MatinSAR
- 673
- 204
- Homework Statement
- Canculate ##\lambda## using information you have.
- Relevant Equations
- ##n\lambda=d\sin\theta##
Hello. In data that the professor sent, I see only ##n## and ##\theta##. So I do not know what is d. Can I find ##\lambda## without it?
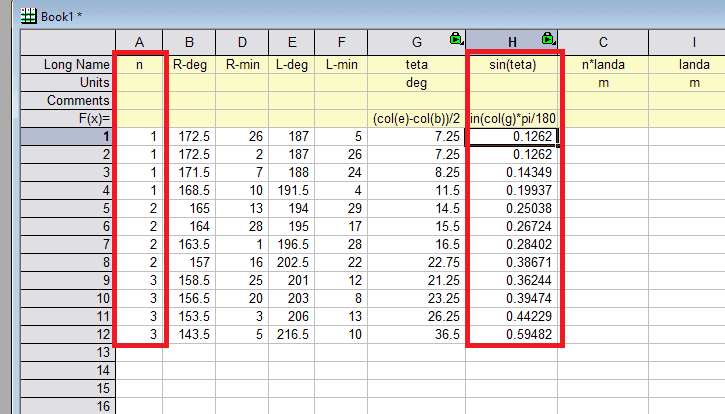
On other thing he mentioned :
Suppose that the diffraction grating consists of 300 lines per millimeter.
I know that d is the distance between two consecutive diffraction grating lines, but I don't know if it has anything to do with what my teacher said.
Can I say that for one line that passes through the diffraction grating d is 1/300 mm ?
On other thing he mentioned :
Suppose that the diffraction grating consists of 300 lines per millimeter.
I know that d is the distance between two consecutive diffraction grating lines, but I don't know if it has anything to do with what my teacher said.
Can I say that for one line that passes through the diffraction grating d is 1/300 mm ?