Time dilation Definition and 999 Threads
-
R
I Muon Decay Example from Morin's Book: Issues Explained
From the Lorentz transformation equations we know that $$t = \gamma(t^{'} - x^{'} v/c^2)$$ but for the Muon decay example where the setup is as follows : "Assume for simplicity that a certain muon is created at a height of 50 km, moves straight downward, has a speed v = .99998 c, decays in...- realanswers
- Thread
- Decay Example Muon Time dilation
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
C
I Effects of time dilation for near-speed-of-light travel
Hello everyone, I've been learning about special relativity, and so far I believe based on what I read that if you are traveling at a velocity of .6c, you will experience time 20 percent slower than people on earth. Each second in the spaceship will be 1.25 earth seconds. Each second on earth...- Chenkel
- Thread
- Dilation Effects Time Time dilation Travel
- Replies: 65
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Time dilation from galactic gravitational mass
I've been thinking about how rotational speeds don't fall off high distances from galactic centers, for which dark matter is generally an explanation for the increase in acceleration Speed = distance / time But time is relative What "time" is used in these calculations? Wouldn't time be...- marcosdb
- Thread
- Dilation Gravitational Gravitational mass Mass Time Time dilation
- Replies: 49
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Time dilation - what is the time on the Earth?
If I understand it well, 10 s did really passed in the rocket, it is according to the observer on the Earth, but if the man in the rocket measured the time, he would measure 10 s. But when we say that the man in the rocket is in an inertial frame of reference as well, he can claim that because...- Lotto
- Thread
- Dilation Earth Time Time dilation
- Replies: 32
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
T
I Time Dilation & Length Contraction: Graphically Explained
The thread "twin paradox without math" inspired me try to find fully graphical solution of length contraction. Here is the result: Graph is 3D as I think that is ilustrative to make all in one graph, but I am sure that it is possible to do it in 2 or 3 2D slices. X and Y are spatial axes, T is...- Tomas Vencl
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Time Time dilation
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Time Dilation in Gravitational Field: Potential vs Field Strength
I'm wondering is whether it is the gravitational potential (in J/kg) at a point in space that determines the rate of passage of time, or whether it is the gravitational field strength (in m/s2). To clarify, suppose you had a very heavy hollow spherical shell. The gravitational potential would...- Green dwarf
- Thread
- Dilation Field Gravitational Gravitational field Time Time dilation
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
I Time Dilation for Photons: Explained
So, I have a question. The time dilation formula is: t = t₀ • 1 / √(1 - v²/c²) Let's take a photon that travels at c. In my opinion, for a photon "clock doesn't tick" and its life is just a moment. But when we calculate time dilation by this formula, then c over c is 1 and the root of 1 minus...- NODARman
- Thread
- Dilation General relativity Photons Time Time dilation
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
B Time Dilation & Bosons: Decay Rate Changes?
Hi, It is easy to find discussions about time dilation and muon Half-Life. Is it meaningful to discuss whether bosons capable of pair production can have their decay rate changed if they pass through material?- Andrew Wright
- Thread
- Bosons Dilation Material Time Time dilation
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
E
I Time difference caused by length contraction
The goal is to calculate the difference in the passage of time between two ends of a cabin which is accelerating upwards due to length contraction. To help in the calculations we can consult: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.05338.pdf There is an old problem called the 4/3 problem which has been...- externo
- Thread
- Contraction Difference Length Length contraction Time Time dilation
- Replies: 52
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B General Relativity & Grav. Time Dilation Qn
hello I'm korean high school student and sorry for my poor English. I saw ## t_0=t_f\sqrt{1 -\frac{ 2GM}{rc^2}} ## in wikipedia. does ## \sqrt{1 -\frac{ 2GM}{rc^2}} ## of this equation have name like lorentz factor ## \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 -\frac{v^2}{c^2}}} ##of ## t=\frac{t_0}{\sqrt{1...- IXWELL
- Thread
- Dilation General General relativity Gravitational Gravitational time dilation Relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
Time Dilation in the ISS: 2 Seconds in a Year
Using the above formula I get that the time goes 6.5∗10−86.5∗10−8 percent faster in ISS. Thus, this is approximately 2 seconds in a year. But the answer is much lower. Where am I making a mistake?- Aristarchus_
- Thread
- Dilation Iss Seconds Time Time dilation Year
- Replies: 50
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
B Calculating Time Dilation w/ Light Clock - Implications & Mistakes?
