You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Acceleration Definition and 1000 Threads
-
J
I Car acceleration if resistance forces don't exist
Let imagine that car with constant 500HP accelerate but resistance forces don't exist (aero drag,internal friction in engine and transmision,tyer rolling resistance etc etc..) neglect fuel loss over time.. From 0-100km/h take in 4sec and burn 200mL petrol Will car accelerate from...- Jurgen M
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Car Forces Resistance
- Replies: 95
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
R
A Hubble Tension and Cosmic Acceleration: A measurement artifact?
By analyzing 91,742 reported extra-galactic distances and their one sigma uncertainties for 14,560 galaxies, it was found that pairs of reported extra-galactic distances of the same galaxy differ from each other by 2.07 the reported uncertainties on average. In my opinion, this indicates that... -
E
Question about the average acceleration
Hello everyone, I have to find the average acceleration in the intervals 0m - 30m, 30m - 60m, and 60m - 90m. Here is the table: Position (m) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Time (s) 0 1,89 2,88 3,78 4,64 5,47 6,29 7,10 7,92 8,75 9,58 My teacher has given us the answers, but we have to...- Emily0203
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Engineering Calculating angular acceleration
I calculate the gravity force F = mg = (-9806.6)*(5.26e-1) = -5158 (mm^2*kg)/s^2 I get the moment M = F*r = (-3.5e5)*(-6.81e1) = 3.5e5 (mm^2 * kg) / s^2 Where r is the y coordinate distance from origin to centroid J = (Ix'...- shreddinglicks
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
F
I Kinematics cases with non-constant acceleration
Hello, I understand that, for 1D kinematic problems where the acceleration function ##a_x## is initially given along with the initial conditions, we can use calculus (differentiation and integration) to get the position ##x(t)## and velocity ##v_x (t)## of the moving object. When the...- fog37
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Kinematics
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
S
Finding acceleration of block with block on top, connected by rope
I have already concluded that the way to solve this problem is through (20 N - (3 kg * 9.8 m/s^2 * 0.16) - (2*(1 kg * 9.8 m/s^2 * 0.16))) / 3 kg I have several questions: Why do we multiply the second set of parentheses by 2? Why do we count the friction between the 1 kg box and the 2 kg box...- sentimentaltrooper
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Block Rope
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Acceleration between two frames
The correct option is given as (d) I think I am able to visualize the problem but not able to put it in the equations shared above. If the the two frames are moving away from the particle at ##4 m/s^2## in opposite directions we get the acceleration between the frames as ##8 m/s^2##...- Monsterboy
- Thread
- Replies: 38
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Zero velocity for a time interval, what about acceleration?
For a particle moving in a straight line, if the velocity is zero for a time interval, the acceleration is zero at any instant within the time interval. I am told the above statement is true. If I look at the equations v = dx/dt a = dv/dt It looks like if the velocity is zero for a time...- Monsterboy
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Centripetal acceleration along a latitude of Earth
Hello, I am attempting to correctly solve this problem, however I end up with an equation that is slightly different as the one provided in the textbook solution. For question (a) I get the same thing, just instead of cos, I have cos^2 and I can't figure out where I went wrong. My process was...- mncyapntsi
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
I Acceleration through curved paths
I would really appreciate some help with a challenge I have. It is illustrated in the figure below: Scenario: The moving object moves with linear velocity until it reaches P1. When it reaches P1, I need to create the motion of the blue dashed path. Whilst the object follows the blue dashed...- Cato11
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration
- Replies: 39
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Stick leaning on the wall, find the acceleration from the initial position
So the acceleration of point A was given by a force F exerted on cylinder that's along the direction of the stick, decomposed into the horizontal direction. so aA = F cos Θ The same force along the opposite direction is exerted on stick, and if we decompose that in vertical and horizontal...- mattlfang
- Thread
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Finding Gravitational Acceleration
Hi if I understand it correctly, this is the process to find freefall acceleration of a falling body. S=ut+1/2at^2 Initial time and displacement is zero so, S=1/2at^2 find acceleration a=2(S/t^2) graph for change in displacement over time squared a= 2(yf-yi/xf-xi) (f=final i= initial) I...- Martyn59
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Is Free Fall Acceleration Constant Until An Object Hits the Ground?
Shouldn't free fall acceleration be constant at -9.8m/s^2 until the object hits the ground and turns zero?- Jynku
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Fall Free fall
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Kinematics chasing problem: Car vs. Motorcycle acceleration question
Im for some reason getting 1.58 s for time. I found 1.75 m as the head start distance and then I do d=d so: 2.45t^2 = 1.75t^2 +1.75 but the answer for "a" should be 6.45s...- jerad908
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Is this equation involving the acceleration of gravity correct?
$$\begin{aligned}v=u+at\\ \Rightarrow v=gt\\ \Rightarrow g=\dfrac{v}{t} \cdots (1)\end{aligned}$$ $$\begin{aligned}s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}at^{2}\\ \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{1}{2}gt^{2}\\ \Rightarrow g=\dfrac{2s}{t^{2}}\cdots (2)\end{aligned}$$ $$\begin{aligned}s=vt-\dfrac{1}{2}at^{2}\\ \Rightarrow...- Huzaifa
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Gravity
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Precalculus Mathematics Homework Help
-

