You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Dilation Definition and 1000 Threads
-

I Time dilation (speed Vs. acceleration)
There's a common example to explain time dilation that states ... "if you traveled at a speed close to the speed of light and came back in a round trip of 1 hour , you may find that on the departure frame of reference 2 hours had passed" but that 2 hours trip can't be done without accelerating...- Crowxe
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Gravitational time dilation, proper time and spacetime interval
Dear all, I'm having confusion about the standard derivation of Schwarzschild's gravitational time dilation. For concreteness I'll follow the explanation of Schutz' "gravity from the ground up", but other texts argue the same. So let me rephrase Schutz's explanation (I surpress factors of c in...- haushofer
- Thread
- Replies: 62
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Special Relativity: Time Dilation Explained
I am trying to get this idea of Time dilation understood. If there exists only two objects in a Universe and one object is stationary and the other object is moving at 99 % the speed of light. Their clocks were both synchronized when both objects were stationary relative to each other. Then the...- mpolo
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Cylinder & Mineral: Thermal Dilation
Homework Statement A hollow aluminum cylinder with a depth of 20.0 cm has an internal capacity of 2.000 L at 20.0 C. It's full with mineral turpentine, at 20.0 C. The two of them are heated slowly, until the temperature reaches 80.0 C. a) How much of the mineral is spilled outside the...- Const@ntine
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
I Time dilation in components of an object
Apologies if this has answered before:rolleyes: Imagine a cannon ball that's been heated up to a very high temperature, say 1000C so it's still solid. The atoms inside it will be moving, but the ball itself is stationary. Does this mean the atoms in the ball will age slower than the ball...- brainierthaneinstein
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Uniform-gravitational time dilation -- exact or approximate
If a clock runs n times faster than another clock due to flawed design, then it is logically necessary (and rather trivial) that the other clock runs 1/n times slower than the flawed clock. I thought the same should be the case for gravitational time dilation; if a clock on a tower runs n times...- Hiero
- Thread
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I How Ebeb's Diagram Reveals Time Dilation
I am starting a new thread as my last one was unceremoniously hijacked by those who should know better and then closed by moderators when boundaries were crossed in the hijacked thread. I am not complaining as it was an interesting diversion, but now, if acceptable, I would like to return to...- Grimble
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Diagram Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 92
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Does gravitational time dilation imply spacetime curvature?
In a recent thread, the question came up of whether the presence of gravitational time dilation implies spacetime curvature. My answer in that thread was no: This was based on the obvious counterexample of observers at rest in Rindler coordinates in flat Minkowski spacetime; two observers at...- PeterDonis
- Thread
- Replies: 230
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Time Dilation, Clocks, & Gravity
In the rest frame , the measured time interval is the time elapsed between the two ticks (so two events T1and T2) of one clock. In moving frame,the time elapsed between the two ticks T1and T2 are measured by the two synchronized clocks kept at two different places x'1 and x'2. The...- Pushoam
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Time Dilation: One Year in Jupiter = How Many Years on Earth?
If we assume I live in Jupiter and there is one year passed in my clock how many years passes in the earth? And how can I use that Equation in the attached?- ahmed emad
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
B Muon Time Dilation: Earth vs Muon Perspective
From the reference frame of the earth, the distance between the surface of the Earth and the muon is longer, but the muon survives because time for the muon is slowed down. From the reference frame of the muon, the time experienced by the muon is not slowed down but the muon survives because...- Allison
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
K
I Muons magnetic field time dilation
muons mean lifetime of 2.2 µs muons in a strong gravitational field or traveling at relativistic speeds experience time dilation would a muon in a strong magnetic field, say near a magnetar experience additional time dilation more than a muon in an non-magnetic field with the same...- kodama
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
G
I Time Dilation Exp: Answers to Questions on A & B's Experiences
Hello everyone, The questions I am about to ask have probably been explained already, but even after everything I've read I still cannot understand how this experiment would play out and how to answer these questions. So without further ado here is the experiment: Imagine you have person A...- Guilherme Mesquita
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Does Traveling Through a Wormhole Affect Time Dilation?