In this picture it shows a light clock. Let's use the moving light clock example. Am I essentially calculating the b component of moving clock. Assume the moving frame is the B frame. Assume the stationary frame is the A frame https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light_clock Or essentially the b...- rgtr
- Thread
- Dilation Relativity Special relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I The Theoretical Minimum: Length Contraction and Time Dilation
Hello, My name is Dave and I'm a physics major at UIUC. It looks like I will be taking the special relativity course (phys 225) this fall. I've always been fascinated by the theory so I decided to get a head start with Lenny and Art's perspective on it. My first head-scratching moment came in...- DavidBalut
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Minimum Special relativity Theoretical Theoretical minimum Time Time dilatation Time dilation
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
B Proving Reciprocity Of Time Dilation
Hopefully the answer on this question is positive. This forum has a very good reference about the Experimental Basis of Special Relativity. The tests of the Twin Paradox conclude that faster moving clocks tick/run slower, however this seems to be an 'absolute' fact. They do not show symmetry or...- DanAil
- Thread
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 44
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B
B Time Dilation & Muon De Broglie Wavelength: Explained
I understand it's experimentally verified muons traveling at relativistic speeds relative to an observer will be observed to have longer half-life than would be observed in the rest frame of the muons, which is explained theoretically by a relativistic time dilation effect. Does this correspond...- bobdavis
- Thread
- De broglie De broglie wavelength Dilation Muon Time Time dilation Wavelength
- Replies: 27
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
I Is Time Dilation Just a Misunderstanding of Clock Errors?
According to a video I watched recently 'time' allegedly runs a tad slower in places on the Earth where the magnetic field is stronger. No doubt that has been tested and confirmed by atomic clock experiments.. to my simple mind that just suggests a timing error caused by the difference in...- paul1365
- Thread
- Dilation Perspective Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
T
B Time Dilation on Rotating Disk: Clocks on Disk Perspective
Obviously, a third observer who is at rest with respect to the disk will see that the clock on the outside has a much faster velocity than a clock on the interior of the disk, so clearly the outside clock will show that it has measured less time. But that's one question. What about looking at...- Thadriel
- Thread
- Acceleration Clocks Dilation Disk Rotating Rotating disk Special relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
J
B Gravitational Time Dilation on Mountaintops: New Member Questions
New member here; just a physics hobbyist. There is probably a simple answer to this question but I could not find it. We know time flows faster on mountaintops relative to sea level due to gravitational time dilation. Over millions of years, wouldn't there be a cumulative effect making the...- jeepdriver74
- Thread
- Dilation Effects Relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
B Build a Time Dilation Clock for 8th Grade Science Project
A science teacher ask if I could help one of her students build a "Time Dilation Clock" so, at launch the Ships chronometer and the local time are in sync. with a 3g continuous thrust, at some point the time, the time at the launch site will be going twice as fast as the ships chronometer. so...- Dc2LightTech
- Thread
- 8th grade Building Clock Dilation Project Science Science project Time Time dilation
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I How Does Time Dilation Affect the Twin Paradox in Special Relativity?
I'm struggling to wrap my head around the twin paradox in special relativity especially when dealing with multiple vectors. In my thought experiment say I have a set of twins. Both set out in opposite directions and intend to sling shot around two different black holes(luckily equidistant from...- sennetor
- Thread
- Dilation Lorents transformations Special relativity Time Time dialation Time dilation
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Time dilation and length contraction for a rocket
Hi, It's not a homework but still thought to post it here as advised in the past. A rocket is going to leave Earth's surface and it is decided that a data pulse encoding emission time of pulse will be sent every second from Earth station to the rocket, and the rocket would do the same. The...- PainterGuy
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Rocket Time Time dilation
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Time Dilation along Multiple Axes
Been studying Special Relativity in Uni. and I've noticed that all examples of relativistic motion provided are motions only along a single axis, like the one below: The particle's Reference Frame is moving only along the X axis in the example above. In this case the Lorentz Transformation for...- Reinhardt Walzer
- Thread
- Axes Dilation Multiple Time Time dilation
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
B Time Dilation: 2 Clocks in Same Ref Frame?
Question about time dilation. What if two clocks used the same reference frame? For instance, 2 countdown clocks using a particular pulsar as a measure of time. One stays here, the other is sent 100 million miles away at a very high velocity. Would they still reach 000 at the same time?- maxpower2020
- Thread
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Help Me Determine Validity of Time Dilation Formula
I recently trying to learn General Relativity by first scraping the surface on ScienceClic's general relativity playlist, and then I stumbled upon a video where it said that we actually move through spacetime on a constant speed of c, and then I remember about time dilation because how speed on...- diazdaiz
- Thread
- Dilation Formula Proof Relativity of time Special relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Check my understanding of Time Dilation and Length Contraction
I just started learning about Special Relativity and have come upon the topics of Time dilation and Length contraction. Its a bit abstract for me and I just want to cross ref my knowledge here and see if someone can tell me if I am understanding this correctly. I've attached an excerpt of a...- guyvsdcsniper
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Time Time dilation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
H
A Time Dilation in Reissner-Nordström Metric: Even or Odd?
