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
3 phase 4 wire conductors radiated electromagnetic interference?
If you have a 3 phase 4 wire distribution where the 3 phase conductors and 1 neutral is inside a pvc conduit, how would you model the force of the electromagnetic field at a certain distance away from the conduit? Assuming the loads are balanced, the currents would sum to zero on the...- djr3203
- Thread
- 3 phase Conductors Electromagnetic Interference Phase Wire
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
C
EM Waves in Conductors: Why Does B Field Lag E Field?
When an EM wave goes in a conductor it says that the B field component lags the E field component, What causes this? I looked in Griffiths and I couldn't find the answer. Does it have something to do with the fact that when the EM wave enters the conductor it is moving the free electrons in the...- cragar
- Thread
- Conductors Em Em waves Waves
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
R
Photoelectric Work Function and its relation to Conductors
Work function of metals: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/tables/photoelec.html#c1 Copper work function - 4.7 eV Silver work function - 4.73 eV Silicon work function - 4.26 eV (http://environmentalchemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Ag.html) The work functions of conductors are...- rohitchaky
- Thread
- Conductors Function Photoelectric Relation Work Work function
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
D
What is scientific reason behind skin effect of conductors?
What is scientific reason behind skin effect of conductors?- djsourabh
- Thread
- Conductors Reason Scientific Skin Skin effect
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
G
Lorentz force of a charged particle between moving parallel conductors
Let us consider a fixed Carthesian reference frame (x y z) with a charged (+) particle locate in its origin. Moreover, let us consider two parallel conductors of infinite lenght, carrying the same current I (in the same direction y). The two conductors move at constant velocity from the origin...- gilbertopin
- Thread
- Charged Charged particle Conductors Force Lorentz Lorentz force Parallel Particle
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
J
Properties of electric charges - insulators and conductors
Homework Statement I have some hypothetical questions. Question 1 There is a conductor with a single electron and proton inside of it. If we try to charge the conductor by induction, we might put a proton close to the conductor. The electron will go towards that proton while the proton in...- joej24
- Thread
- Charges Conductors Electric Electric charges Insulators Properties
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
What is the force between the two (AC) current carrying conductors?)
what is the force between the two (AC) current carrying conductors??) in case of dc currents,they repel or attract when the two conductors carry current in the same or opposite direction,what about two wires carrying ac currents.:smile:- rampriya1729
- Thread
- Ac Conductors Current Force
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
M
Force Between Parallel Conductors
Hi there, I really need help with one question and help/hints would be greatly appreciated 1. A wire 3meters long, mass 0.10kg and carrying a current of 70.0 Amps floats without support above a horizontal wire 2.0cm below and parrallel to it. Find the current in the lower wire 2. I'm...- miniradman
- Thread
- Conductors Force Parallel
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
By definition, superconductors are conductors with zero resistance at
By definition, superconductors are conductors with zero resistance at low temperatures. Do superconductors exist ideally, i mean whether zero resistance is practically possible?- logearav
- Thread
- Conductors Definition Resistance Superconductors Zero
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
U
Potential energy of a system of conductors
According to Jackson the potential energy of a system of conductors is W=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^n C_{ij} V_{i}V_{j} He calls the coefficients C_{ii} coefficients of capacitance and C_{ij} coefficients of induction. I want to derive from this formula the well known result for... -
N
Electric Resistance of Conductors & Semiconductors with Temp Change
1.What happens to the electrical resistance of conductors, semiconductors, with increase in temperature? And explain why?- noor.lalu
- Thread
- Change Conductors Electric Resistance Semiconductors
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Why is (B) Incorrect in This Electrostatics Question?
Homework Statement Which of the following statements about conductors under electrostatic conditions is true? (A) Positive work is required to move a positive charge over the surface of a conductor. (B) Charge that is placed on the surface of a conductor always spreads evenly over the...- flyingpig
- Thread
- Conductors Exam
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Why is Neutrality Important in Electrostatics of Conductors with Cavities?
Homework Statement when a conductor under electrostatic equlibrium with cavity has charge inside,we say -ve charge is induced at inner surface by Gauss Law,but why do we say +ve charge induced at surface , I mean thru Gauss Law we we say Electric field has been canceled out ,why the hell...- vibhu_baronia
- Thread
- Conductors
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Understanding Potential Between L & K Conductors
L and K are two conductor tables, L is grounded (his potential is zero). In this situation the scales are balanced. To measure the charged object's potential, it is being connected to K with thin long conduct wire. just L and K are conductors. when the object is connected to K, L and K are...- blmatan
- Thread
- Conductors Potential
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Conductors with off-centered cavity
Suppose we had an uncharged solid spherical conductor with radius R, and some spherical cavity of radius a that is located b units above R, where a+b<R. If we place a charge inside the cavity at the center, how would you quantitatively express the E-field lines outside of the conductor?- raging
- Thread
- Cavity Conductors
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
F
Two questions regarding conductors and their properties.
Homework Statement I am so close to this breakthrough I can taste it. I say this because I haven't taken a shower in four days. Anyways go to this link http://physics.bu.edu/~duffy/py106/Electricfield.html My questions 1) This part. OKay so a conductor is charged, all the excess...- flyingpig
- Thread
- Conductors Properties
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
What are they doing? Charges and Conductors
Homework Statement http://img823.imageshack.us/img823/236/40553004.png [PLAIN][PLAIN]http://img717.imageshack.us/img717/1561/15355872.png The Attempt at a Solution I am a bit confused isn't the 6.00nC sending its own E-field? For part b) Why do they say Qinside is 0...- flyingpig
- Thread
- Charges Conductors
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium problem
Homework Statement In fair weather, over flat ground, there is a downward electric field of about 150 N/C. A) assume that the Earth is a conducting sphere with charge on its surface. If the electric field just outside is 150 N/C pointing radially inwards, calculate the total charge on the...- dimpledur
- Thread
- Conductors Electrostatic Electrostatic equilibrium Equilibrium
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help