zenterix
- 774
- 84
- Homework Statement
- We are asked to write a boolean expression that describes the function of the circuit below.
- Relevant Equations
- We can solve this problem by inspection. (The alternative is to go through a truth table of A, B, and C and figure out the corresponding values for $V_{OUT}$ and then write out the desired function).
This problem is from a problem set in the course 6.002 "Circuits and Electronics" of MIT OCW. There are no solutions, unfortunately.
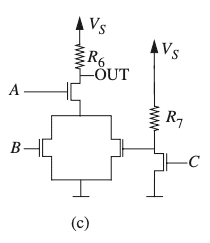
By inspection, we can see that the voltage ##V_{OUT}## at terminal OUT in the picture above is high when
1) ##A=0##, because this leaves an open circuit between OUT and ground.
OR
2) ##A=1## and ##B=0## and ##C=1##, because though there is a short circuit at A, the circuit is open below A.
Thus, the function ##f(A,B,C)=\bar{A}+(A\bar{B}C)## represents the voltage at OUT.
We can simplify this to ##F(A,B,C)=\bar{A}+(\bar{B}C)##.
Is this correct?
One additional question: I simply mentioned that the output voltage is "high".
When this is the case, what is ##V_{OUT}## exactly?
It seems that this voltage should be a function of ##V_S## and the resistance ##R_6##.
I have a difficult time with this part. We don't know what is connected at the terminals of this circuit. If there were no ##R_6##, then ##V_{OUT}=V_S##. But due to the resistor, there seems to be a voltage difference.
If there is nothing connected at OUT, then what is the voltage there?
Suppose we connect OUT to some known voltage ##V##. Then ##V_{OUT}=V## and the current flowing through ##R_6## is determined (and it could flow either way depending on the potential difference ##V_S-V_{OUT}##.
In any case, it seems that the potential at OUT will be high relative to ground, which seems to be the most important thing. But again, how do I know the exact magnitude of the voltage at OUT?
By inspection, we can see that the voltage ##V_{OUT}## at terminal OUT in the picture above is high when
1) ##A=0##, because this leaves an open circuit between OUT and ground.
OR
2) ##A=1## and ##B=0## and ##C=1##, because though there is a short circuit at A, the circuit is open below A.
Thus, the function ##f(A,B,C)=\bar{A}+(A\bar{B}C)## represents the voltage at OUT.
We can simplify this to ##F(A,B,C)=\bar{A}+(\bar{B}C)##.
Is this correct?
One additional question: I simply mentioned that the output voltage is "high".
When this is the case, what is ##V_{OUT}## exactly?
It seems that this voltage should be a function of ##V_S## and the resistance ##R_6##.
I have a difficult time with this part. We don't know what is connected at the terminals of this circuit. If there were no ##R_6##, then ##V_{OUT}=V_S##. But due to the resistor, there seems to be a voltage difference.
If there is nothing connected at OUT, then what is the voltage there?
Suppose we connect OUT to some known voltage ##V##. Then ##V_{OUT}=V## and the current flowing through ##R_6## is determined (and it could flow either way depending on the potential difference ##V_S-V_{OUT}##.
In any case, it seems that the potential at OUT will be high relative to ground, which seems to be the most important thing. But again, how do I know the exact magnitude of the voltage at OUT?