B Acceleration of time due to entropy
Hello, I am a 15 year old who has done research around the topic of why the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate, and how it will come to an end. After years of thought (since I was 11) I have come up with my hypothesis that time itself is accelerating and slowing down, and has been...- R0dr1go
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Special relativity and acceleration
A particle is moving along the x-axis. It is uniformly accelerated in the sense that the acceleration measured in its instantaneous rest frame is always g, a constant. Find x and t as functions of the proper time τ assuming the particle passes through x0 at time t = 0 with zero velocity.I n...- LCSphysicist
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
I Non-Constant Angular Acceleration
Hello, I am trying to solve a problem involving a mass with known moment of inertia about an axis with a lever arm at angle theta and length r with a non-constant spring force acting at the tip of the lever arm and fixed distance away from the axis of rotation. I am wondering what the best...- DCELL
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Tangential & Normal acceleration in Circular Motion
- Shreya
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
I What is the acceleration of the expansion of the Universe?
I can't find any values of acceleration or rate of change of acceleration of the expansion of the universe when I looked it up and I need these values for a theory I'm working on that could supersede dark energy and show the universe is closed even if everything accelorating away from us and...- JamesGarderiner
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Cosmology
-

Is Negative Acceleration Always Indicative of Slowing Down?
I've written in that only the first statement was False, however my classmates aren't getting the same answer? Please help clarify...- mncyapntsi
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
I Is acceleration a more absolute/fundamental quantity in the universe?
Was wondering if acceleration seems to be a more fundamental property/quantity in the universe as compared to velocity or distance because acceleration can be defined in more absolute terms in a frame depending on the forces acting inside that reference frame. Considering a very simple example... -
L
I Relativistic Force & Velocity Relation to Acceleration
According to this link here https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relativistic_mechanics#Force , we can inverse the relation of force in terms of velocity and acceleration: $$ \mathbf{F} = \frac{m\gamma^3}{c^2}(\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{a})\mathbf{v} + m\gamma\mathbf{a} $$ to get: $$ \mathbf{a} =...- lriuui0x0
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Can we measure acceleration of galaxies and stars?
As for example we see a large void, the Great Repeller, which in fact is an underdense region, and with respect to this region, matter seems to be repelled by this region. The explenation for that is that matter outside that regions pulls on the matter inside it. But if that is really the... -

B Charged Particle on Earth's Surface: Will It Emit Radiation?
General relativity tells us that an object in free-fall is actually inertial, following a geodesic through curved spacetime, and not accelerating. Instead, it's objects like us, on the surface of a large body, that are accelerating upwards. Maxwell's equations also tell us that accelerated...- Amaterasu21
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B How is the acceleration proportional to the removed force?
Image above is the question. Below image depicts solution. if F1 is removed then the acceleration of that mass must be sum of accelerations of remaining forces. Right?? But answer says that acceleration of that mass is equal to acceleration of F1. I don't understand it. Can someone explain it?? -
M
I Time Dilation in Gravitational Fields vs Acceleration on Earth
If I'm standing on Earth, is my time dilation actually greater than if I was in a rocket accelerating at 9.8m/s^2 in deep space due to me being in a gravitational field on top of the acceleration? Geodesics experience time dilation in gravitational fields, so it seems like there is an additive...- mcgnms
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
O
I Maximum acceleration of an alpha particle?
I would like to estimate the maximum acceleration (or deceleration) of an alpha particle that is backscattered by a heavy atom, like in Rutherford backscattering. I am interested in the order of magnitude, not in a precise value. I am assuming the collision is elastic. The kinetic energy of the...- Orthoceras
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

I Calculating Force & Acceleration in Electrostatic Field (B=0)
For a case of electrostatic field (B is equal zero), how should the force acting on a moving charge be calculated if we want to take into account all the relativistic effects? Also would it be correct to calculate the acceleration of the charge as a=F/m, or should some other formula be used? For...- MichPod
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Acceleration of Moving Particles: Explained
I am not able to understand the following paragraph from my Physics textbook; -

I Force on Scale in Rocket Scenario: Calculation & Discussion
[Moderator's note: Spin-off posts from previous thread have been included in this new thread. Also, the OP's re-post of the scenario for discussion has been moved to this top post for clarity.] Yes. Physically, scales measure a force (and indirectly the energy) in their frame. Consider the...- Sagittarius A-Star
- Thread
- Replies: 33
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