Hi, I've been trying to work this out for quite a while and I just can't seem to get anywhere. My question is, if I were to travel between two points, say from Earth to a planet in the Trappist system, I know that if I traveled in a vehicle I would experience time dilation, but if I were to...- sleeperservice
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
B Space Dilation Interaction Between Two Masses
Edit: Disclaimer, this post contains faulty ideas I'm a 'pedestrian' to physics trying to wrap my mind around various concepts of relativity, and one of those is a visualization of two, say, planets, say each starting at rest. By my understanding, their mass causes space to relatively...- MistySaa
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Time dilation of an orbiting ship
I'm sure this has become a tedious question, but wasn't able to ween out an exact answer through searching. A ship orbits an asteroid using retro rockets to maintain an orbit. The gravity is insignificant and can be ignored. A clock on the ship will tick more slowly than a clock on the...- Buckethead
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Ship Time Time dilation
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Time Dilation Equation: Why is it to the Power -1/2? | AQA Exam Board
Hello, AQA is a British exam board and on their paper they have a list of equations. Can someone tell me why the time dilation equation is to the power -1/2? Thanks.- AishaGirl
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Power Time Time dilation
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
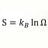
B Does Distance Contraction Cause Time Dilation?
Its my understanding that relativistic length contraction l = l0√ 1-v2 also applies to the space itself in the moving S' system. For example a rocket traveling at .6 c. A distance that is 1000 meters in S frame is contracted to 800 meters in rockets frame. (1000/γ) Therefore the elapsed time /...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
I Gravitational time dilation near Earth
We know (measured) that a clock on a mountain "ticks" faster than a clock at sea level. At higher altitude, the clock runs even faster. Now, if we go much higher, towards the Sun, on the line between the center of the Earth and the center of the Sun, the clock should begin, at some point, to...- DanMP
- Thread
- Replies: 37
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Length Contraction & Time Dilation: Relative Velocity Impact?
So an object moving close to the speed of light will be length contracted. Does that mean the distance it covers also contracts in length? From the traveling object's point of view it's surrounding's would contract as he sees them moving along. In these scenarios wouldn't velocity be a...- sqljunkey
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
I Why is time dilation not symmetric for satellites and Earth?
Hello, I read that satellites is effected by the time dilation caused by gravity and also by that one from special relativity. And so there is a need to prepare the onboard clock to ensure that the time is synchronized with a clock on Earth. But why is this effect not symmetric? The...- Neutrinos02
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Uniform motion and time dilation - real or perspective based
Does time dilation in relative UNIFORM motion REALLY happen or is it merely a perspective from one reference frame relative to another as in the simple case where objects appear smaller the further away they are from the perspective of an observer in a particular reference frame? Putting it...- Rob-NYC
- Thread
- Replies: 30
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
B Time dilation and quantum entanglement.
Please forgive any misconceptions or grevious errors, quantum mechanics and relativistic physics is something I read and think about as a hobby and not a career. My question is this, does the entanglement or two particles transcend time difference? To expand, let's say we have two...- ArmChairPhysicist
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
T
B Confused About the Length of Time Between Ticks in Time Dilation
I am confused about time dilation. I understand that a common pedagogical device used is a light clock, in which a pulse of light flashes back and forth between two objects. I understand that when an observer in a vehicle carrying such a contraption is moving, to an external observer, as the...- Troodon Roar
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Gravitational time dilation calculation near a Black Hole
Hello to everyone! I am trying to understand in practice the Gravitational Time Dilation by calculating the time distortion near the supermassive black hole Sgr A* in our Galactic Center. According to Einstein's Theory of General Relativity, the time distortion near a black hole is calculated...- Antonio
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I How Does Time Dilation Affect Jill's Perception of Jack's Clocks?