In the Reissner–Nordström metric, the charge ##Q## of the central body enters only as its square ##Q^2##. The same is true for the Kerr-Schild form. This would seem to imply that all effects are even functions of ##Q##. For example, the gravitational time dilation is often written as $$\gamma =...- H_A_Landman
- Thread
- Charge General relaivity Metric Time dilation
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Time Dilation at Moving Black Hole Event Horizon
Hello everyone, I have a hard time to conceptualize the case of a moving black hole. We know from SR that time slows down for moving objects; but time dilation at the event horizon is already equal (tends) to zero. It seems that it can create some sort of conflict for the black hole movement...- sha1000
- Thread
- Acceleration Black hole Dilation Event horizon General relativity Hole Horizon Special relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Gravity & Time Dilation: Quantum Level Questions
If gravity is the affect of time dilation because of the distance from the bottom of an object to the top then wouldn’t that mean that gravity doesn’t exist at the quantum level?- curiouschuck
- Thread
- Dilation Gravity Quantum Time Time dilation
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I Time Dilation vs. Doppler Effect: Similarities & Differences
Does time dilation in Special Relativity relate to the Doppler effect? If you move near the speed of light you experience time differently and the sound is stretched. Are these similar phenomenon?- BadgerBadger92
- Thread
- Dilation Doppler Doppler effect Relativity Special relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Confused about time dilation and cosmic speed limit
[Moderator's note: Thread spun off from previous thread due to topic/forum change.] Time dilation sounds really weird, can i assume it has a logical explanation?- Sciencelad2798
- Thread
- Confused Dilation Limit Speed Time Time dilation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
T
B Time Dilation: How Does Speed Affect Aging?
Hello everyone, I wanted to know how speed can dilate time. For example, if there is a star 100 light years away from Earth and I started traveling at light speed, how long would it take for me to get there? I understand that the time differs from the point of reference (ie time from Earth's...- Tristan1607
- Thread
- Dilation Space and time Time Time dilation
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Time Dilation on 3D Torus: Clock Speed & Why It Matters
Assume that space is a three-dimensional torus ( a 3D donut) . If there is a clock traveling at a CONSTANT speed in a direction parallel to the torus (inside out of the hole) and one clock that is still. Which clock ticks faster and why? I know that the clock rotating will tick slower, but I...- appot89
- Thread
- Dilation Relativity Special relativity Time dilation Torus
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Time Dilation: Gravitational & Velocity Effects Explained
I'm trying to understand what the time dilation looks like when moving through space and then approaching a planet's gravity field. So I have the broad understanding that if you are moving near the speed of light in a spaceship, your clock ticks normal but the clocks on other stationary objects...- ronald_hinh
- Thread
- Dilation Forces Gravitation Time Time dilation Velocity
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
Time measured by two clocks (involves time dilation)
Proper time (to) is the time interval between two events measured by an observer who sees the events occur at the same point in space. I am confused how to determine which one is proper time for this question. How to know which events occur at the same point from the question sentence? Thanks- songoku
- Thread
- Clocks Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
B Time Dilation in a Galaxy: Calculating Mass Effects
Hello everyone - The gravitational force near the edge of the galaxy at point A (see attached image) can be calculated by assuming that all the galactic mass is located in the center of the galaxy. - In order to calculate the gravitational force in the middle of the galaxy (point B) we take...- sha1000
- Thread
- Dilation Galaxy General General relativity Time Time dilation
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
I
I Kinetic vs Gravitational Time Dilation: Perceived Speed
As an object approaches a black hole’s event horizon, it experiences increasing gravitational time dilation, causing it to appear to an outside observer to slow down, until, at the event horizon, it appears to stop. An object traveling in space that increases its velocity from one...- Involute
- Thread
- Dilation Gravitational Gravitational time dilation Kinetic Speed Time Time dilation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
V
B Time Dilation: Traveling to a Distant Star in 4.5yr
If there is a spaceship traveling at 0.999c, the time to reach a star 100 lyr away would be approx 100 yr (assuming no accel and decel). But on the spaceship, It would be 100 yr * sqrt(1-0.999^2) = 4.5yr. Why do we take 100 yr as the time seen on Earth and not the time on the spaceship?- versine
- Thread
- Dilation Relativity Special relativity Star Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
Question on special relativity from "Basic Relativity"
Summary:: Require confirmation regarding answers to a question posed by the book "Basic Relativity" by Richard A. Mould. Here is a problem which I encountered while going through Basic Relativity by Richard A. Mould- I'd like to receive a confirmation regarding the answers I've come up with to...- PhysicsTruth
- Thread
- Length contraction Relativity Special relativity Time dilation
- Replies: 67
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
I Does time dilation occur due to the speed limit of light or c?
