lee123456789
- 90
- 5
- Homework Statement
- writie about engines
- Relevant Equations
- none
Writing about Engines and just muddled up diagrams and confused now. Which PV diagrams is for Compression Ignition and which one for Compression Ignition.
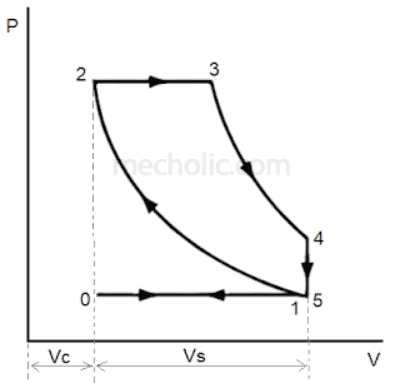
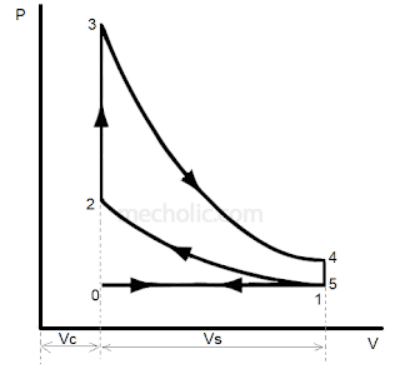
I think one on left is CI and right SI.
Cheers
I think one on left is CI and right SI.
Cheers