Hi guys, I have a question to all of you. This question is based on the example which is located here: http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/time_dil.html I understand it but there is one thing is still unclear to me. So, here it is: Again we have Jill on the rocket and poor Jack on the...- Dimani4
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Example Time Time dilation
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Time Dilation - measured vs observed time interval
Homework Statement Consider an observer Bob in S standing close beside the x-axis as Alice, who is holding a clock, approaches him at speed VS'S along the axis. As Alice and her clock move from position A to B, Alice’s clock will measure a (proper) time interval ∆t0, but as measured by Bob’s...- astrocytosis
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
B Ideal demonstration of time dilation
In thousands of years time (when we have the technology to do almost anything) what would be the ideal demonstration of time dilation? Imagine I am a child. ps. Sorry if this post is over speculative. Feel free to move it if that helps.- Andrew Wright
- Thread
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Time Dilation Test: No Deviation From Relativity Predictions Found
I would just like to draw some attention to this recent preprint https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.04426 It reports on a test of time dilation based on a fiber network of optical clocks. No deviation from relativity predictions found.- Orodruin
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Test Time Time dilation
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
J
I Time dilation of a rotating disk
Iv'e been recently interested in time dilation, but the relative time difference between two observers confuses me (i.e. that a high speed observer, and a stationary observer will each perceive the other's clock to run slow.) I thought of the following experiment to help me understand, but I'm...- JonnyHilbert
- Thread
- Replies: 35
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Relativity of simultaneity, time dilation misunderstanding
Hi everybody, I'm new on this forum so I apologize in advance if I don't respect some formalities (and sorry for my English). It is known that in the perspective of the stationary observer the events in the back and in the front of the moving spaceship are not simultaneous. If I understand well...- sha1000
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
H
B Time Dilation, Interstellar Travel, and "The Forever War"
Dear community, I have no formal education in physics, but I think I have understood some of the basic concepts and ideas in SRT. I am currently trying to find a solution to a problem that came up during my reading of Joe Haldeman's "The Forever War", a Sci-Fi novel that deals with the impact of...- hawi
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Time Dilation: Hafele-Keating Experiments
Hi, I went ahead and read through all the similar discussions and none are on this particular topic so I'll go ahead and shoot. I did find this topic as well, but my question is pretty simple. I think I understand how time dilation works, I read through the explanation here, this jives with the...- Maaruk
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
B How Do Proper Acceleration and Gravity Affect Time Dilation in Free Fall Orbits?
I had been informed that for objects in free fall orbit no proper acceleration would be measured. https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/stationary-frames-of-reference.899195/page-2#post-5658771 But I also understood it that for objects in free fall orbit gravity time dilation would be observed...- name123
- Thread
- Replies: 87
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
C
Special Relativity: Time Dilation Prob
It has been 2.5years since I last did any special relativity so am rather rusty on it, I have a simple time dilation problem and its making my head hurt which way around it should be. Any help much appreciated! 1. Homework Statement Bob leaves Sarah on Earth and travels in a spaceship at 0.8c...- ChrisJ
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
B Time dilation and length contraction question
Hi All, Bob and Alice are both 21. I'm imagining a scenario where Alice starts on a journey at 0.8c towards a distant planet. Bob (stays still) says this planet is 16 light years away and that it takes Alice 16/0.8 = 20 years to get there (so Bob is 41 years old when Alice gets there). So Bob...- Glenn G
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
W
Relativity: Time dilation and distance calculations
Homework Statement Could someone help point out certain conceptual errors in my interpretation of the mirror clocks time dilation thought experiment? Say S' is the frame of reference traveling at speed V w.r.t to frame S, which means that events happen at the same coordinate in S'. We know...- WWCY
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
I Length Contraction & Time Dilation Beyond Planck Scale: Correct?