The universal speed limit is c, and as a consequence light is confined to that limit. I was thinking about the time dilation in SR and was wondering if this is result of reaching speeds close to the speed of light or because of reaching speed close to c? For example, let's say light could be...- mucker
- Thread
- Dilation Light Limit Speed Time Time dilation
- Replies: 47
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
I Time Dilation in Gravitational Fields vs Acceleration on Earth
If I'm standing on Earth, is my time dilation actually greater than if I was in a rocket accelerating at 9.8m/s^2 in deep space due to me being in a gravitational field on top of the acceleration? Geodesics experience time dilation in gravitational fields, so it seems like there is an additive...- mcgnms
- Thread
- Acceleration Dilation Fields Geodesics Gravitational Time Time dilation
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
I Time Dilation: Variables Beyond Speed & Gravity?
Can time dilation vary without a gravity well or accelerating a viewer towards light speed? Are there other variables that affect the flow of time?- LightningInAJar
- Thread
- Dilation Gravity Speed Time Time dilation
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
Time dilation for a simple problem — Light propagating inside a moving bus
So I drew the problem and tried to derive t1 for an external observer by making the following assumptions. Inside observer sees light travel a distance of d0 meters in t0 seconds at a speed of c m/s. Bus moved Δd meters in t1 seconds at V m/s. Outside observer sees light travel a distance of...- name
- Thread
- Bus Dilation Light Time Time dilation
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Time Dilation: Does Observer See Your Time Speed Up?
If time slows down for an observer traveling at some speed relative to your proper time, shouldn't the traveling observer also see your time slow down relative to his proper time? Or does the observer see your time speed up relative to his proper time. Also, is dilation exactly the same in...- AdvaitDhingra
- Thread
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Time Dilation Effect: Corrections to Clocks on ISS
Hello All The Hafele-Keating experiment in 1971 confirmed measurable time dilation effects on atomic clocks flown around the Earth on aircraft. Presumably clocks aboard the International Space Station suffer worse time dilation because of their greater speed in orbit. How often are corrections...- saddlestone-man
- Thread
- Clocks Dilation Iss Time Time dilation
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Kerr Metric Time Dilation Formula: Deriving Absolute Form
Just as the time dilation formula for the Schwarzschild metric in terms of the position ##r## away from center of mass for a gravitational body and the Schwarzschild radius ##r_s = {2GM}/{c^2}## is given by $$ \tau = t \sqrt{1 - \frac{r_s}{r} } $$ so I'd like to know the corresponding...- Dukon
- Thread
- Dilation Formula Kerr Kerr metric Metric Time Time dilation
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
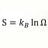
B Time like spacetime interval, proper time, and time dilation
Since the time like spacetime interval is equal to proper time for stationary or traveling observers, then it seems time dilation (proper time) seen with traveling clock is necessarily frame invariant. Then the so called time between ticks of both identical clocks, with stationary and traveling...- morrobay
- Thread
- Dilation Interval Proper time Spacetime Spacetime interval Time Time dilation
- Replies: 37
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
R
I Length contraction and time dilation
A long time ago, I was very impressed by a lecture on elementary special relativity which showed in simple math how the correct conclusion to the null results of the Michelson-Morley experiment were obtained by concluding a constant c but then adding a length contraction and time dilation. I...- rasp
- Thread
- Contraction Dilation Length Length contraction Time Time dilation
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Time-Dependent Lagrangian Leads to Time Dilation?
This is just something unexpected that I noticed recently, and I hadn't heard anyone mention it before. The relativistic Lagrangian for a particle moving under a scalar potential ##\Phi## is this: ##L = \frac{1}{2} m g_{\mu \nu} \dfrac{dx^\mu}{d\tau} \dfrac{dx^\nu}{d\tau} - \Phi## This leads...- stevendaryl
- Thread
- Dilation Lagrangian Time Time dilation
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Hyperbolic Time Chamber: Is Time Dilation Theoretically Possible?
Has anyone ever watched dragon ball Z before? In this TV show, there is something called the hyperbolic time chamber. 1 day on Earth is equivalent to 1 Year in the time chamber. In other words, if you stayed in the chamber for a full 24hours than exactly 1 year would have passed when you left...- Nick tringali
- Thread
- Chamber Dilation Hyperbolic Time Time dilation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Time Dilation Question: Two Men's Watches Differ after Space Travel
Sometime in the future two men meet at a space port and they synchronize watches, one boards a spacecraft and goes on a round trip around the solar system, when he returns the two men compare wristwatches to find they have different times. Q. Do the two men still exist at the same time or not?- Julius Ceasar
- Thread
- Dilation Time Time dilation
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Special and General Relativity