MHB Understanding Velocity and Acceleration of a Moving Particle
A particle moves so that its position vector is given by $\vec{r}=\cos{(\omega t)}\hat{i} + \sin{(\omega t)}\hat{j}$. Show that the velocity $\vec{v}$ of the particle is perpendicular to $\vec{r}$ and $\vec{r} \times \vec{v}$ is a constant vector. How to answer this question?- WMDhamnekar
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Velocity
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Linear and Abstract Algebra
-

MHB Question on velocity and acceleration
How to answer this question? Any math help, hint, or even correct answer will be accepted.- WMDhamnekar
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Velocity
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Math
-

MHB Velocity and acceleration vectors and their magnitudes
How to answer this question? I am working on this question. Any math help, hint or even correct answer will be accepted.- WMDhamnekar
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Linear and Abstract Algebra
-
P
Centripetal Acceleration grade 12 (forces on a bird pulling out of a dive)
How come the solution requires you to do mv^2/4 when the formula is just v^2 /r?- Physicsstudent2
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Understanding Galileo's Theory of Acceleration
I am not able to understand the following paragraph from my Physics textbook; "The velocity of an object, in general, changes during its course of motion. Should it be described as the rate of change in velocity with distance or with time? This was a problem even in Galileo's time. It was first...- Huzaifa
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Theory
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Mechanics
-
D
Is Fgy the Same as FN in a System with Two Masses and Friction?
I am just confused on how to find the normal force/ FN of the first object. My classmates are saying Fgy is the exact same as Fn but I don’t get why Fgy= Fg sin theta Fgy= (20)(9.81) (sin35) Fgy= 112.5 Fgy = FN- danielsmith123123
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Average acceleration of an arrow by a bow
Distance= (Intial Velocity + Final Velocity / 2) Time 0.75 = (0+75 / 2) Time 0.75 = (37.5) Time 0.02 seconds = Time Acceleration = (Final Velocity + Intial Velocity) / Time Acceleration = (75 - 0) / 0.02 Acceleration = 3750 m/s2 Idk if this is correct can someone help pls.- rxhim631
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Average acceleration of a car changing speed and direction
Nevermind I found what I had to do, thank you though.- danielsmith123123
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
I The Acceleration and the density of galaxies
In the Lambda-CDM model, the density of galaxies goes decreasing and should even vanish in the far future. I would be grateful if someone could point me to a paper where this is calculated. -

I Acceleration of Universe Expansion: 1/r2
It seems to me as the space between galaxies expands it reduces the gravitational attraction between them. Assuming that this is happening between the majority of the galaxies in our Universe it would cause the acceleration of expansion by a factor of 1/r2. -
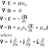
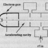
Measure angular velocity and acceleration from missing tooth wheel
Hi, I need to come up with a math model for a digital ignition system. I've been thinking about it and I think that I need to measure 2 things to be able to calculate when I have to start charging the coil. They are the angular velocity and the acceleration but how can I do it? the idea is to... -
C
I Non-uniform Circular Motion & Acceleration
I would really appreciate some help with this problem regarding non-uniform circular motion, in which a body is accelerating as it follows a circular path. If we take Example 1, a body starts at Point A with an angular speed of 180°/s. The body accelerates to Point B and reaches it some time...- Cato11
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: General Math
-
Acceleration in Polar Coords, Intuitive Definition video
Summary:: I wish this video (and YouTube in general) was around when I took intermediate level mechanics as an undergraduate physics student: I wish this video (and YouTube in general) was around when I took intermediate level mechanics as an undergraduate physics student:- CPW
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Definition Polar Video
- Replies: 2
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-

A Graph analysis problem to find when the acceleration is zero
I had deduced that B,E,H are the places where acceleration will be zero, but when I read the solutions it showed that K also has a = 0. It said it had maximum slope and then said a = 0. But I couldn't understand why? Please help.- uranium92
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Calculating Track Acceleration Due to Gravity
The force is driving the rotation is gravity. My question is that what is the track acceleration? How do I calculate it?- robax25
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Gravity Track
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A steel shuttle is pulled along a rail, what is its initial acceleration?
it sounds like you just need to use F/m = a which gives 25 / .76 = 32.89 = a this didn't work so I tried to get the x component of acceleration so I did 32.89cos(45) = 23.26 and this didn't work. what am I missing, the force is tension right so it should be 25N?- potatotimer
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Initial Steel
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Orbital mechanics: is ballistic capture possible without acceleration?
All spacecraft that have been put into orbit around other planets have required engines to decelerate them and inject them into their orbits. So-called "ballistic capture", from what I've read, always seems to call for at least a minimum application of force to change the trajectory; I get...- James Demers
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Mechanics
-

A Deriving Acceleration in Gravity from E = mc^2
I want to derive an acceleration in the case for a stationary mass in the gravity field. I found the total energy in the GR is provided by a simple equation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schwarzschild_geodesics ## E = mc^2\sqrt{1 - rs/r} * \gamma ## So, this is easy to provide acceleration...- boniphacy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Gravity
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity