Gozupa
- 1
- 0
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
TL;DR Summary: help with assignment: find CV joint torque in 3 different situations
Hi, I need help for my assignment. I need to calculate torque of CV joint of truck in 3 cases:
a) CV joint torque on take off
b) CV joint torque on take off on a slope in reverse
c) CV joint torque while driving on straight asphalt road
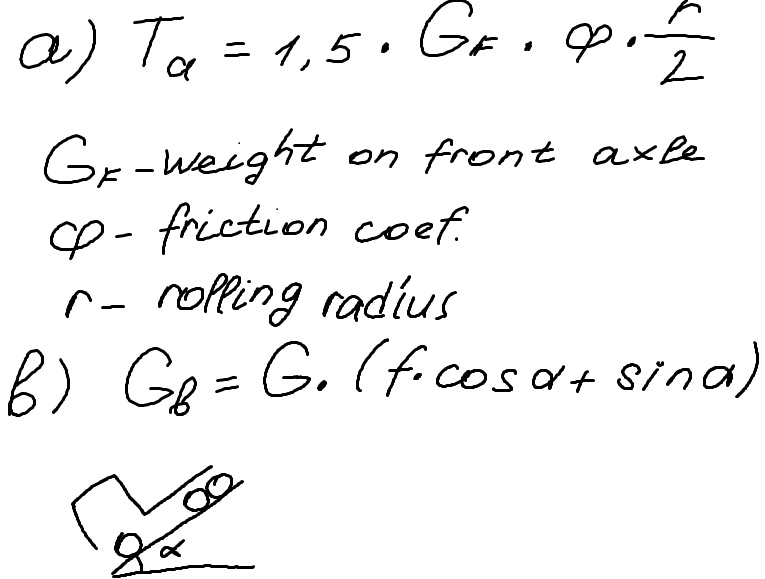
i've found formula (a) in one of my textbooks, but i'm not sure it's correct one. I don't know how to calculate (b) or (c) tbh.
Hi, I need help for my assignment. I need to calculate torque of CV joint of truck in 3 cases:
a) CV joint torque on take off
b) CV joint torque on take off on a slope in reverse
c) CV joint torque while driving on straight asphalt road
i've found formula (a) in one of my textbooks, but i'm not sure it's correct one. I don't know how to calculate (b) or (c) tbh.