If an object was traveling fast enough relative to an observer such that it's length is contracted down to the Planck scale (as with time), I would imagine that any further increase in speed would result in no more observable relativistic effects? Please correct me if I'm wrong.- Flatland
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Relativity's "time dilation" or clock accuracy alteration
i've seen the double slit experiment and the delayed choice . my mind rejected the conclusion, but the experiment setting and configuration of delayed choice is rational and holds water so i accepted the experiment outcome even if it means the world isn't real. i had to give that intro that...- Crowxe
- Thread
- Replies: 59
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B Time dilation and thermodynamics
Hi guys, I was watching an episode of stargate and I got this idea, I've been trying to explain to myself. It has to do with time dilation and the first law of thermodynamics. So here it is. Imagine a small time dilation field, a small sphere or something, with an accelerated time. A simple...- Thebugger
- Thread
- Replies: 31
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Why was time dilation under GR a new concept?
Edit: I mean a new concept as in new with regards to the century before. I'm aware that lorentz and maybe others had some idea even before GR So time slows down for the individual under a stronger gravitational field than for an individual under a weaker gravitational field. But why does this...- FallenApple
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Concept Dilation Gr Time Time dilation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
O
B Earth time dilation vs Sun time dilation
In the MinutePhysics video "How long is a day in the Sun?" it is said 24 hours on Earth is 86,400.0 seconds, but on the Sun 86,400.2 seconds would pass. However, if time passes slower with more massed objects, then wouldn't a twin on the Sun be younger than a twin on the Earth? If so, is the...- orion1977
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Earth Sun Time Time dilation
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

V=? for Relativistic Mass,length contraction & time dilation
Homework Statement Velocity Equations for Relativistic Mass,length contraction and time dilation. I was able to figure out one. This is not for homework. I want to learn these equations for future reference. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Length Contraction : v = c...- Axidecimal
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Exploring Time Dilation: Questions and Insights from a Hobby Mathematician
Hi, I'm a (hobby) mathematician and only an amateur physicist, so maybe below there are only trivia questions. Thank you in advance for conversation and clarification. All mathematical proofs of "time dilation" I have looked at so far were based on the Pythagorean theorem. In all such proofs...- bookofproofs
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Gravity Defying Ships Cause Time Dilation and Paradoxes?
If a ship could cancel out the effect of gravity, wouldn't it be able to pass through the event horizon of a black hole, and take a tour of the singularity, and then just report back with its observations? Also, if a ship had the capability to cancel out the effect of gravity, wouldn't this...- Ghost117
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Sci-Fi Writing and World Building
-
I
B Time dilation problem question
So there is a problem I don't get. I special relativity, things moving relative to me, I see them as experiencing more time/ slower time. Ok...so then I should also see it's velocity decrease. If I see it's clock running slower, so should I it's velocity. V=...m/s So if I see it's time slow down...- IvicaPhysics
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 134
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
I Does time dilation prevent event horizon formation?
I read that time dilation near a black hole's event horizon causes the infalling matter to "freeze" just above the event horizon and never cross it (in a distant observer's frame of reference). Doesn't the same phenomenon prevent the event horizon and singularity from being formed in the first...- Petr Matas
- Thread
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
P
B Does time dilation work this way?
Suppose, a ball is thrown upwards. The proper time interval between the throw and the instant at which it attains max height is t. And, the dilated time interval between the same events for a different moving observer is 2t. Now, my question is: Both observers see the same instants happening...- Prem1998
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dilation Time Time dilation Work
- Replies: 26
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
B Examining Time Dilation and the Effects of Velocity on Perception of Time
In explaining time dilation we usually say, if velocity of A is greater than velocity of B, then time is slower for A as compared to B. However, if vA> vB, using the equation for time dilation, tA>tB. So if 60 seconds passed for B, 100 seconds passed for A. How does that imply that time slowed...- Faiq
- Thread
- Replies: 74
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Time Dilation in the same frame of referance?
Homework Statement A rocket ship is accelerating through space. Clocks P and Q are at opposite ends of the ship. An astronaut inside the rocket ship is beside clock P and can also observe clock Q. What does the astronaut observe about the passage of time for these clocks? Justify your answer...- Klairence Leitch
- Thread
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help